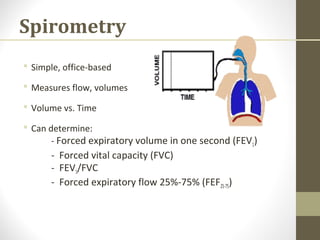
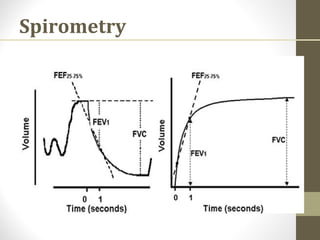
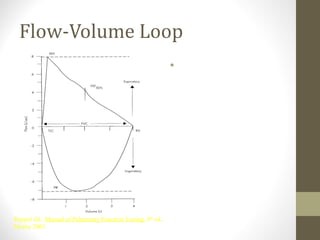
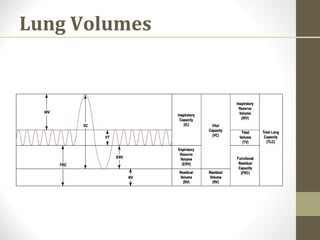
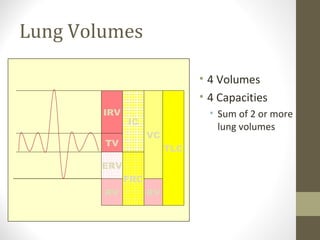
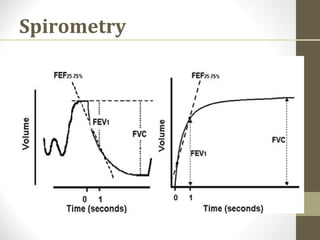
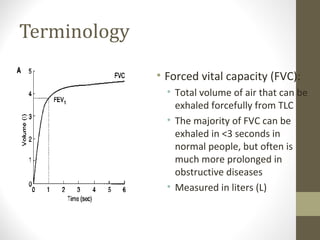
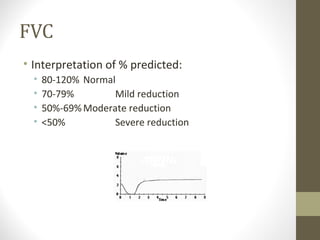
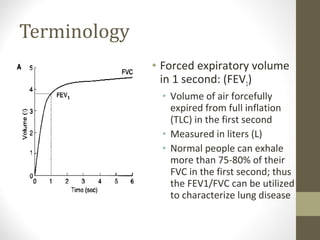
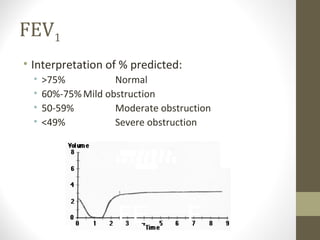
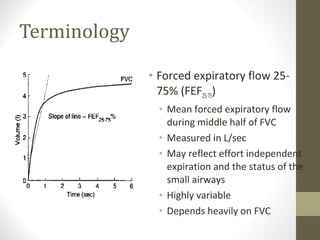
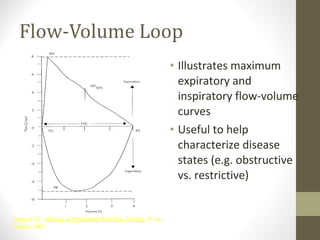
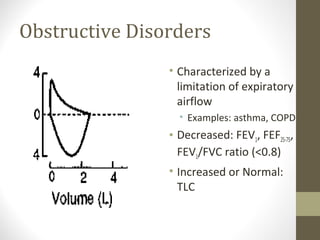
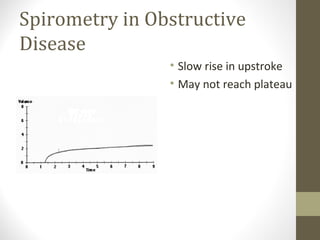
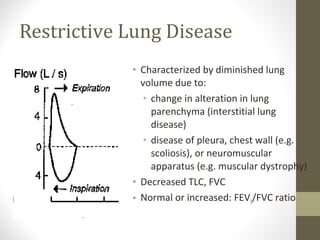
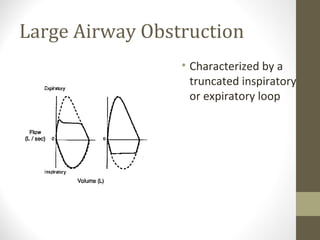
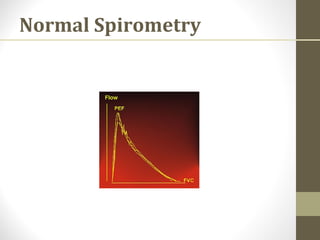
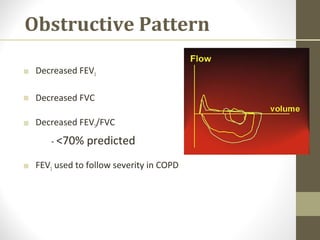
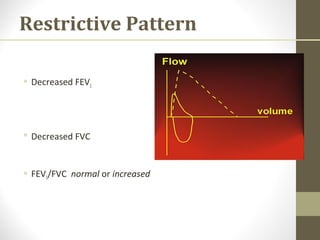
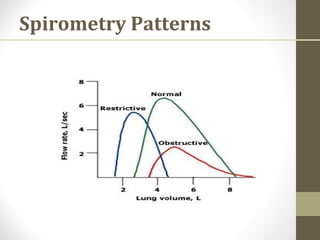
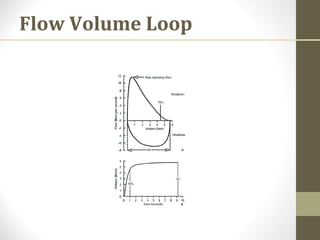
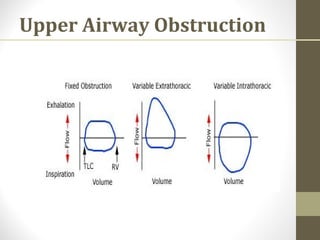
