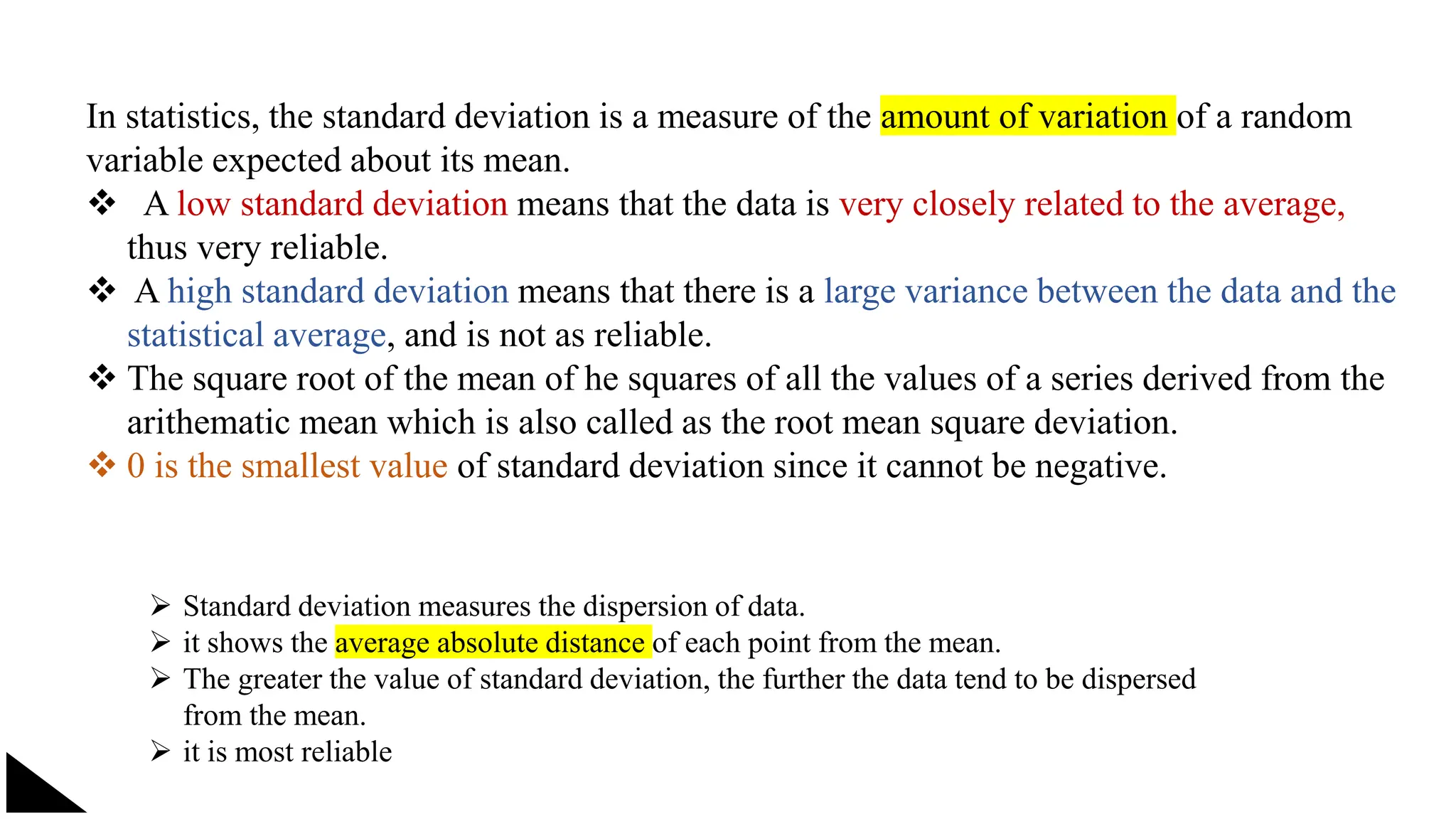
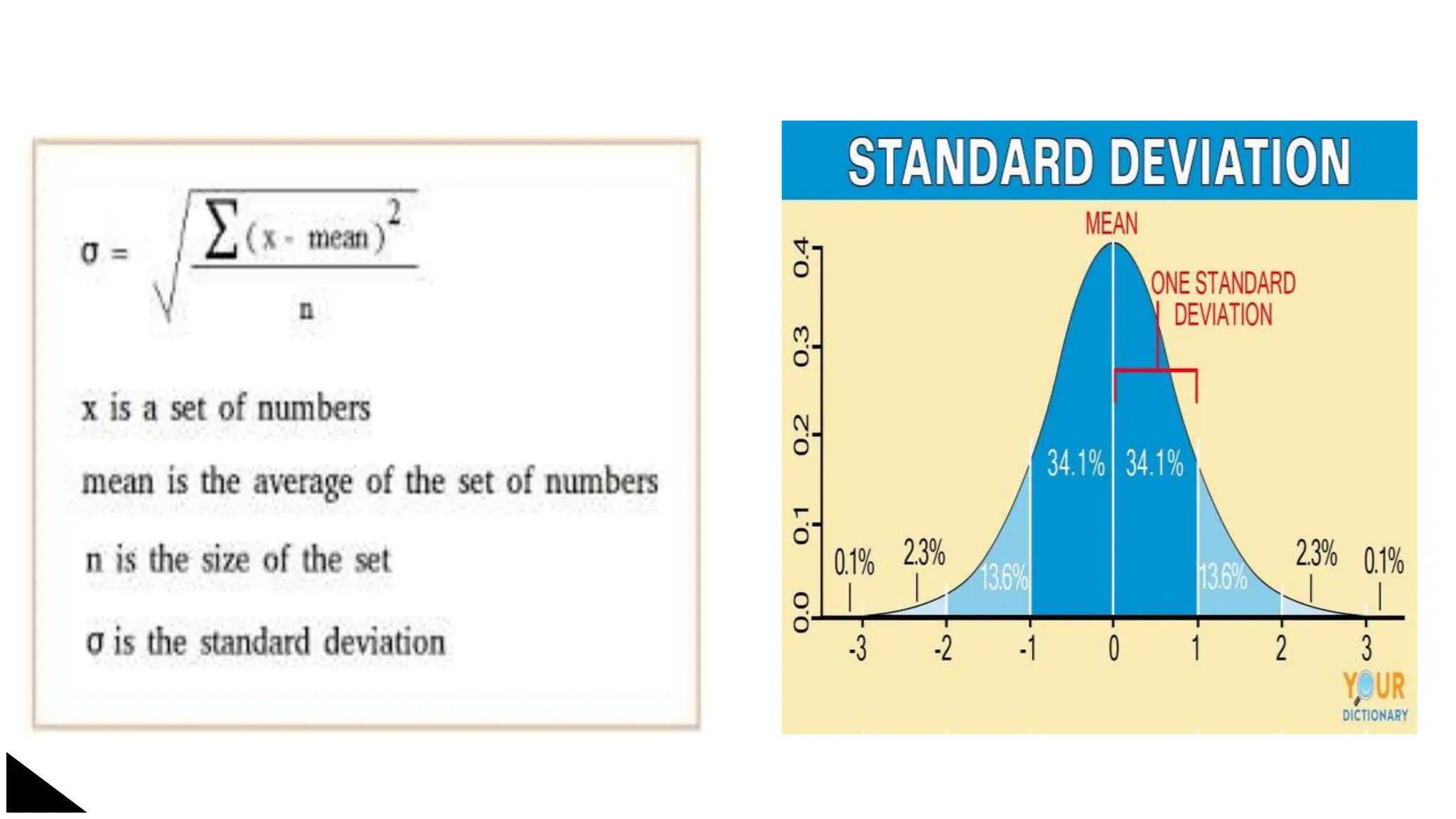
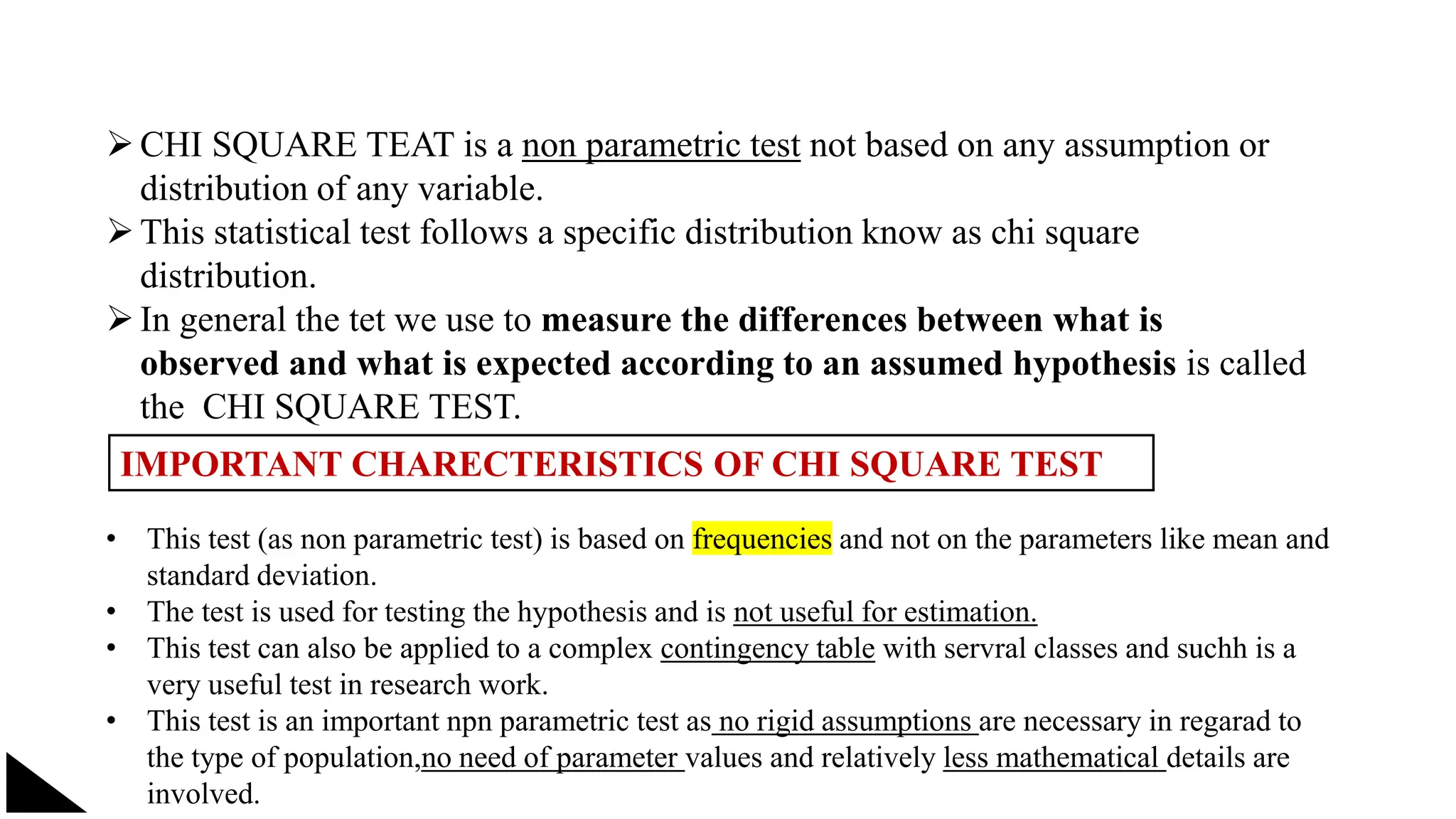
