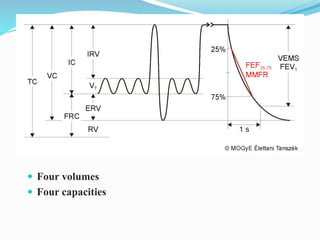
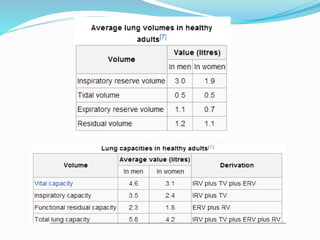
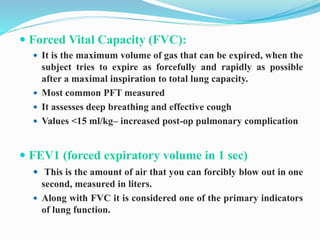
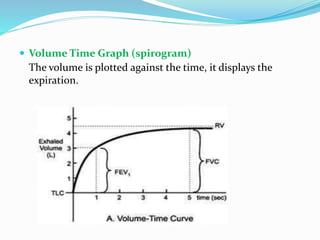
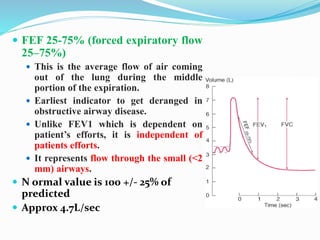
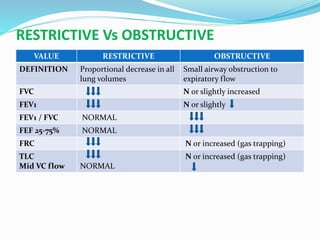
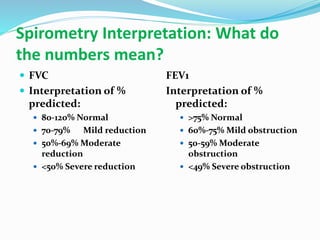
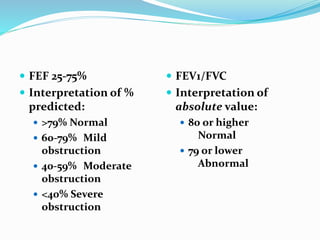
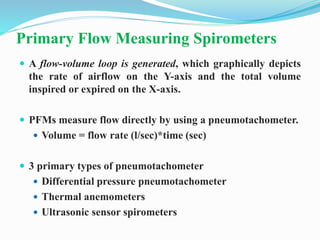
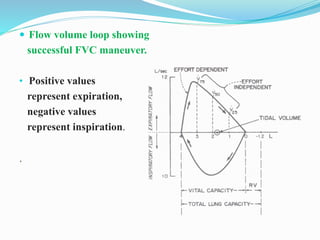
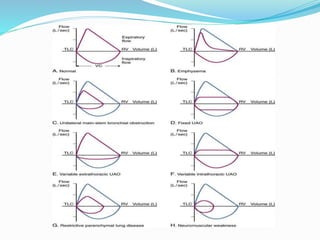
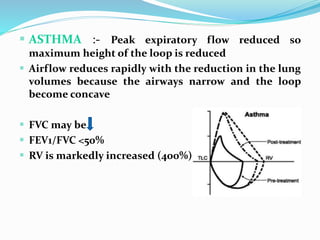
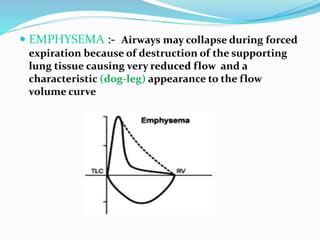
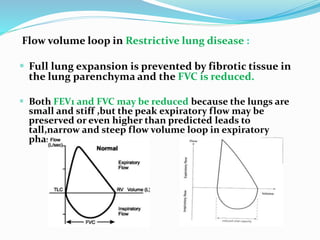
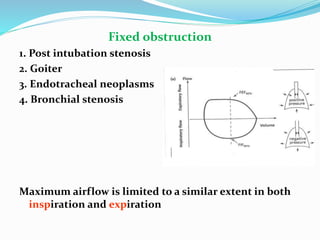
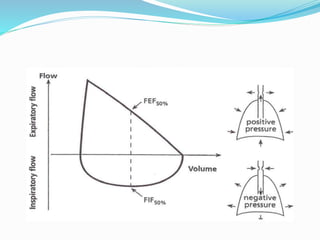
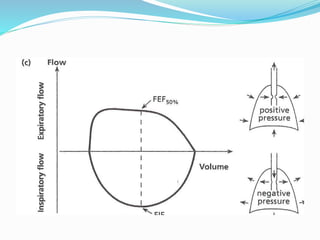
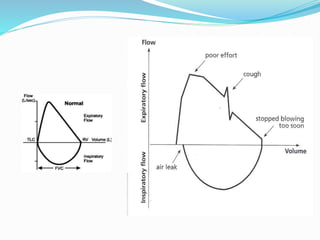
This document discusses pulmonary function tests (PFTs), including their goals, uses, limitations, procedures, and interpretations. PFTs are used to assess lung function before surgeries and characterize any pulmonary dysfunction. Key information obtained from PFTs includes measurements of forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), their ratio (FEV1/FVC), and peak expiratory flow rate. Interpretations of these values can indicate restrictive or obstructive lung disease. The document outlines how PFTs are performed using portable devices or clinic spirometers and flow-volume loops.