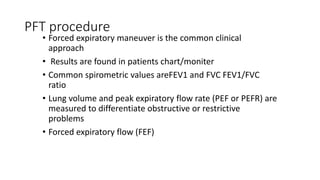
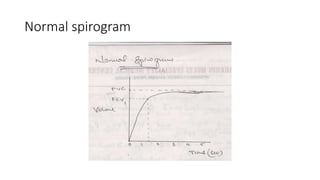
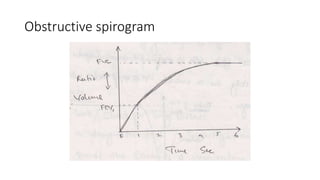
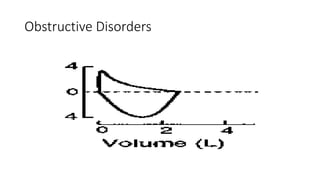
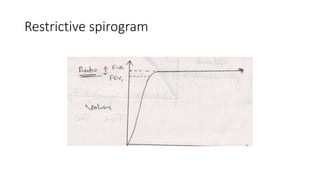
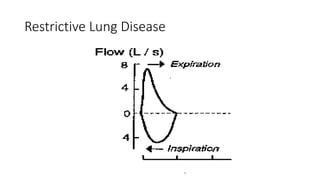
This document discusses various pulmonary function tests (PFTs) including spirometry. PFTs measure how well the lungs work by assessing lung volumes, airway function, and gas exchange. Spirometry specifically measures airflow and lung capacity. It involves taking a deep breath and then forcibly exhaling for 6 seconds into a spirometer. Key measurements include FEV1, FVC, and their ratio (FEV1%), which can help identify obstructive or restrictive lung diseases. Abnormal PFT results are below 80% of predicted values and indicate the severity of lung impairment. PFTs are useful diagnostic tools that also monitor treatment effectiveness.













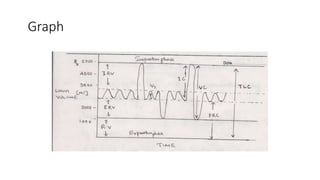
![• IC-max: amount of gas inspired in to the lungs after a
normal tidal exp: [IC=TV+IRV] 3500ml
• FRC-amount of gas remain in the lungs after normal exp:[
FRC=ERV+RV] 2500ml
• VC-max: amount of gas expired from the lungs after a max:
insp: [VC=IRV+TV+ ERV] 4500ml
• TLC-max: amount of gas inspired to expand the lungs to its
max:extend [TLC=TV+IRV +ERV +RV] 6000ml
Lung capacity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmonaryfunctiontests-nursingmaseno-240405191709-85a64b6d/85/Pulmonary-Function-Tests-Nursing-Maseno-pptx-16-320.jpg)