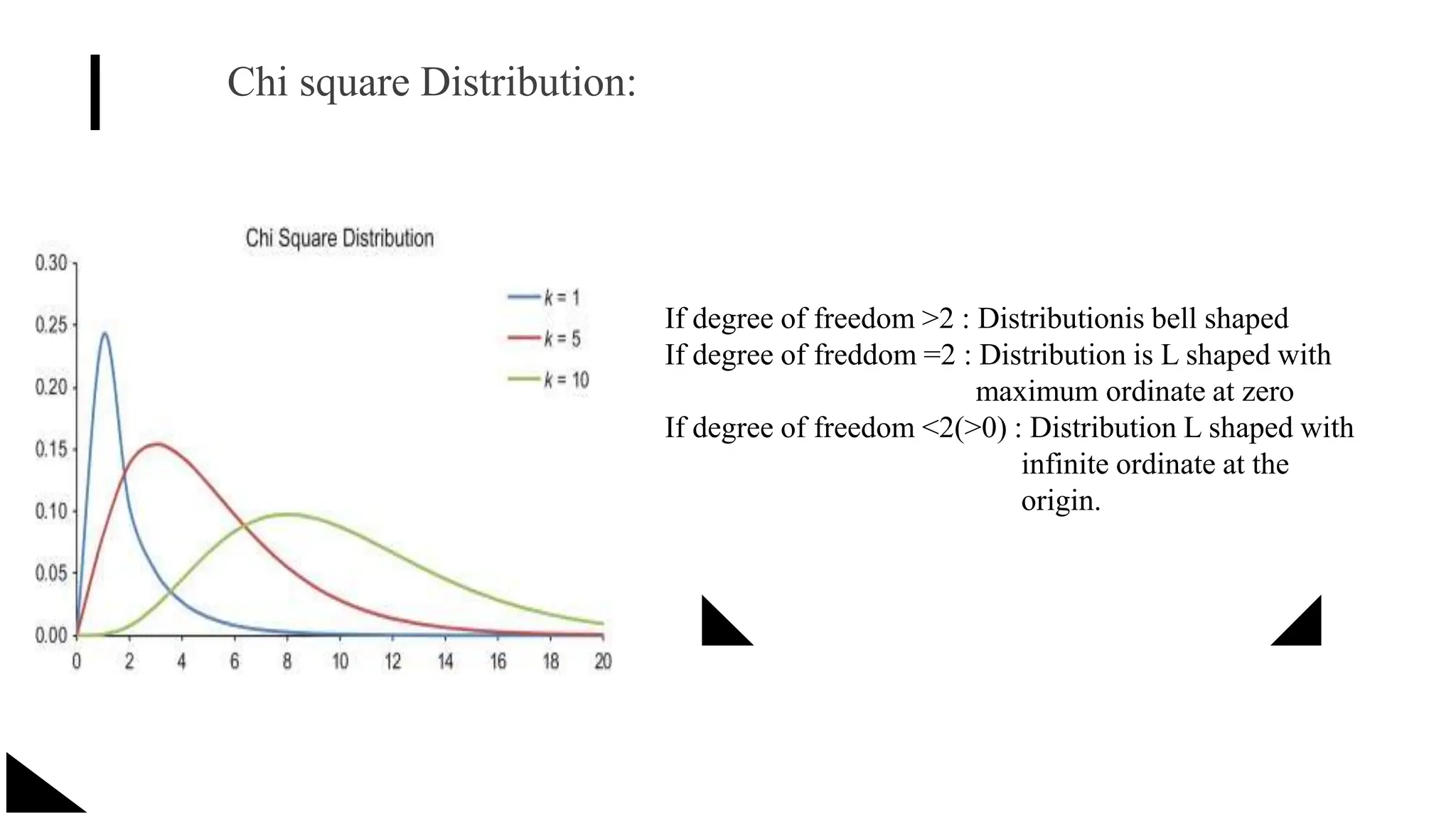
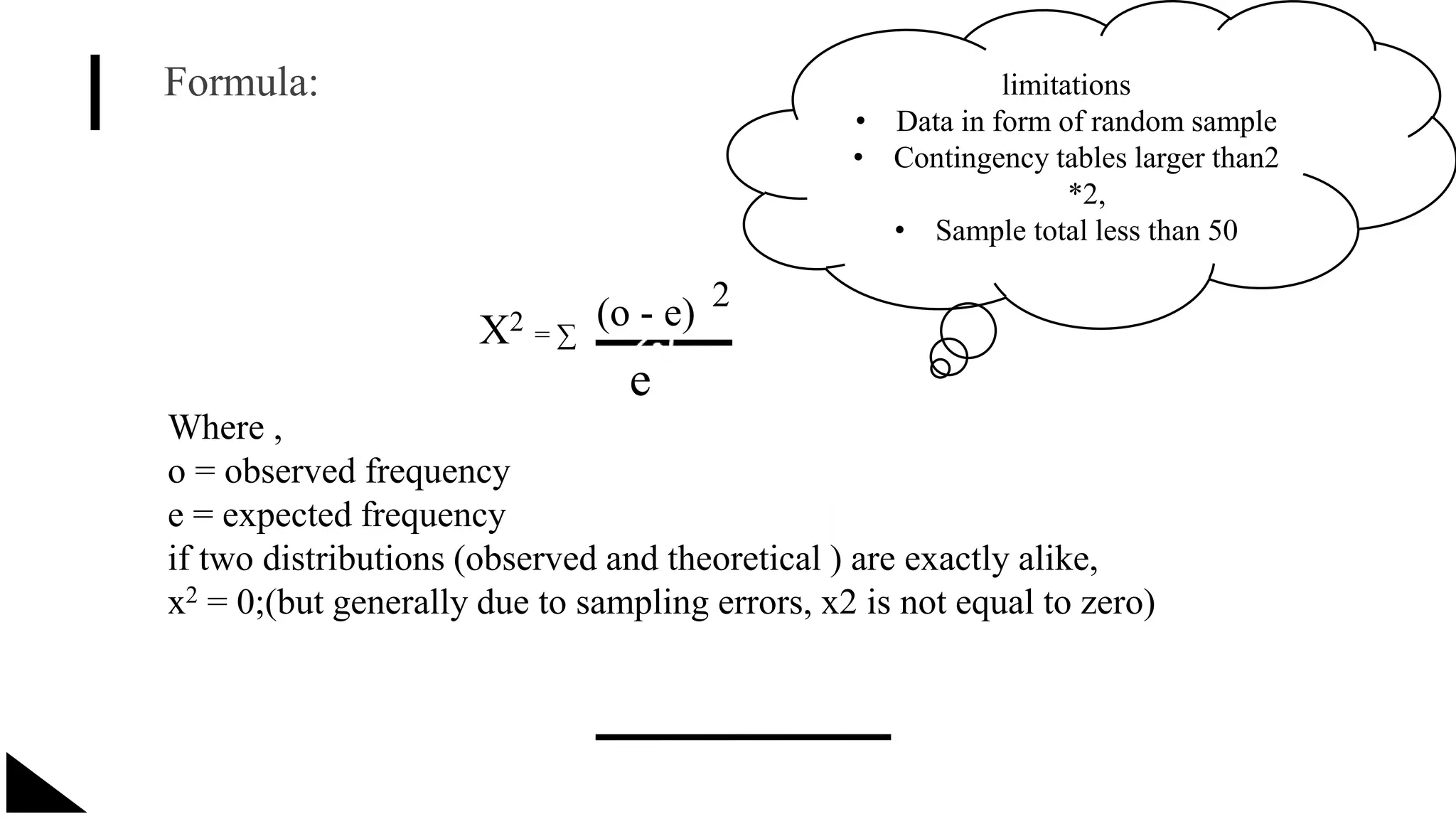
