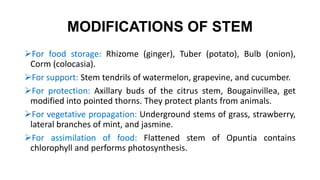
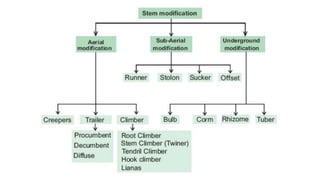
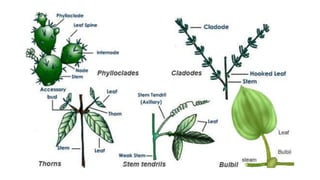
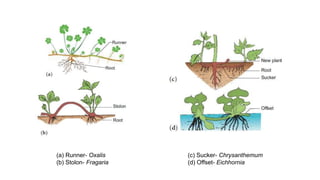
This document discusses the morphology and modifications of plant stems. It describes the basic structure of stems and their functions of transport, storage, and vegetative propagation. Various stem modifications are outlined for different purposes like food storage (tubers, bulbs, corms), support (tendrils), protection (thorns), and climbing. Aerial modifications include climbers, phylloclades, cladodes, and thorns. Underground modifications are bulbs, corms, rhizomes, and tubers. The document also discusses stem branching patterns.