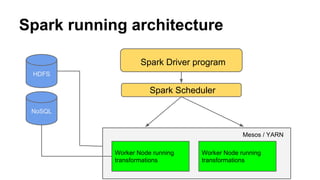
Spark uses Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs) as its fundamental data structure. RDDs are immutable, lazy evaluated collections of data that can be operated on in parallel. This allows RDD transformations to be computed lazily and combined for better performance. RDDs also support type inference and caching to improve efficiency. Spark programs run by submitting jobs to a cluster manager like YARN or Mesos, which then schedule tasks across worker nodes where the lazy transformations are executed.





![Immutability in collections
Mutable Immutable
var collection = [1,2,4,5]
for ( i = 0; i<collection.length; i++) {
collection[i]+=1;
}
Uses loop for updating
collection is updated in place
val collection = [1,2,4,5]
val newCollection = collection.map(value
=> value +1)
Uses transformation for change
Creates a new copy of collection. Leaves
collection intact](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-architecture-150224035228-conversion-gate02/85/Spark-architecture-6-320.jpg)
![Multiple transformations
Mutable Immutable
var collection = [1,2,4,5]
for ( i = 0; i<collection.length; i++) {
collection[i]+=1;
}
for ( i = 0; i<collection.length; i++) {
collection[i]+=2;
}
val collection = [1,2,4,5]
val newCollection = collection.map(value
=> value +1)
val nextNewCollection = newCollection.
map(value => value +2)
Creates 3 copies of same collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-architecture-150224035228-conversion-gate02/85/Spark-architecture-7-320.jpg)







![Type inference in action
● val collection = [1,2,4,5] // explicit type Array
● val c1 = collection.map( value => value + 1) // Array
only
● val c2 = c1.map( value => value +2 ) // Array only
● val c3 = c2.count( ) // inferred as Int
● val c4 = c3.map(value => value+3) //gets error. As you
cannot map over an integers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark-architecture-150224035228-conversion-gate02/85/Spark-architecture-15-320.jpg)