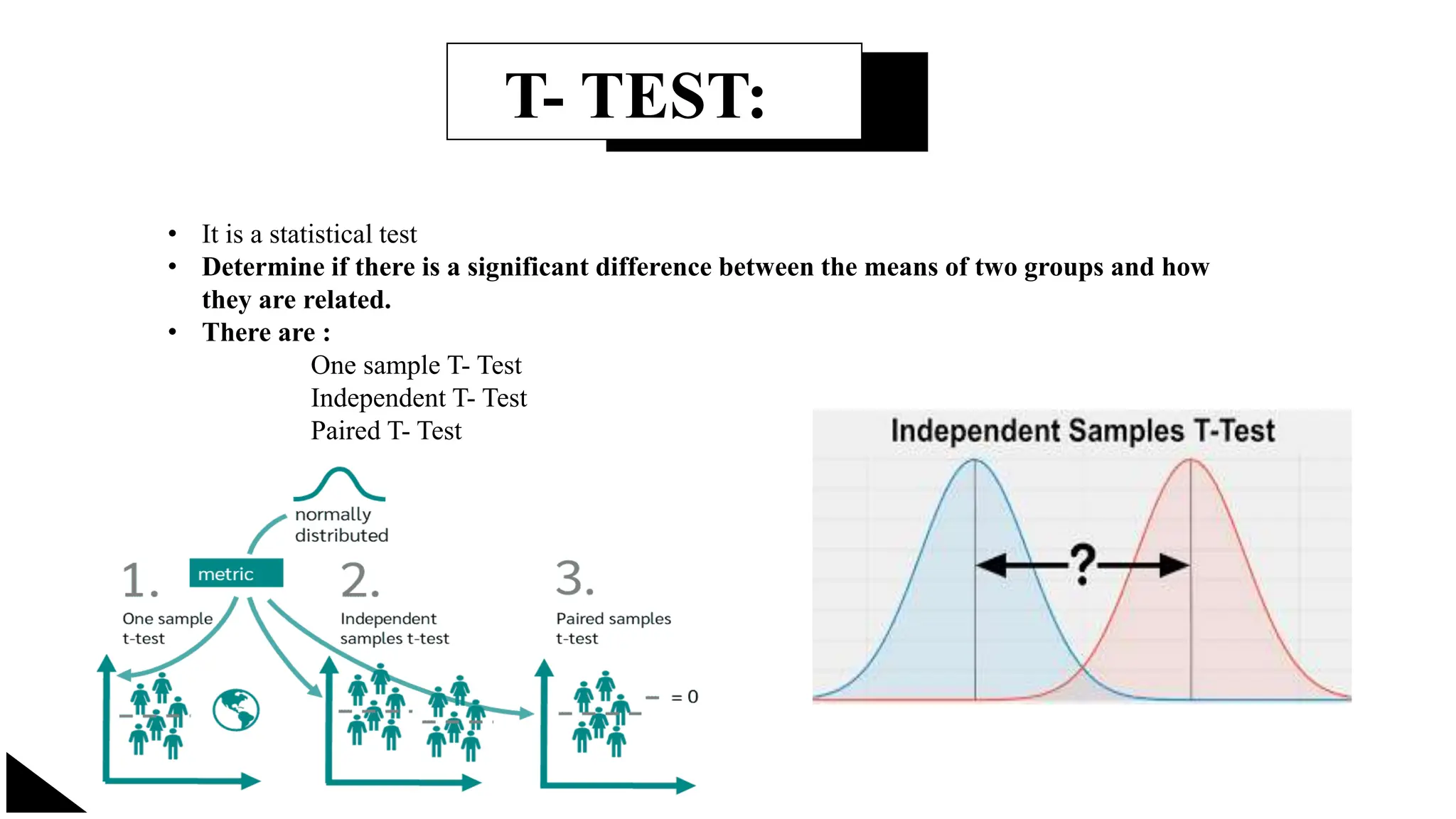
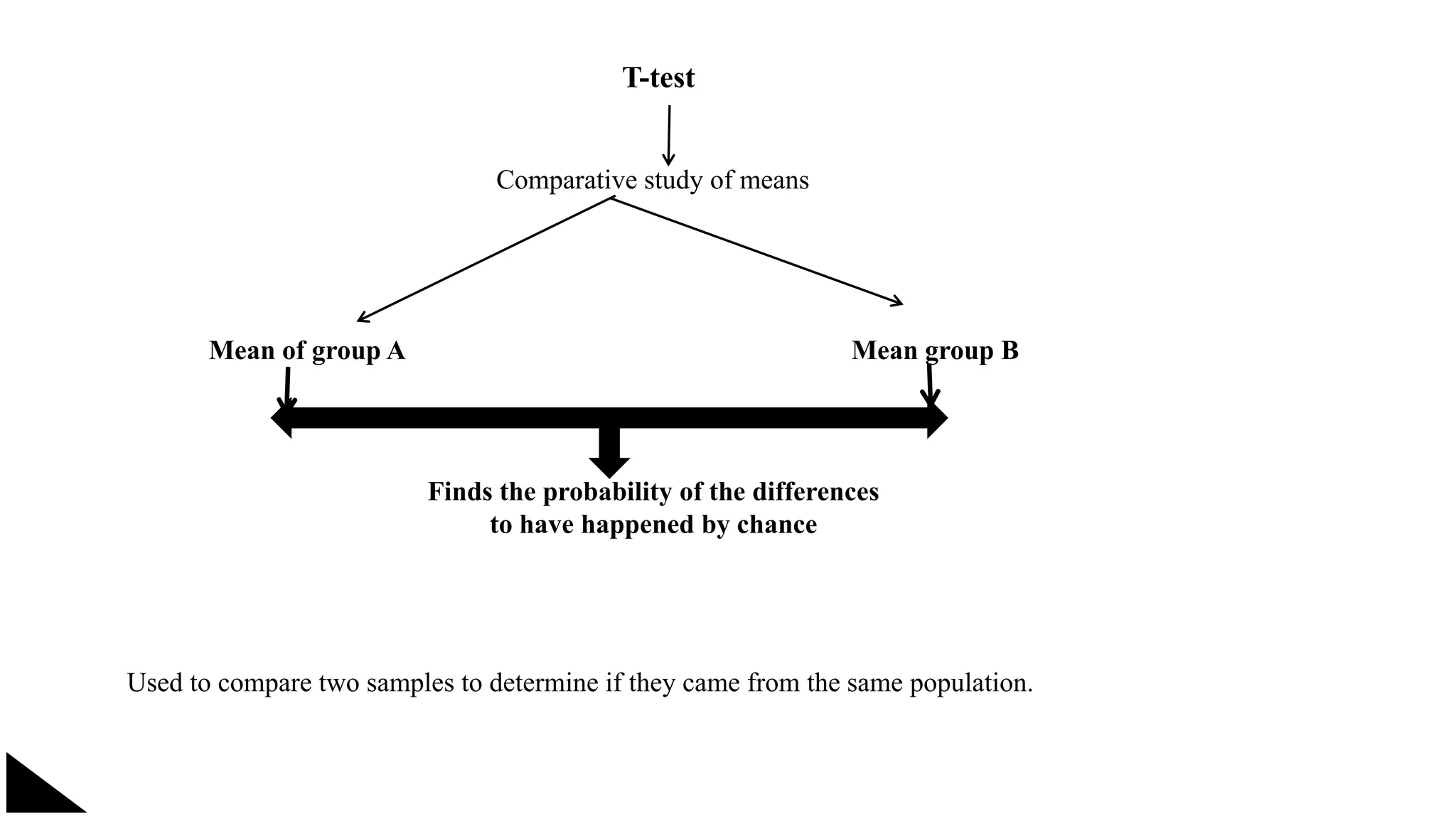
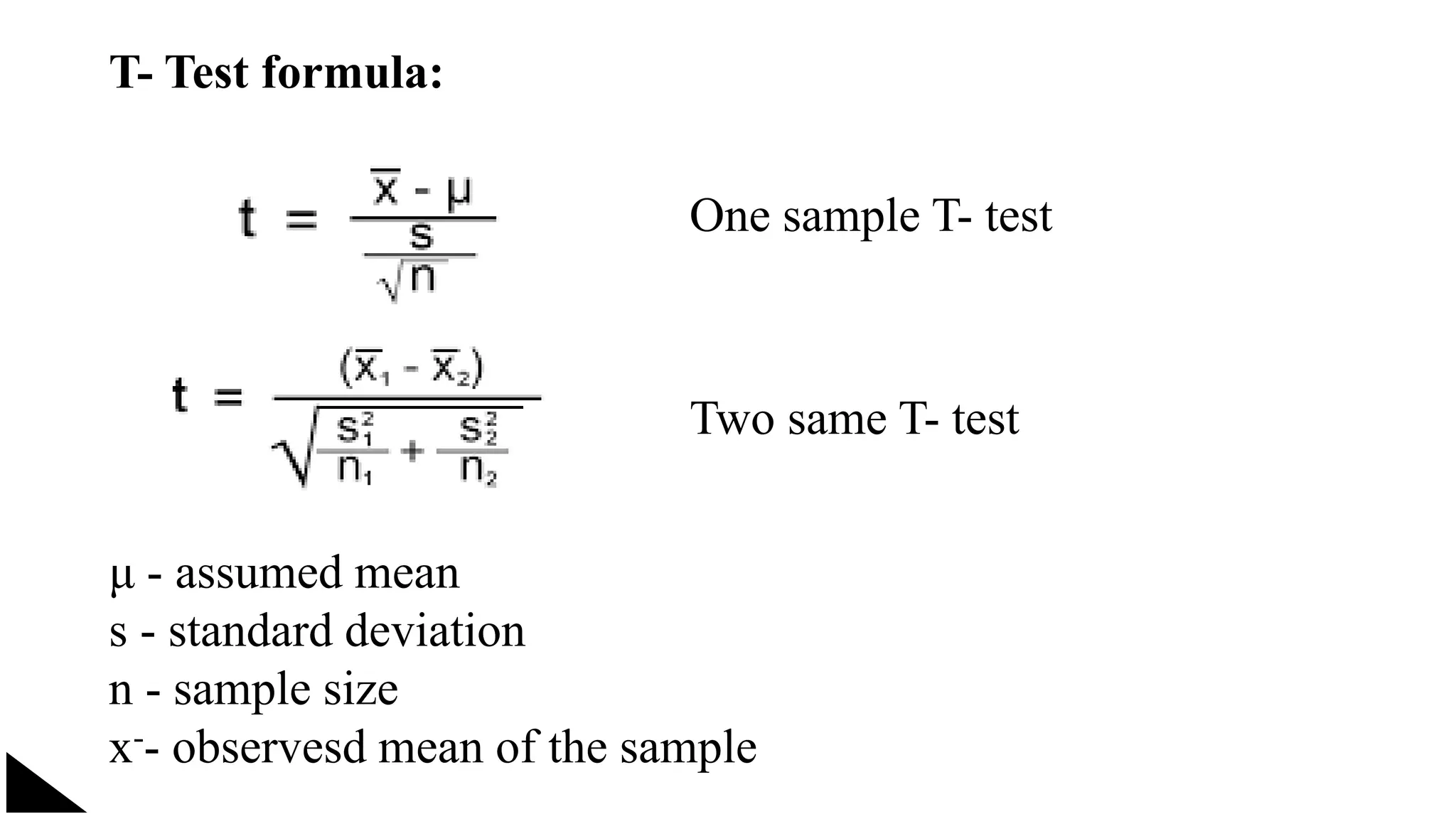
