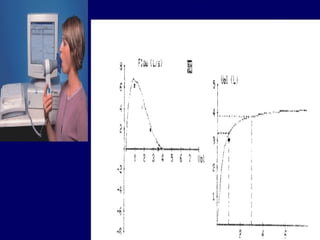
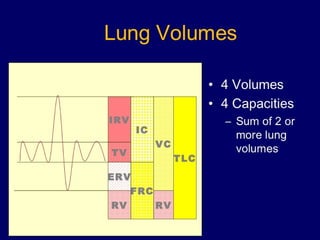
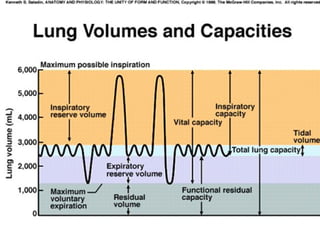
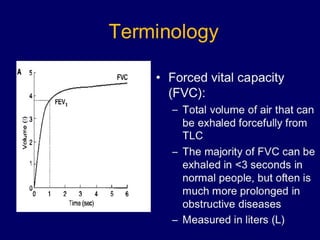
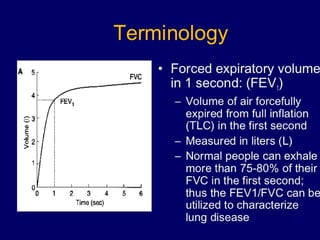
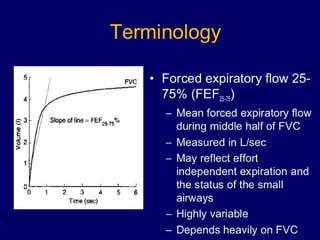
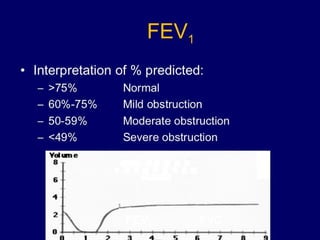
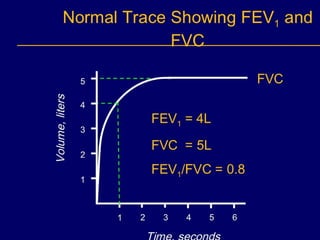
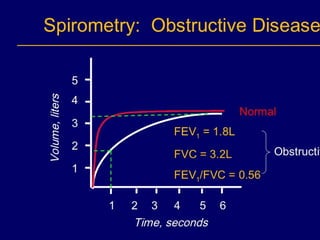
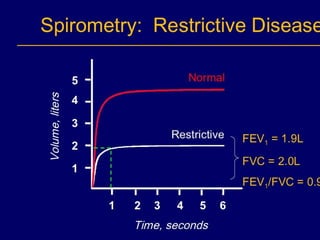
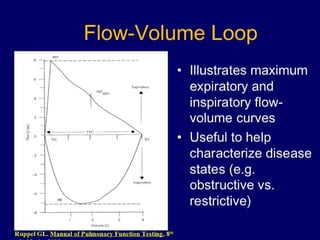
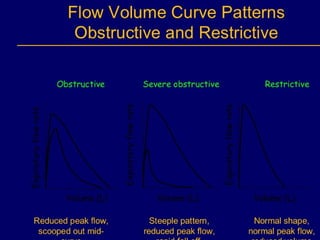
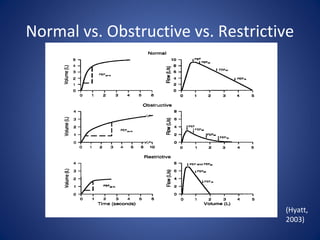
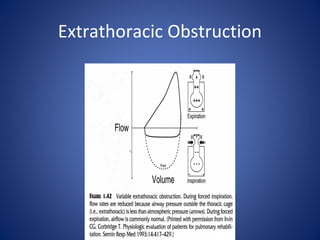
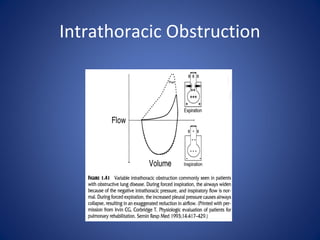
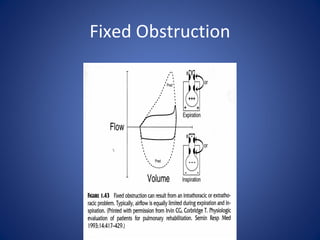
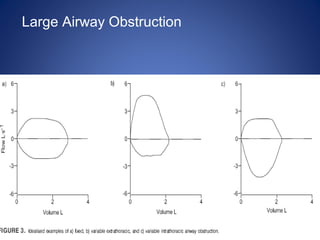
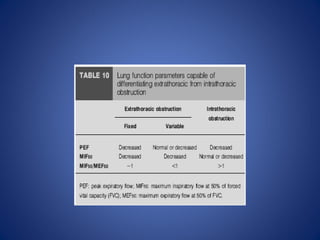
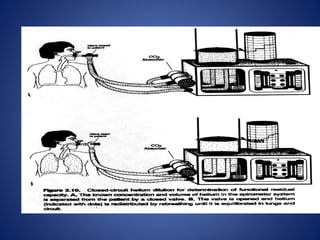
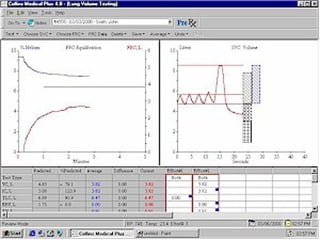
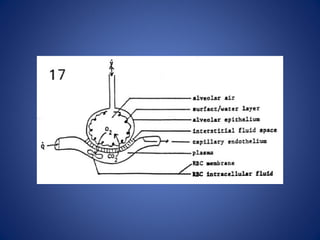
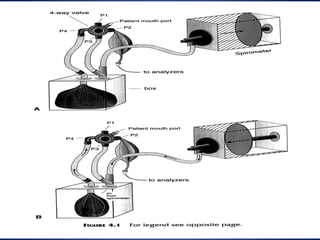
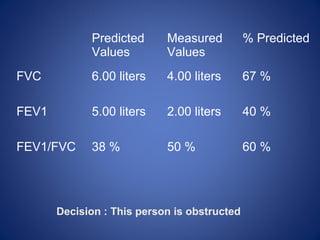
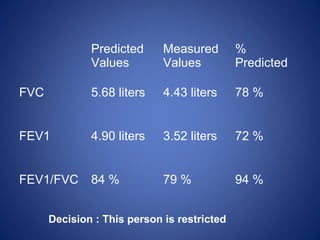
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) objectively assess lung function using tests such as spirometry, lung volume measurements, and diffusing capacity measurements. PFTs can predict, diagnose, and monitor pulmonary dysfunction. They can distinguish between obstructive and restrictive lung diseases and determine disease severity and treatment responses. PFTs also assess surgical risk and postoperative pulmonary complications. Simple bedside tests include breath counts, cough strength tests, and peak flow measurements. Laboratory PFTs precisely measure volumes, flows, gas exchange, and generate flow-volume loops. Proper interpretation of PFTs involves comparing values to predicted normals.