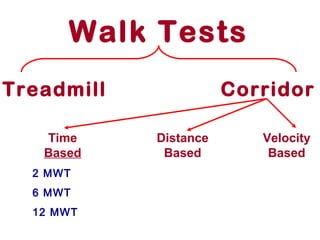
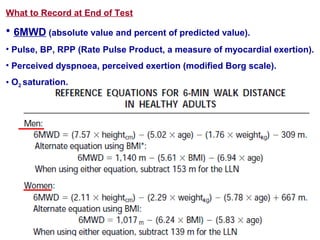
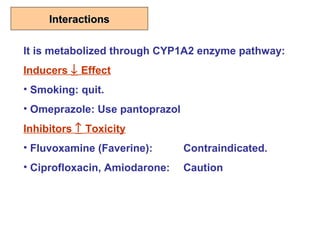
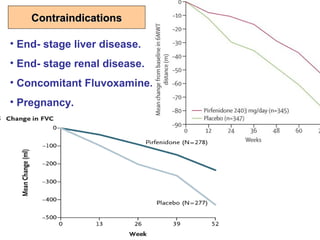
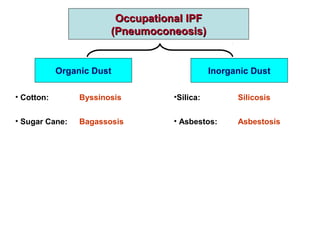
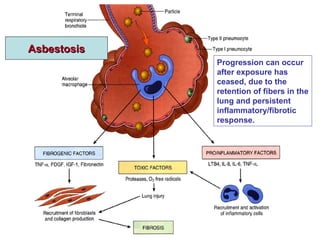
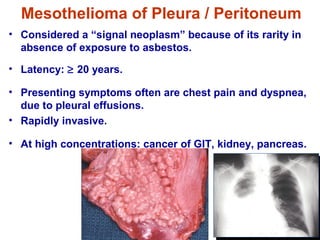
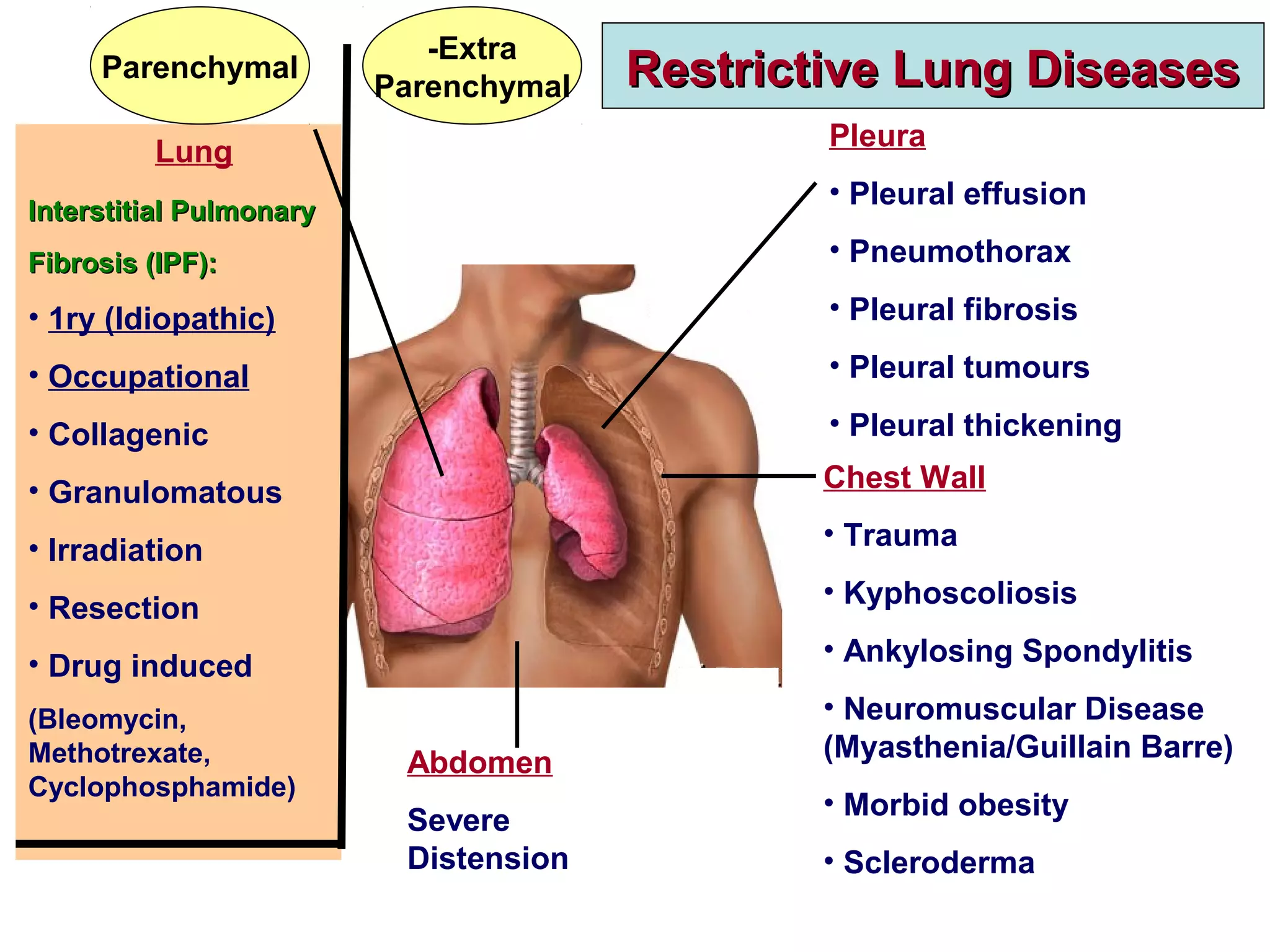
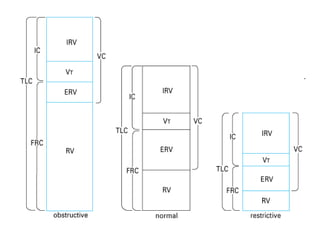
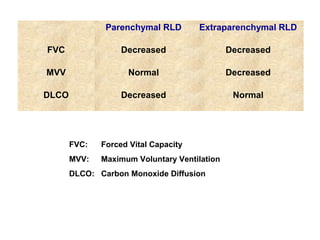
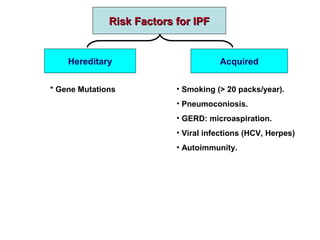
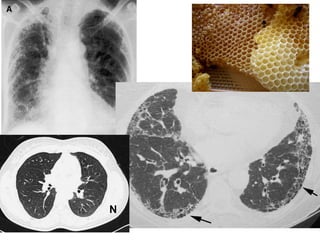
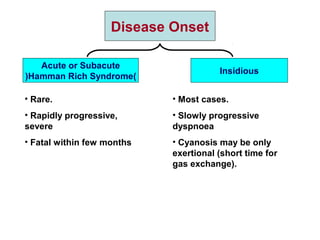
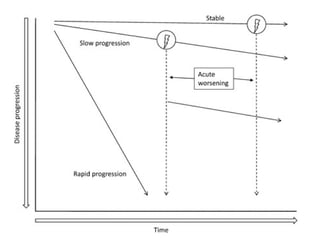
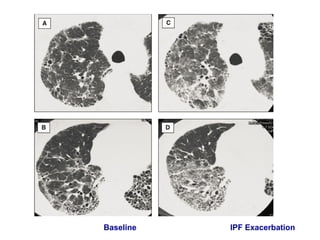
This document discusses restrictive lung diseases including interstitial lung fibrosis and asbestosis. It defines interstitial pulmonary fibrosis as a chronic, fibrosing interstitial pneumonia of unknown cause typically affecting adults over 50. Usual interstitial pneumonia is the most common form and has a median survival of 3 years. Asbestosis is an occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of asbestos fibers, which can lead to pleural thickening, effusions, rounded atelectasis or fibrosis. Prevention focuses on never disturbing asbestos materials and smoking cessation.


![Cause of Death in IPF
IPF
]N=543[
1-7year Follow up
60%Died
]N=326[
Respiratory
failure
39%
Lung
cancer
10%
Pulmonary
embolism
3%
Pulmonary
infection
3%
Cardiovascular
disease
27%
Other
18%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/restrictivelungdiseases-140402150424-phpapp02/85/4-Restrictive-Lung-Diseases-15-320.jpg)