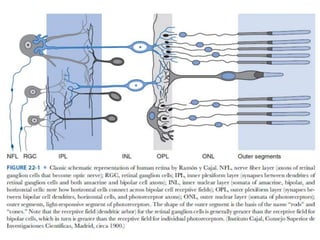
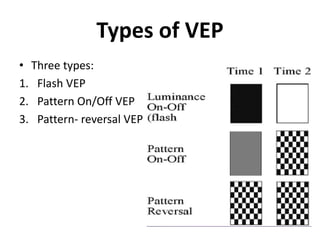
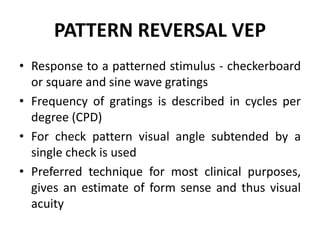
1. Visual Evoked Potentials (VEPs) provide an objective assessment of visual function, especially of the retina and optic nerve.
2. VEPs measure the electrical response of the visual cortex to visual stimuli, such as flashing lights or patterns.
3. The major components of the VEP response are the N75, P100, and N145 waves. Abnormalities in the latency and amplitude of these waves can help localize lesions along the visual pathway.