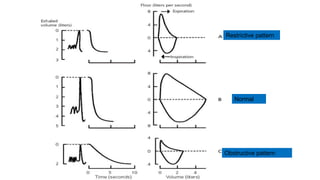
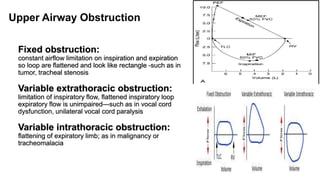
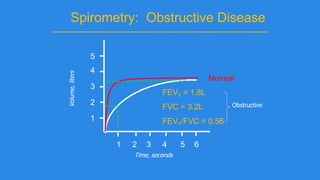
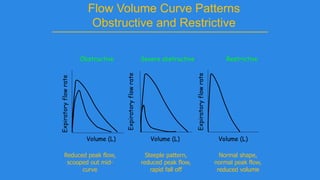
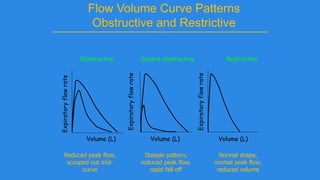
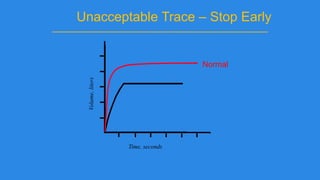
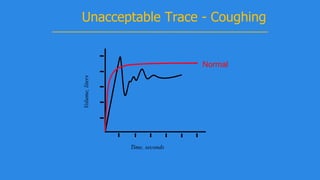
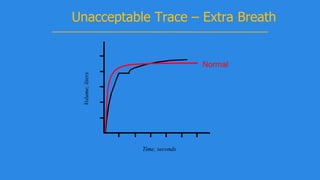
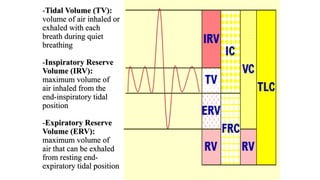
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) evaluate aspects of lung function using standardized equipment. Common PFTs include spirometry, which measures volumes of air inhaled and exhaled over time; diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO), which measures gas exchange; and body plethysmography, which measures lung volumes. Spirometry was invented in the 1800s and measures parameters such as forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and their ratio (FEV1/FVC). Normal values vary based on age, height, sex, and ethnicity. PFTs can detect obstructive and restrictive lung diseases based on patterns of airflow






















![Performing spirometry
Spirometry can be performed at the bedside, physician’s
consulting room or a laboratory and must be recorded.
Sitting is considered safe in order to prevent falling due
to syncope. However, in obese and pregnant subjects, the
standing position may be preferred. In children[more
than 4 yrs] seated position is preferred.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bydrgirishpulmonaryfunctiontests-180313141020/85/By-dr-girish-pulmonary-function-tests-24-320.jpg)