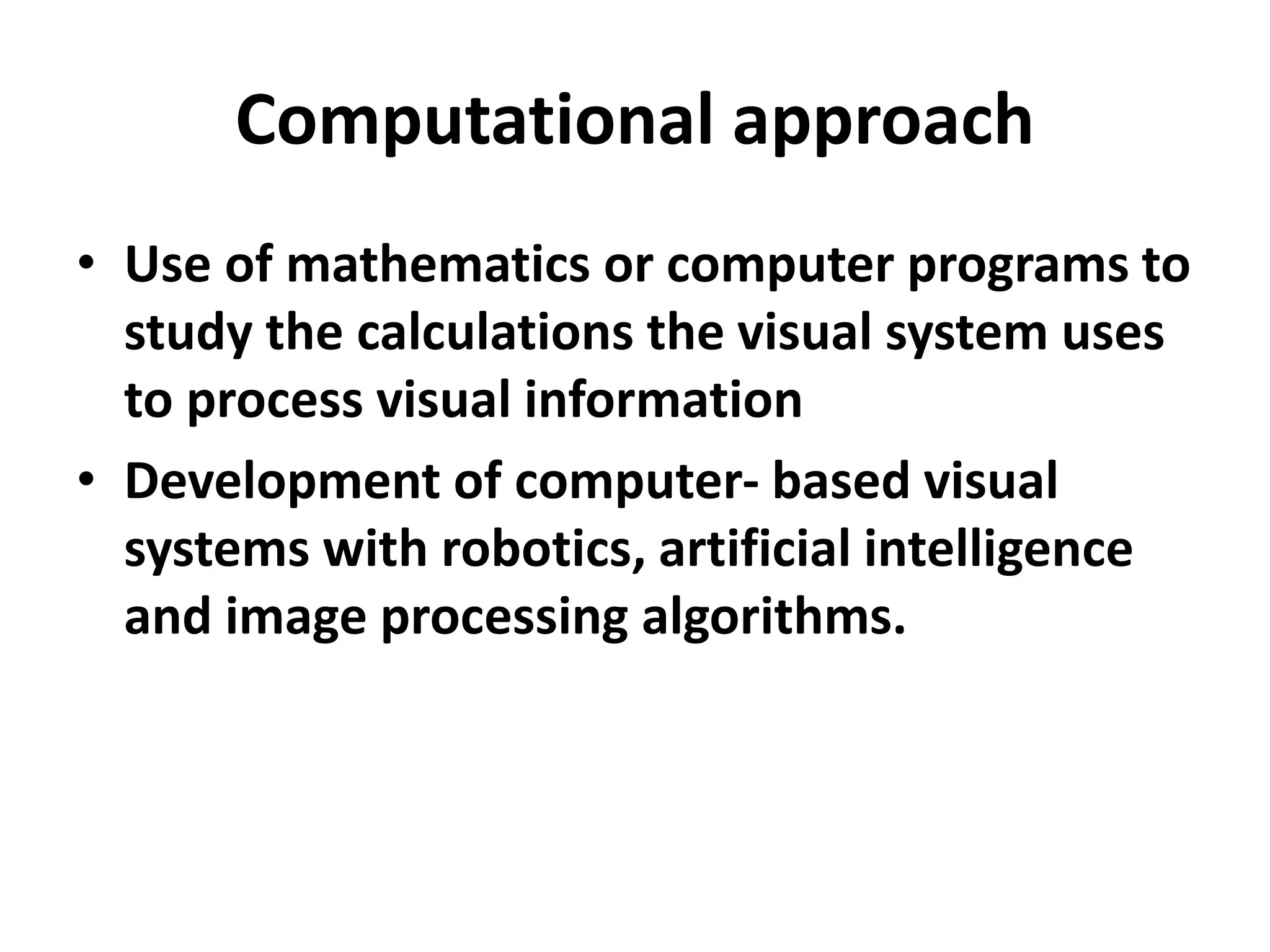
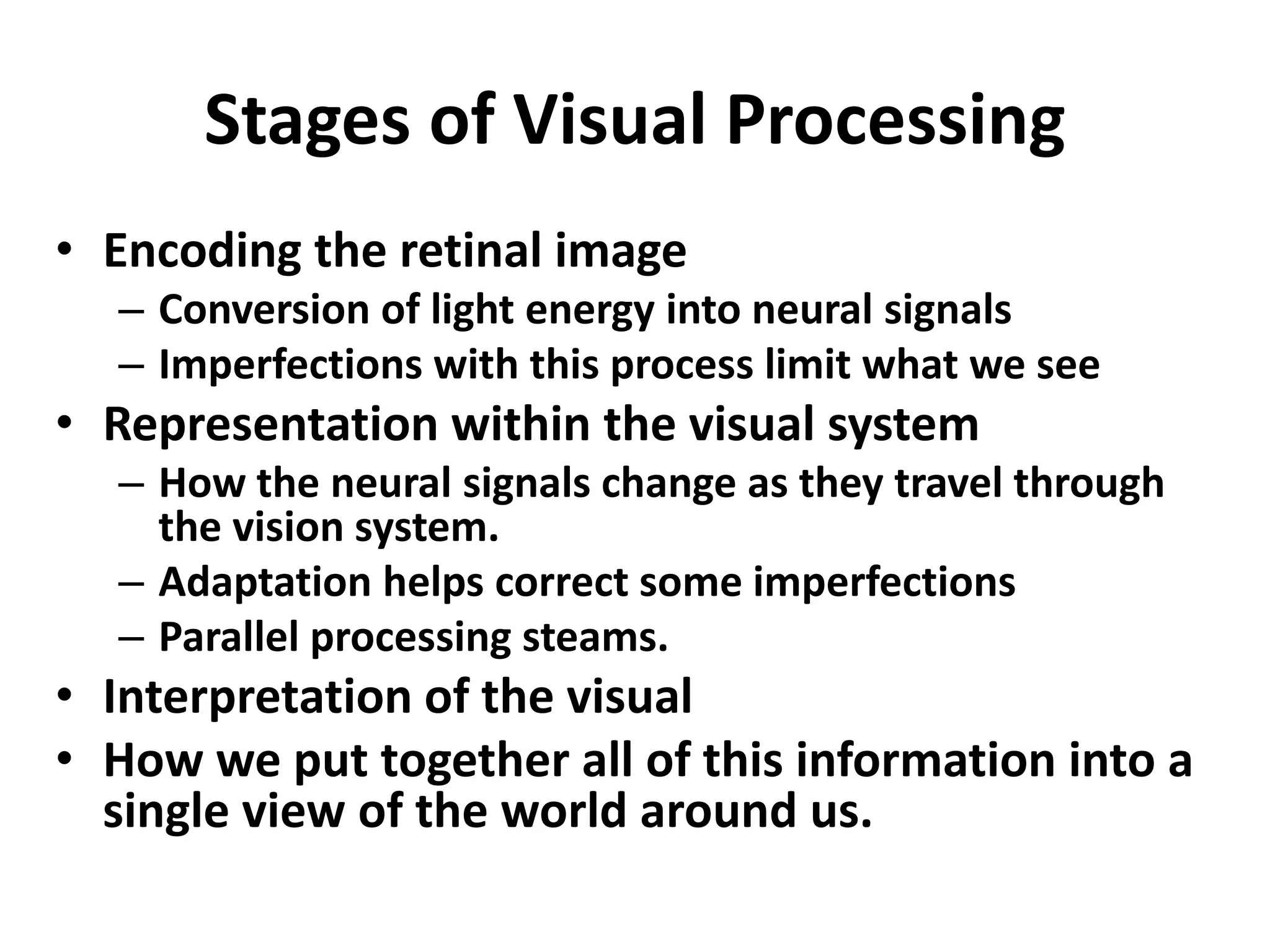
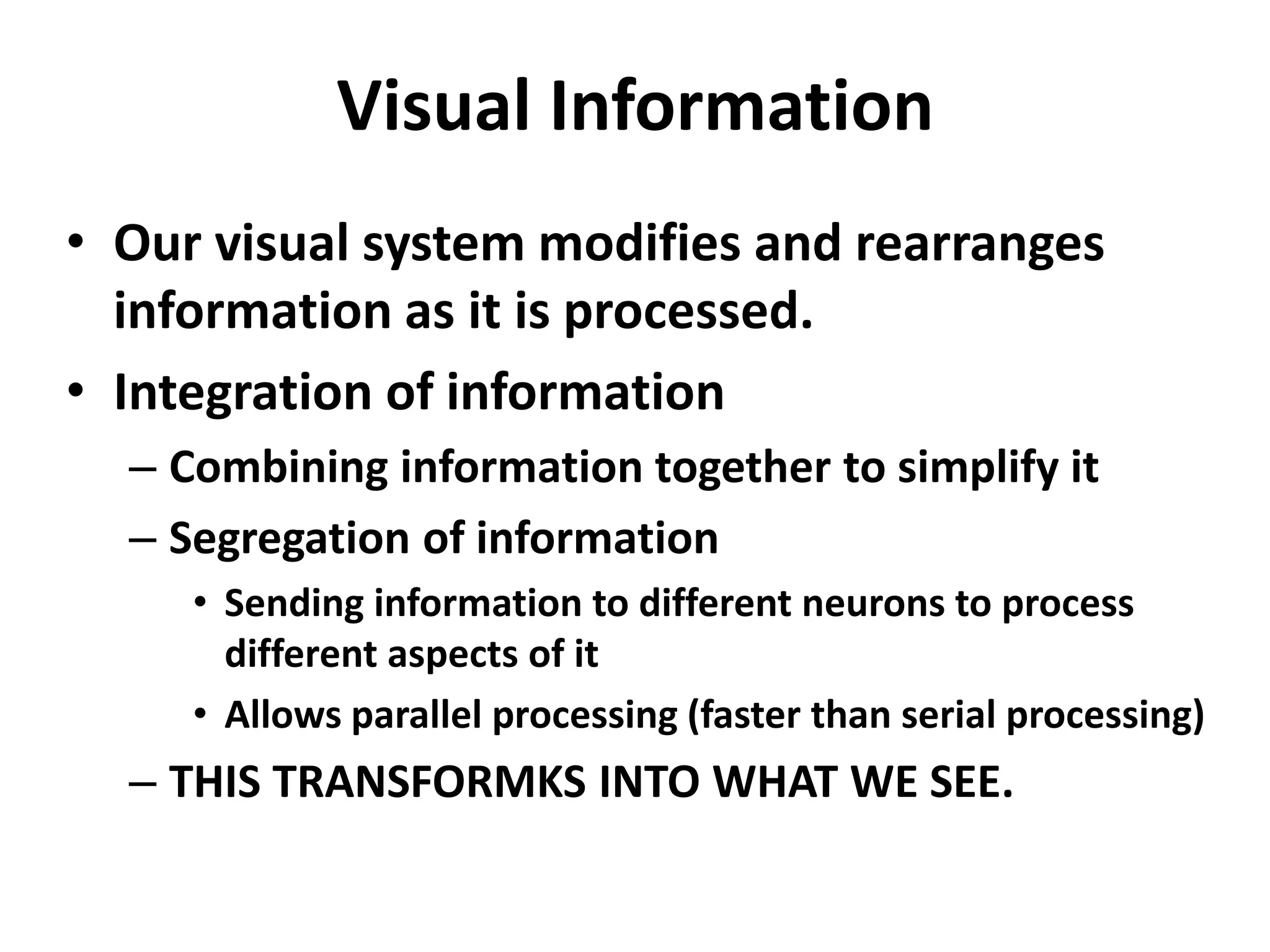
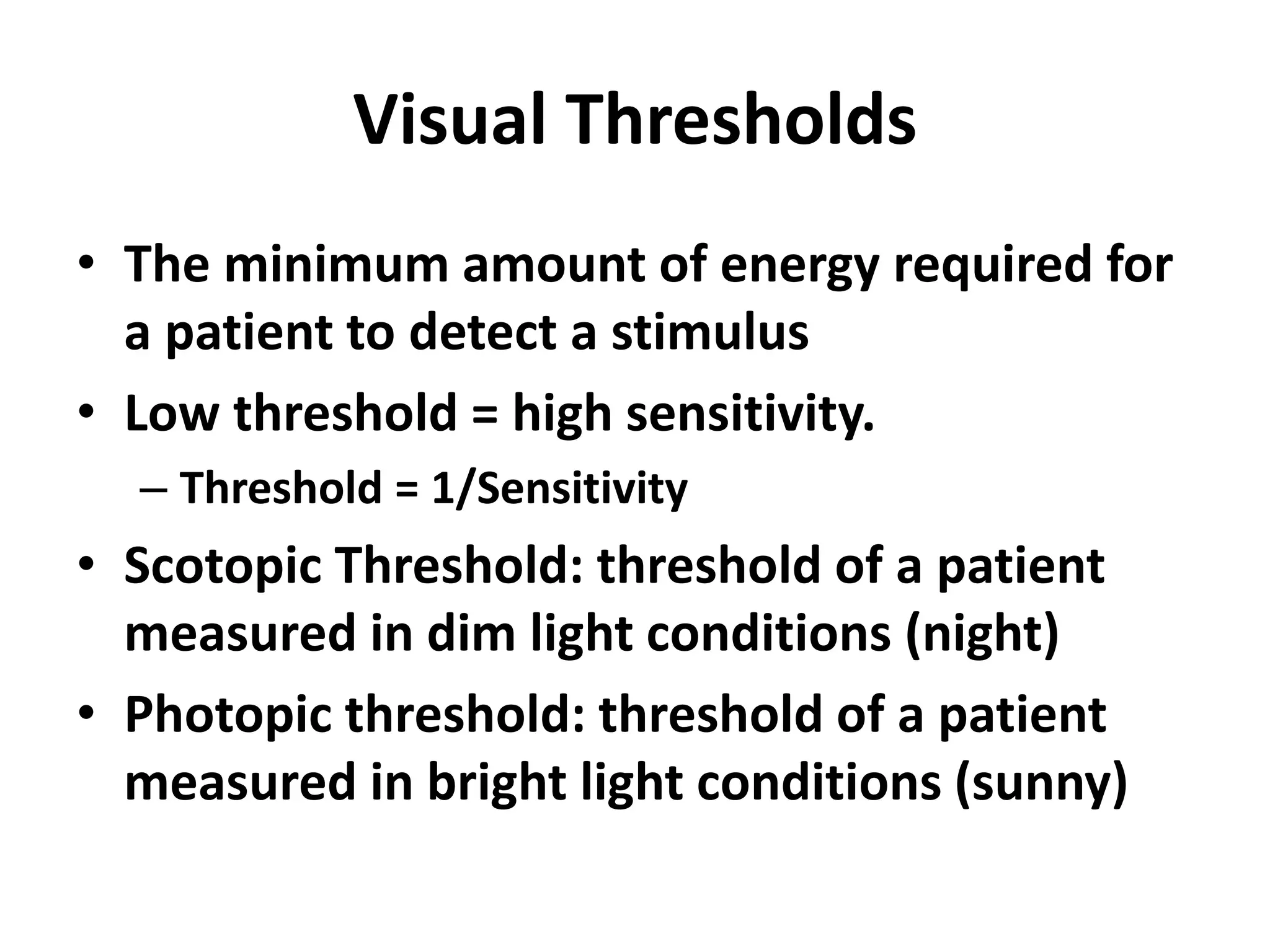
