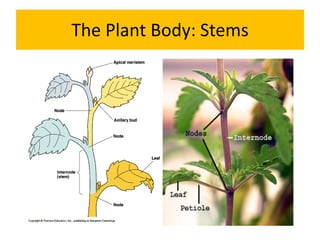
Stems have four main functions: support, conduction, growth, and storage. Stems can be modified in various ways including tendrils, thorns, hooks, phylloclades, and bulbils. Some stems are sub-aerial and include runners, stolons, suckers, and offsets. Multipurpose underground stem modifications include rhizomes, corms, stem tubers, and bulbs which store food, allow vegetative propagation, are protected underground, and allow for perennation.