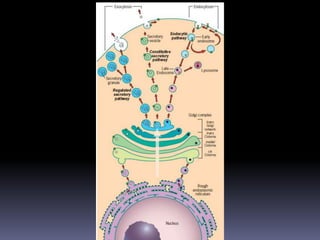
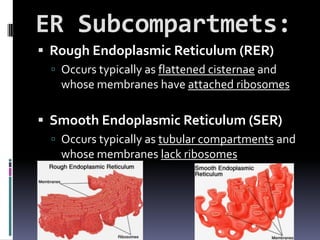
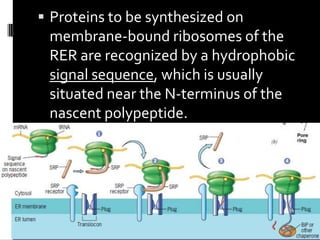
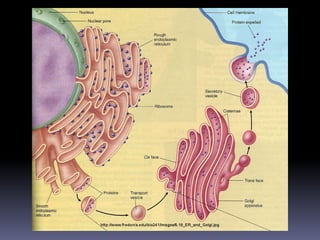
The document discusses the endomembrane system, including the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi complex. The ER is divided into rough ER, where proteins are synthesized, and smooth ER, which functions in lipid and steroid synthesis. Newly synthesized proteins are modified in the Golgi complex through glycosylation as they progress through cis, medial, and trans cisternae. The trans Golgi network sorts proteins to their final destinations, such as secretion or lysosomes.