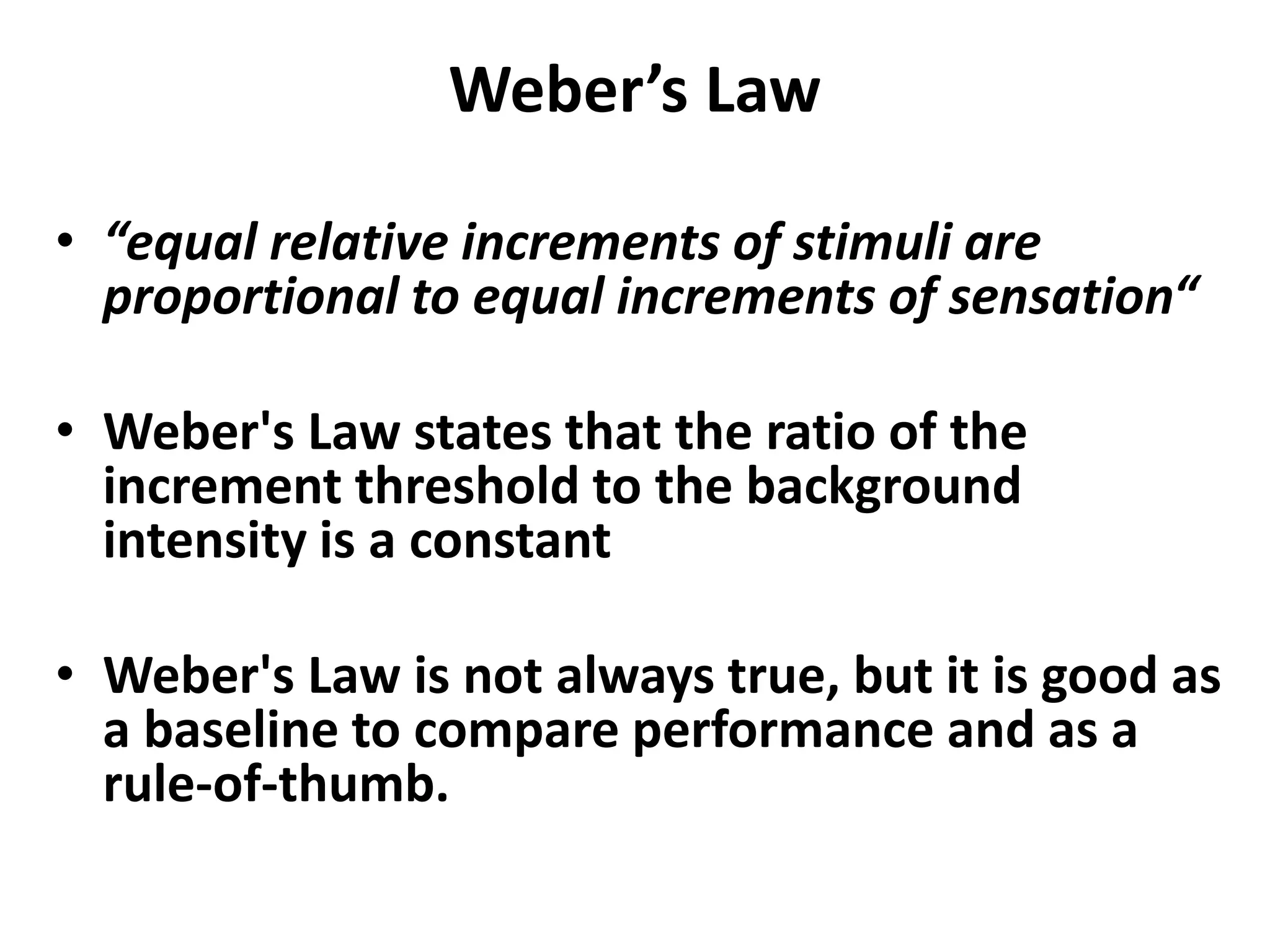
Vision science studies the mechanisms by which light is transformed into visual perception and appreciation of the world. It draws on many disciplines like neuroanatomy, psychophysics, and clinical data. Psychophysics methods measure visual thresholds and sensitivity to understand the limits of human vision. Weber's law states that the minimum detectable difference between a stimulus and background is proportional to the background intensity. This relates to clinical tests like visual acuity which use different background light levels and stimulus contrasts.