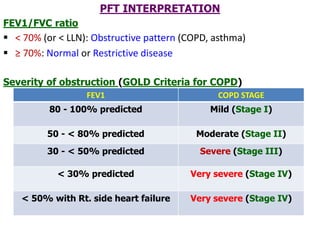
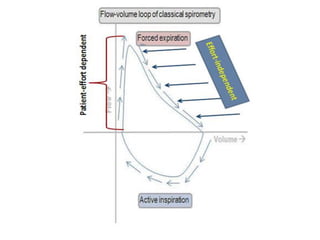
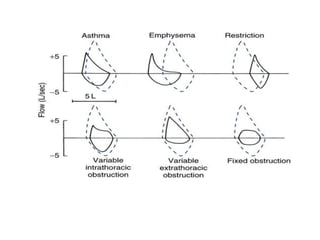
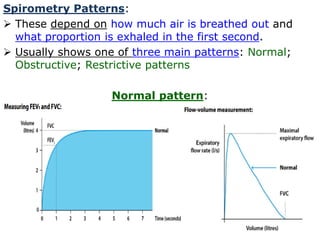
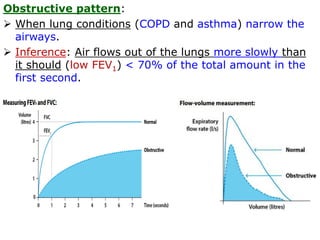
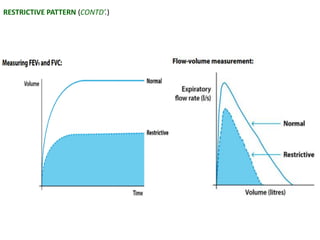
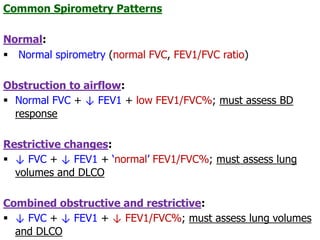
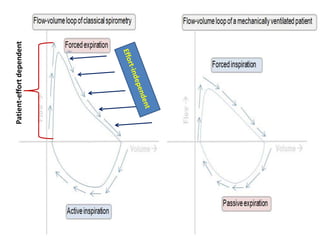
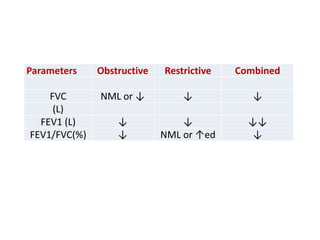
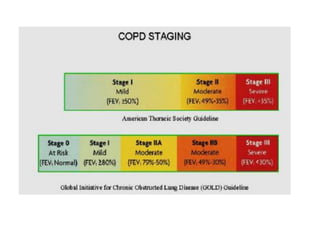
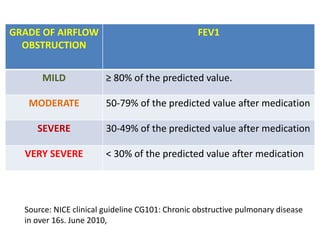
PFTs measure lung function through tests of ventilation, gas exchange, ventilation control, and exercise response. Key measurements include FEV1, FVC, FEV1/FVC ratio, DLCO, and arterial blood gases. PFT results are interpreted to identify obstructive, restrictive, or combined patterns and determine the severity of lung abnormalities.







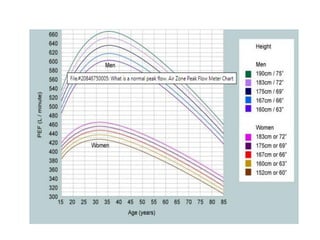
![Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR):
Done using the peak flow meter;
It is the largest expiratory flow achieved w/ a
maximally forced expiratory effort from a position of
maximal inspiration.
Best of three successive readings are noted.
Males (450 – 550 L/min.); Females (350 – 450 L/min.);
PEFR (L/min.) = [Height (in cms.) – 80] x 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpretationofpfts-230522001155-e1a4f713/85/INTERPRETATION-OF-PFTs-pdf-8-320.jpg)