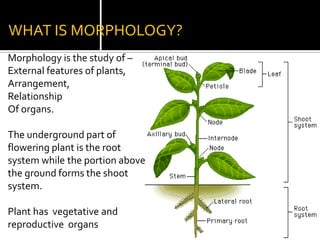
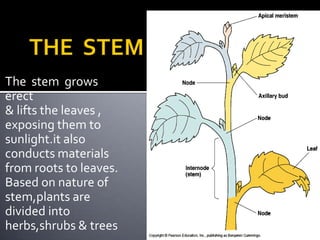
1) Morphology is the study of the external features, arrangement, and relationships of plant organs. Roots grow underground and absorb water and minerals, anchoring the plant. Stems grow above ground and transport nutrients between roots and leaves.
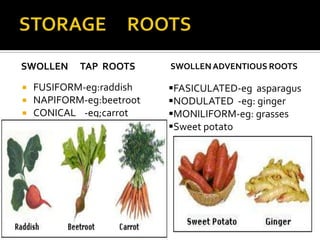
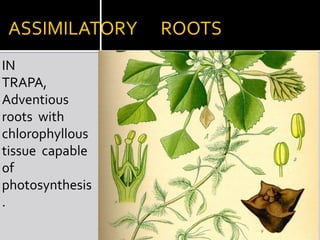
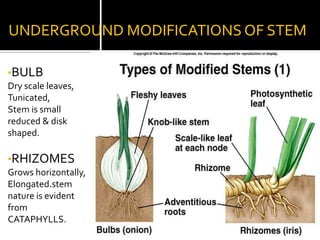
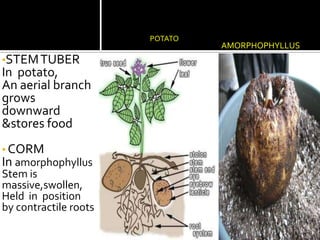
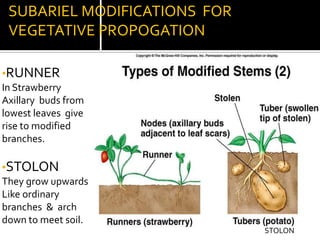
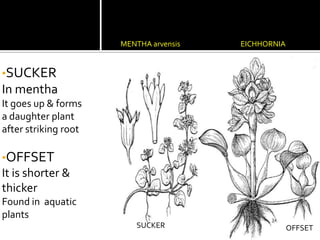
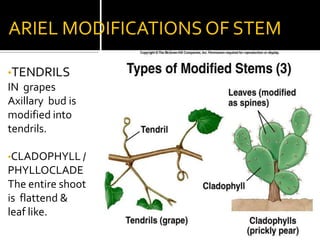
2) Roots have various modifications including storage roots, prop roots, stilt roots, climbing roots, and parasitic roots. Stems also have modifications underground like bulbs, corms, rhizomes, and above ground like runners, stolons, and suckers.
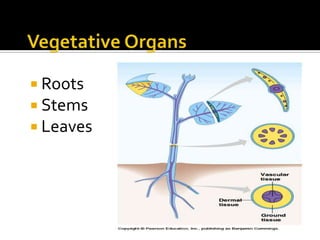
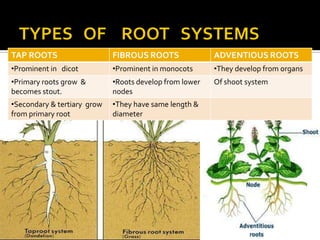
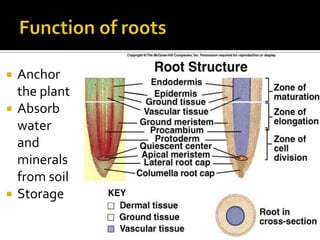
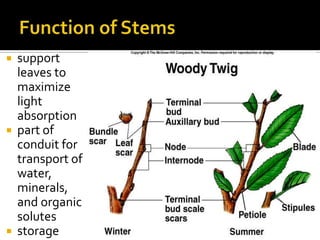
3) Vegetative plant organs include roots, stems, and leaves. Roots have different root systems and serve functions of anchoring, absorption, and storage. Stems support leaves and