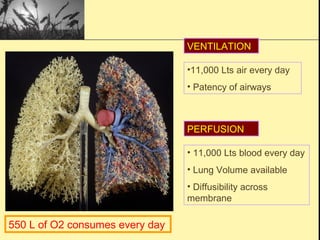
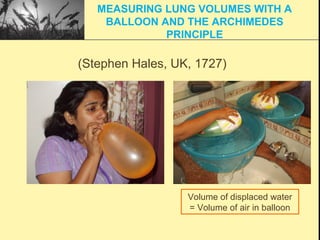
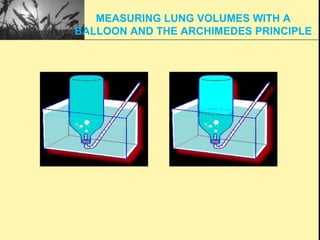
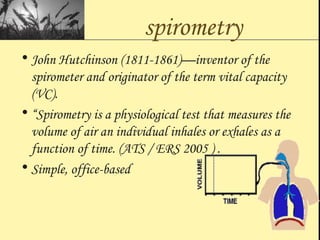
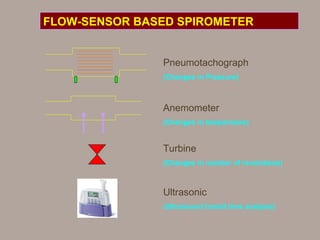
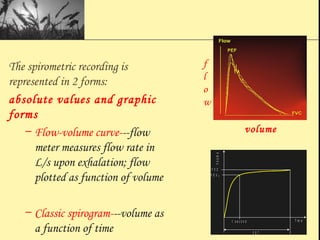
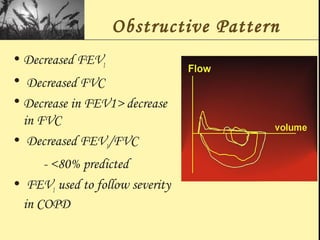
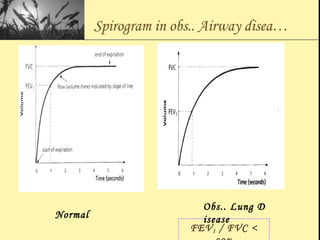
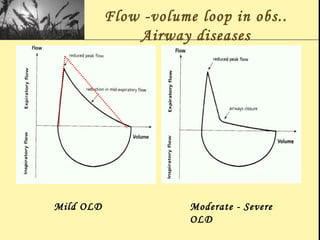
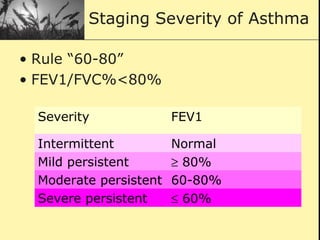
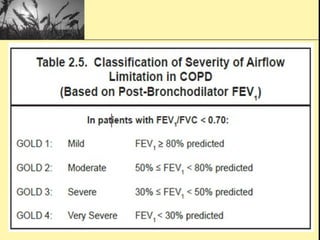
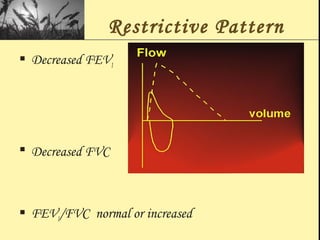
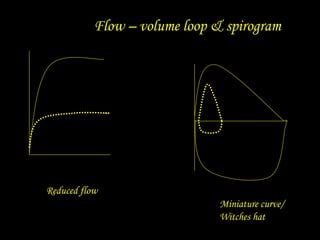
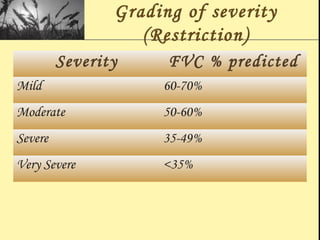
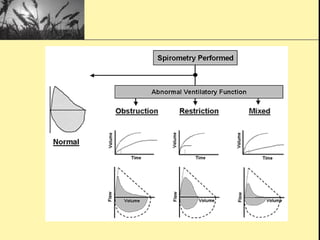
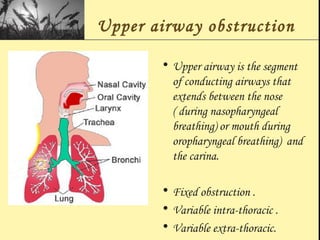
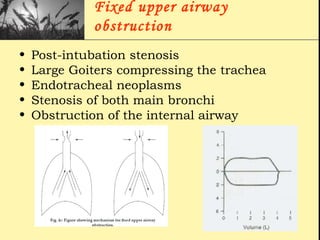
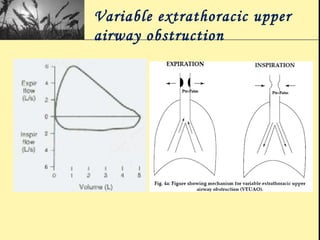
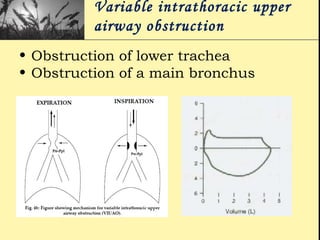
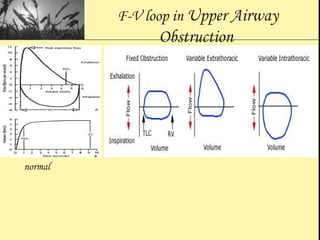
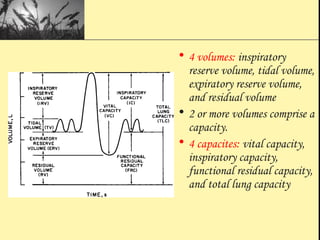
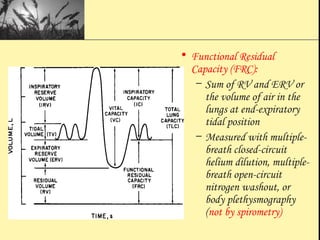
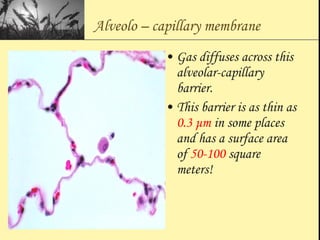
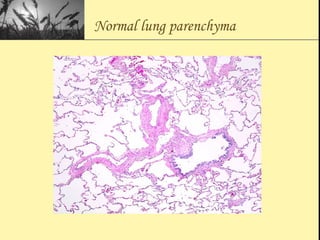
