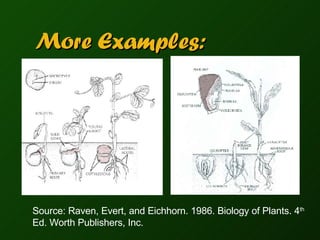
This document provides an overview of plant structures and their functions, including roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds. It defines basic root systems like taproots and fibrous roots, and describes root functions such as anchoring, water absorption, and food storage. The document also outlines stem structures and functions, common leaf shapes and arrangements, parts of flowers and inflorescences, and different types of fruits and seeds. Definitions and examples are included for each plant structure.