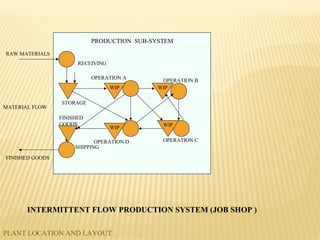
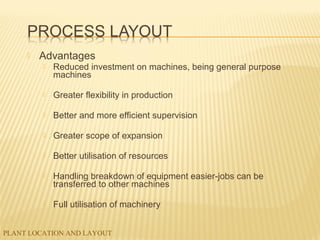
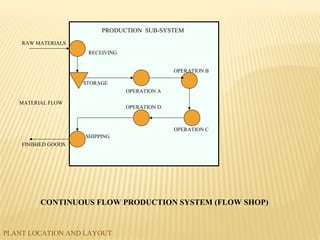
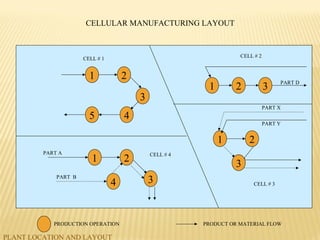
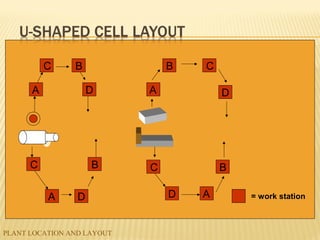
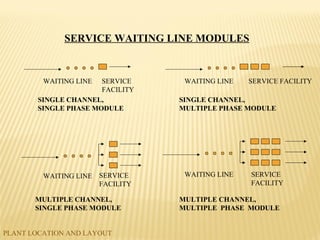
The document discusses factors to consider when planning a plant's location and layout. Key factors in choosing a location include proximity to markets and suppliers, availability of labor and transportation. The main types of layouts are process, product, and fixed position. Process layout groups similar machines together while product layout arranges machines in line by production steps. Cellular layout forms cells to produce individual parts. Effective location and layout ensure efficient material and labor flow to maximize production capacity.