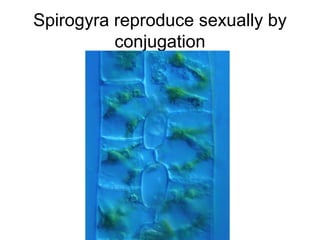
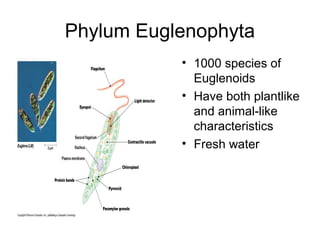
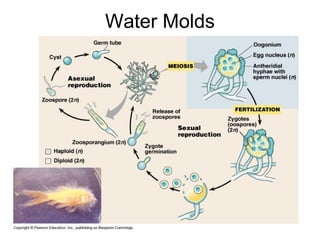
Algae are a diverse group of organisms that range in size from microscopic to large seaweeds. They are typically photosynthetic and aquatic, with some containing flagella or pyrenoids for storing starch. Algae exist as unicellular, colonial, filamentous, or multicellular forms. They are classified into seven phyla based on attributes like pigmentation and cell structure. Algae reproduce both sexually through meiosis and gamete fusion or asexually through mitosis, and may alternate between haploid and diploid generations in their life cycles. Major phyla include the green, brown, and red algae, along with euglenoids and other representatives.