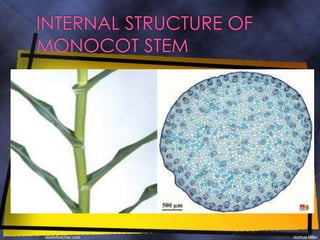
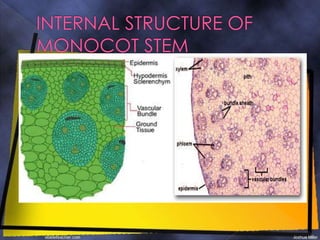
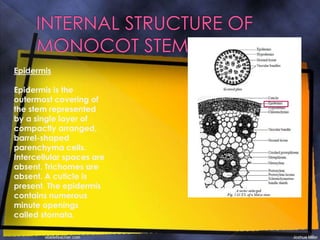
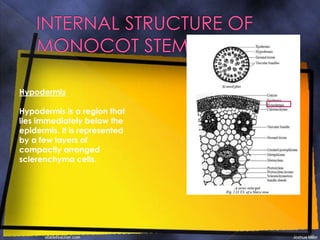
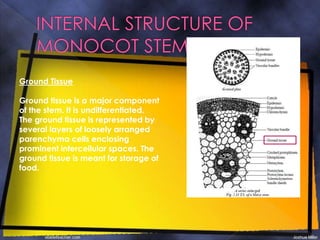
The epidermis is a single layer of compact parenchyma cells with a cuticle and stomata. Below this is the hypodermis of compact sclerenchyma cells. The ground tissue makes up most of the stem and contains loosely arranged parenchyma cells with spaces. Vascular bundles are irregularly scattered throughout the ground tissue and each has a sclerenchyma bundle sheath. The bundles are conjoint, collateral and closed with endarch xylem formation.