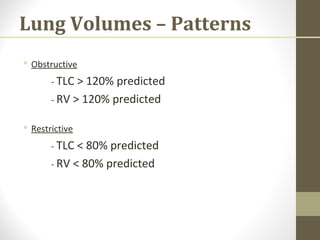
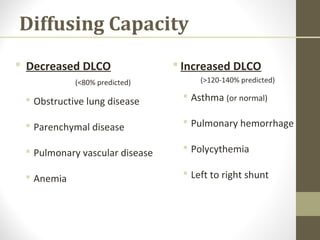
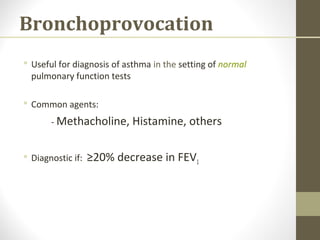
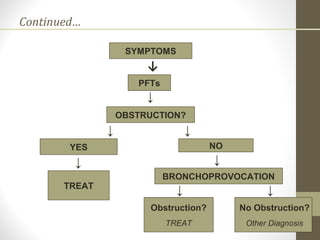
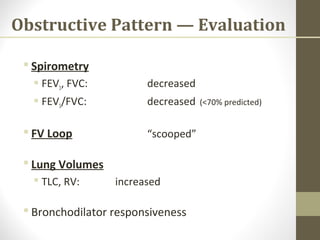
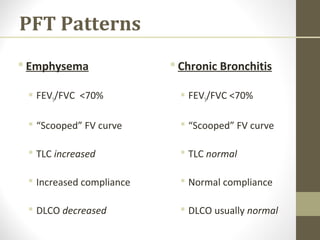
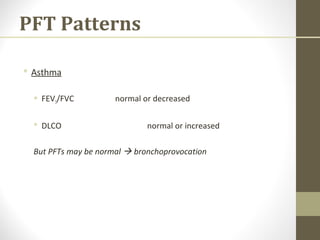
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) evaluate the different components of the respiratory system including the airways, lungs, blood vessels and chest wall muscles. Spirometry is the most common PFT and measures how much air the patient can inhale and exhale. It evaluates values like the forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), and the FEV1/FVC ratio. Obstructive patterns show reduced FEV1 and FVC with a low FEV1/FVC ratio while restrictive patterns have reduced FVC but a normal or increased FEV1/FVC ratio. PFTs are useful for diagnosing conditions like asthma, COPD, and inter