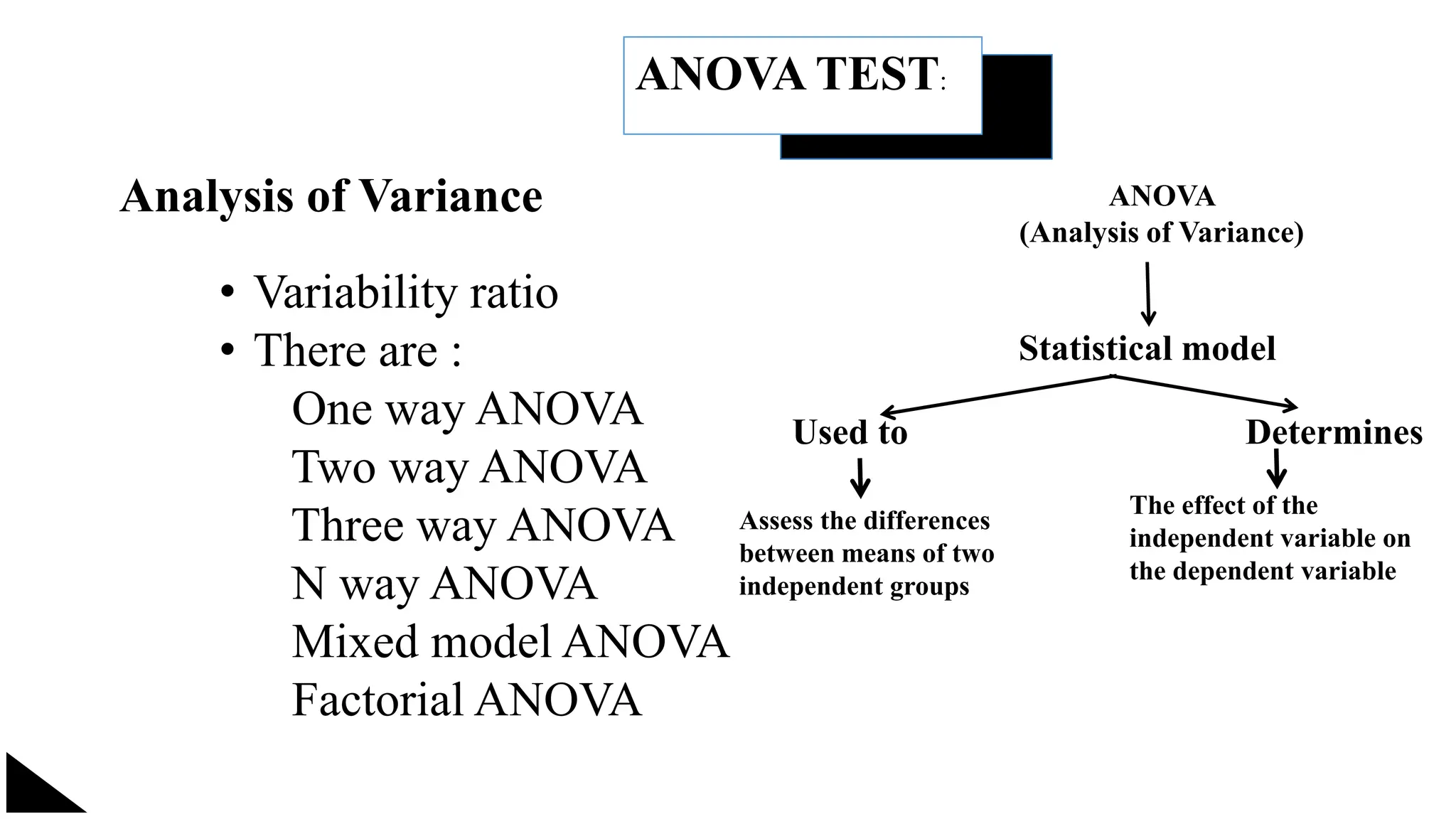
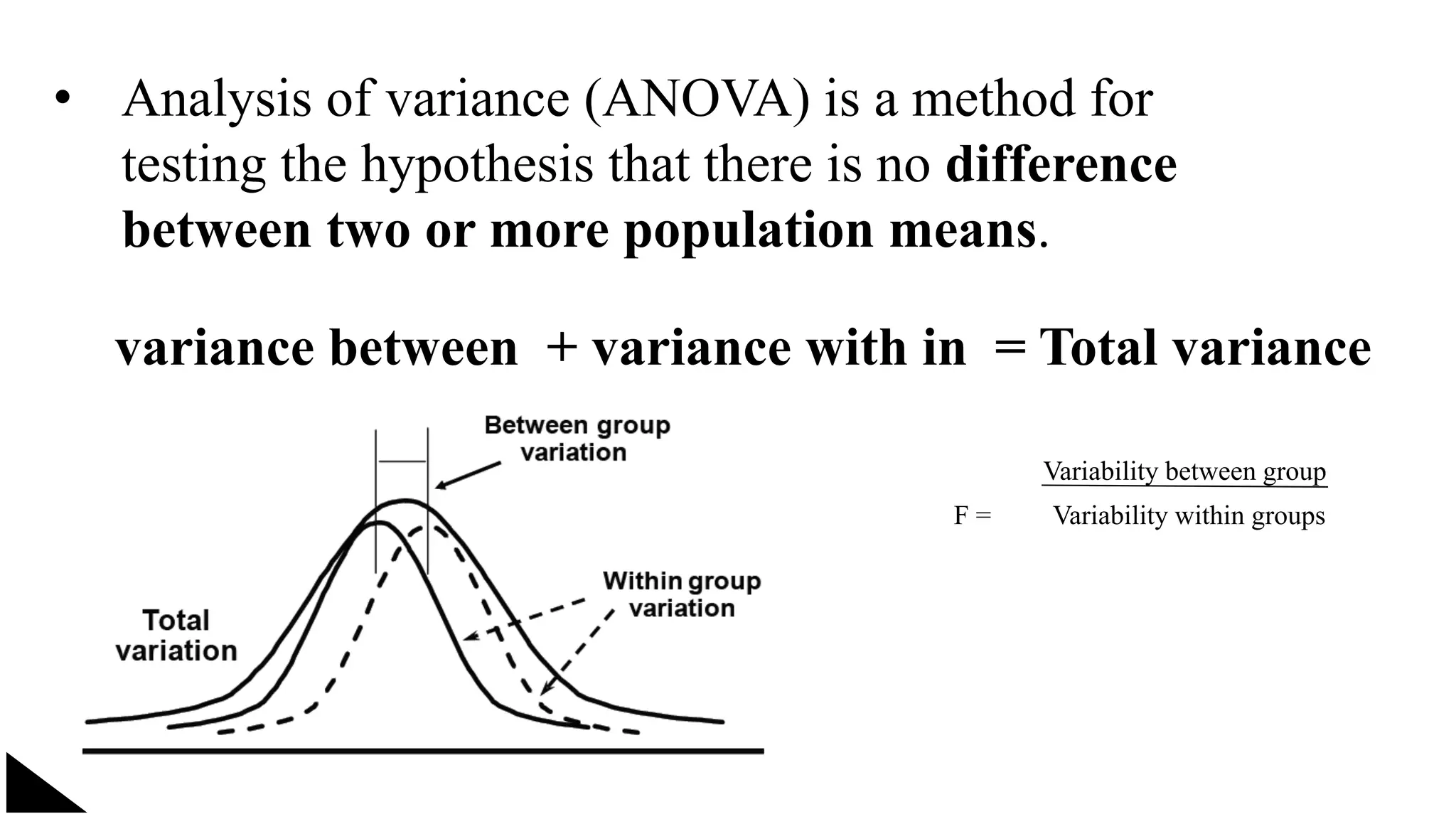
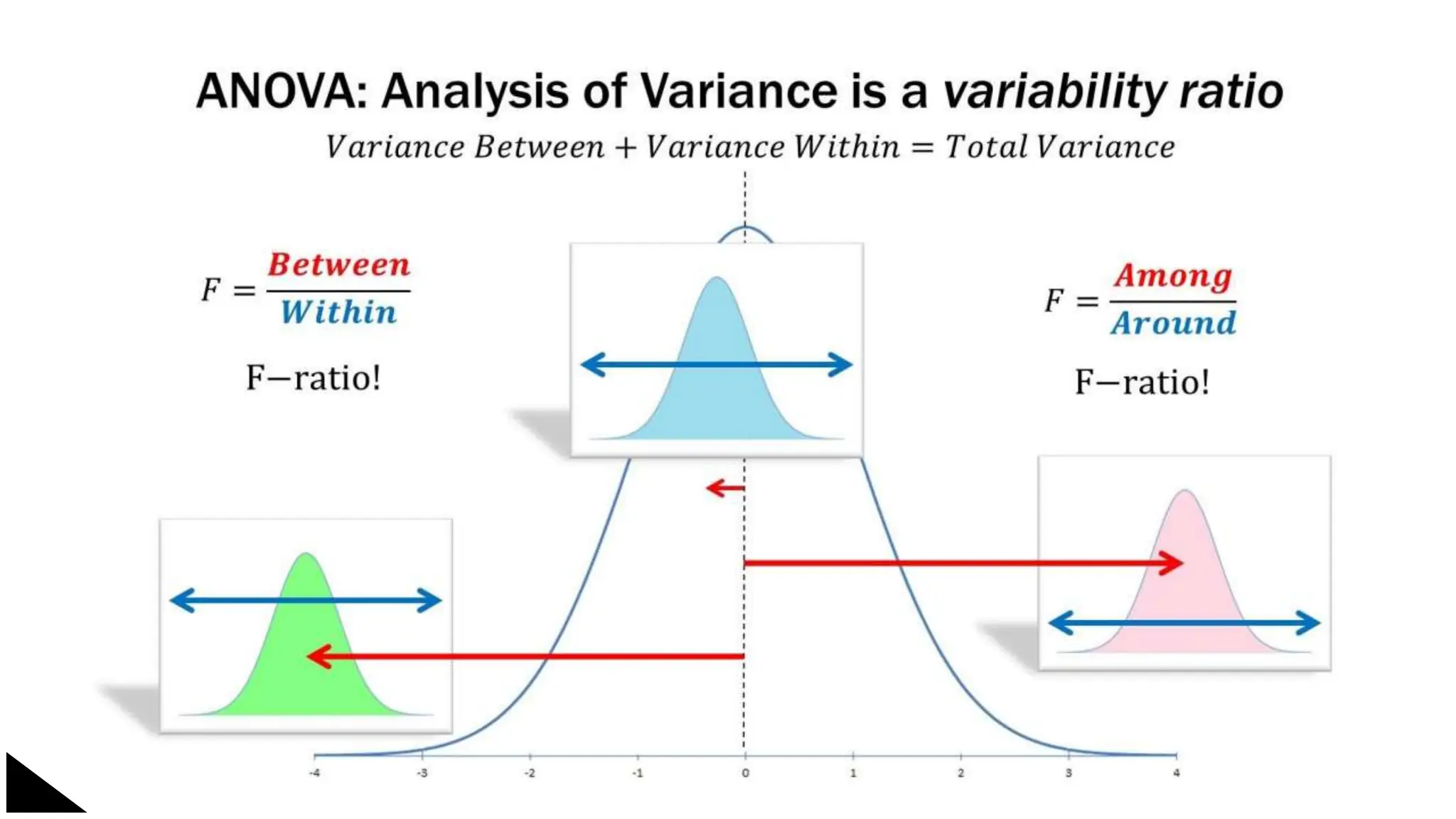
