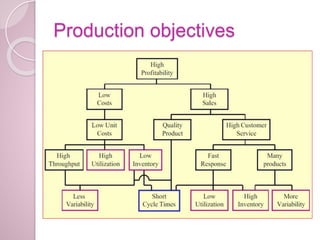
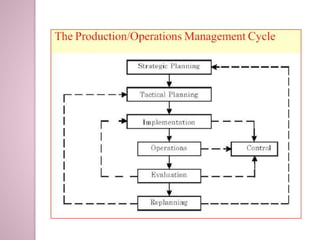
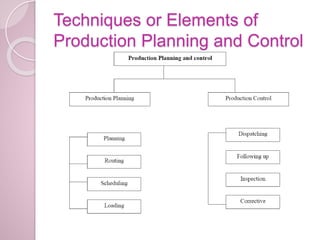
Production planning and control involves determining the resources needed for manufacturing operations, scheduling those resources to efficiently produce goods to meet demand, and ensuring production proceeds according to plan. It aims to maximize output while minimizing costs through techniques like routing, scheduling, dispatching, inspection, and corrective actions. Effective production planning and control benefits organizations through higher quality, better resource use, reduced costs and inventory, and improved profitability and customer satisfaction.