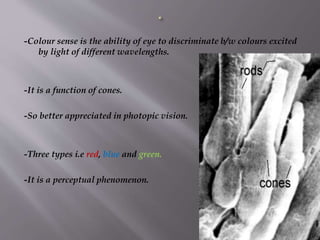
The document summarizes colour vision and the mechanisms underlying it. It discusses that colour vision is mediated by three types of cone photoreceptors sensitive to red, green and blue wavelengths. The signals from the cones are processed in the retina through opponent colour coding systems and transmitted to the lateral geniculate nucleus and visual cortex via the optic nerve pathways. Theories like the trichromatic and opponent process theories attempt to explain the perception of different hues. Defects in colour vision occur due to abnormalities in cone photoreceptors.



































![- [yellow-blue] and [red-green] represent opponent signals
producing four colour primaries red,green,yellow and blue, and
not just three.
- [ white-black ] opponency proposed by him has been abandoned in
most modern version of the theory.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colourvision-160802123736/85/Colour-vision-37-320.jpg)