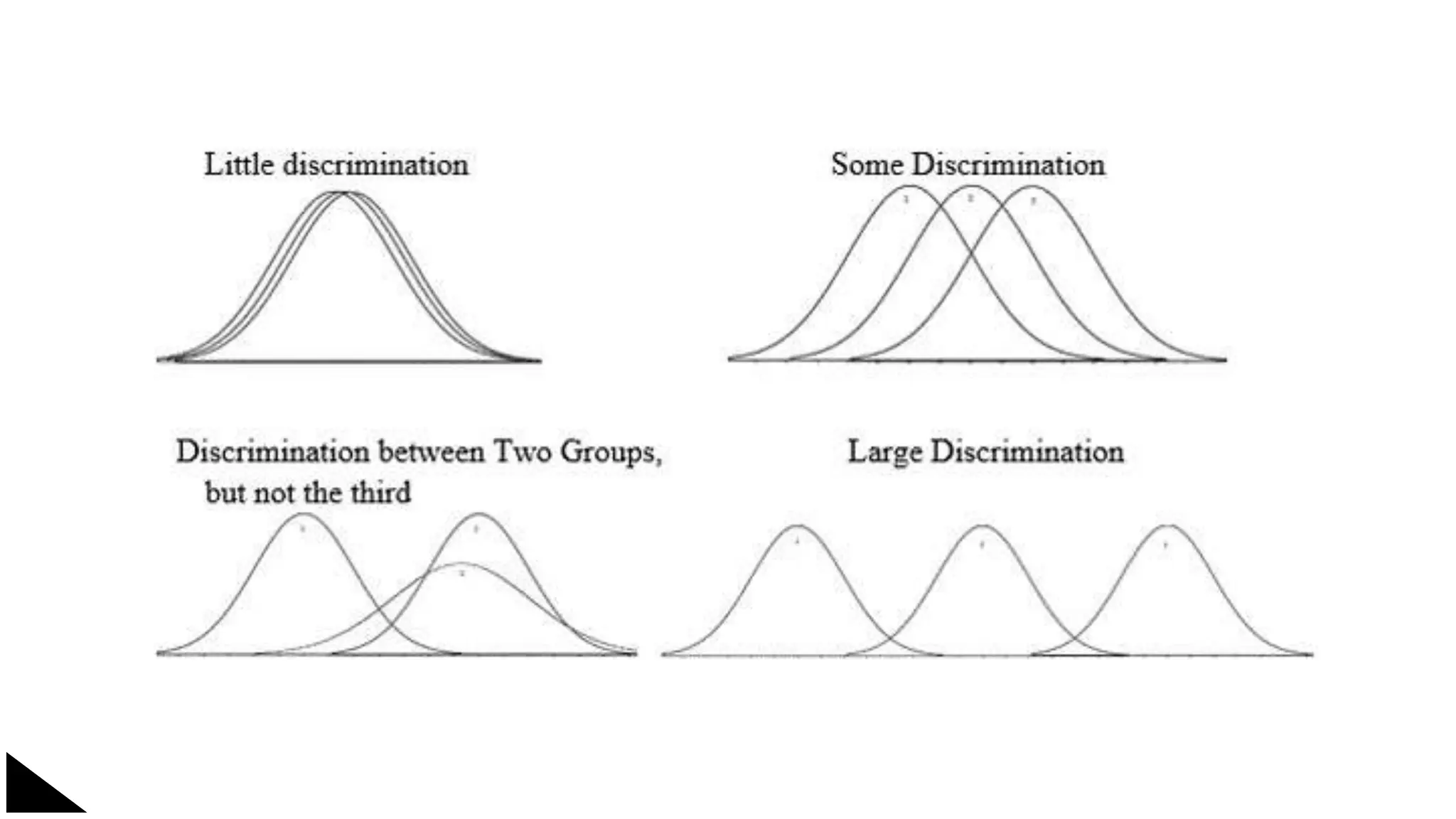
The document explains the concept of significance testing in statistics, outlining methods such as standard deviation, chi-square test, t-test, and ANOVA. It describes the significance test process, including formulating hypotheses, error levels, and interpreting results. Each statistical method is detailed regarding its application, characteristics, formulas, and limitations.