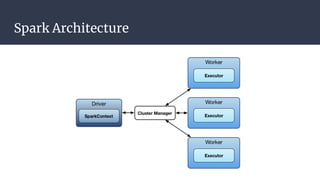
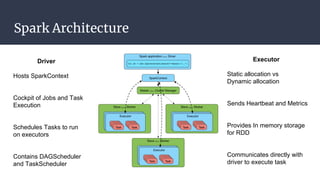
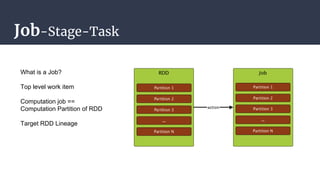
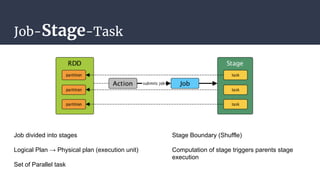
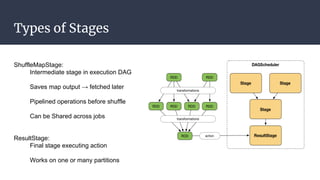
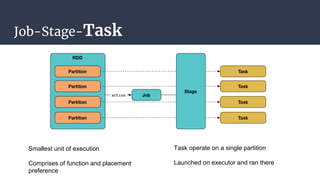
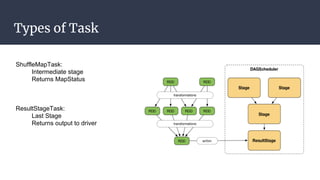
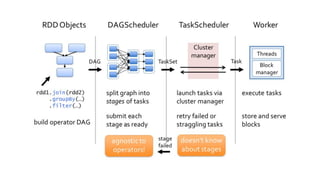
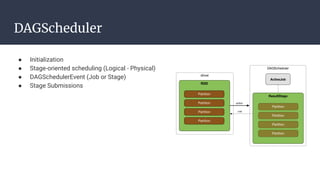
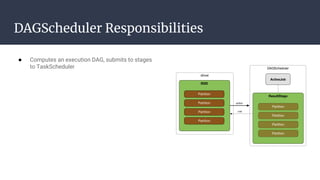
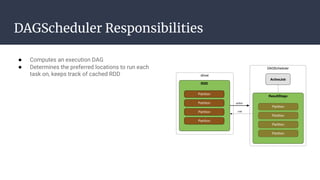
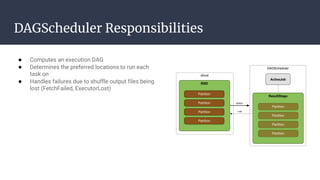
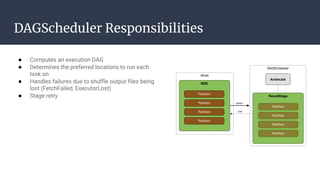
The DAGScheduler is responsible for computing the DAG of stages for a Spark job and submitting them to the TaskScheduler. The TaskScheduler then submits individual tasks from each stage for execution and works with the DAGScheduler to handle failures through task and stage retries. Together, the DAGScheduler and TaskScheduler coordinate the execution of jobs by breaking them into independent stages of parallel tasks across executor nodes.