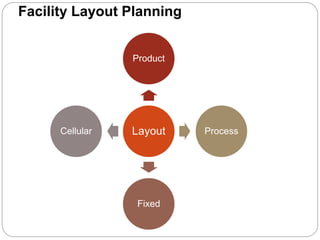
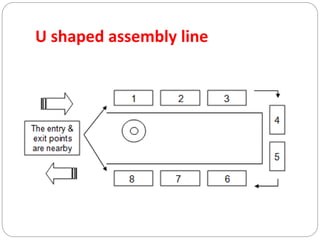
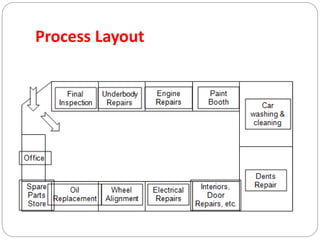
The document discusses various types of plant layouts including product, process, fixed-position, and cellular layouts, detailing their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. It emphasizes the importance of efficient layout planning to enhance industrial productivity, minimize costs, and ensure safety. Additionally, it highlights factors influencing layout decisions such as management policies, plant location, product nature, production volume, and space availability.