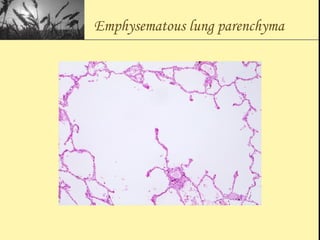
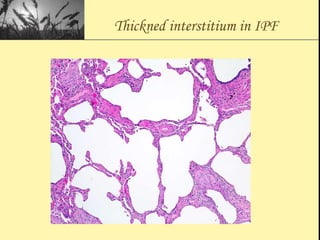
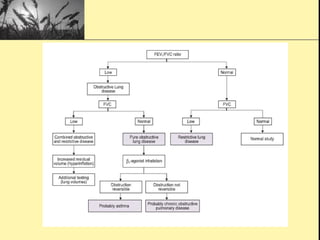
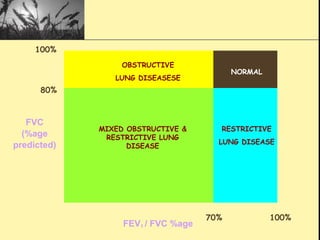
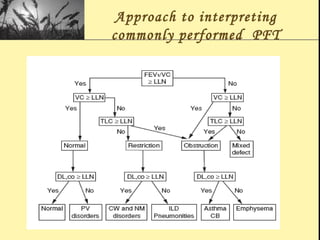
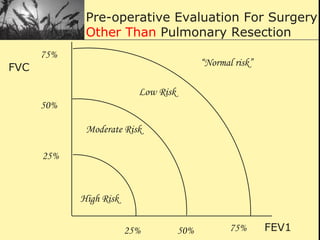
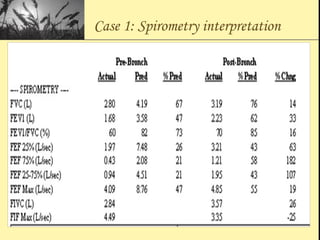
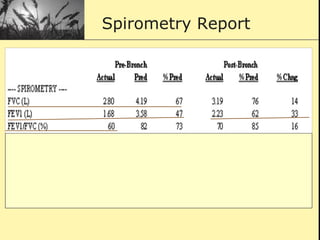
Pulmonary function tests provide objective measurements of lung function through various tests. Spirometry is the most basic and widely used test that measures volumes of air inhaled and exhaled over time through a spirometer. It can detect obstructive or restrictive lung diseases patterns based on evaluations of parameters like FEV1, FVC, FEV1/FVC ratio, and flow-volume loops. Other tests measure lung volumes, diffusion capacity, and assess ventilation/perfusion ratios to further characterize lung abnormalities. Together, pulmonary function tests provide quantifiable data to support diagnoses suggested by symptoms and physical exams.