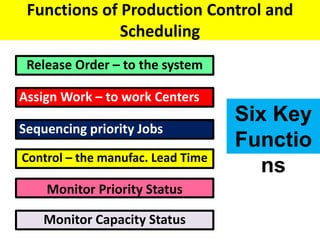
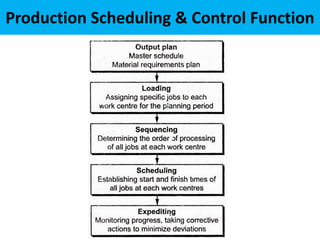
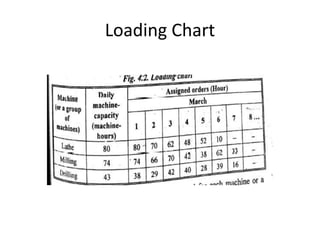
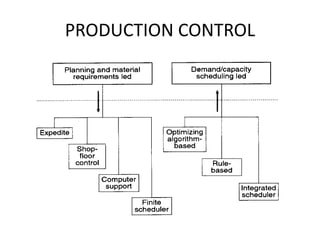
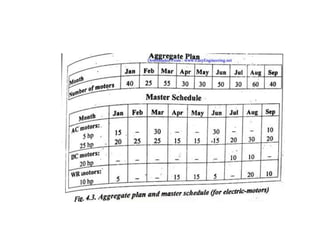
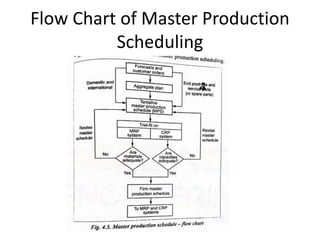
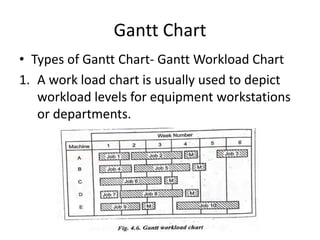
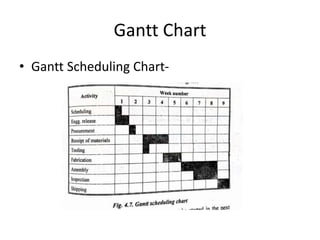
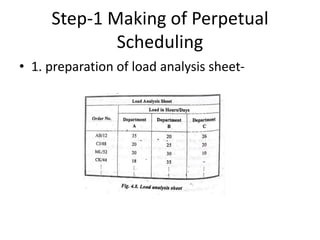
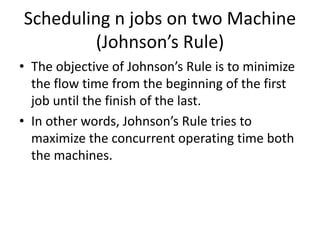
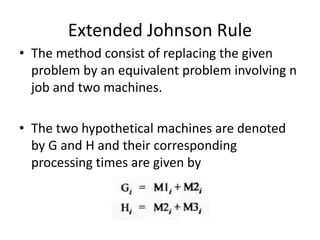
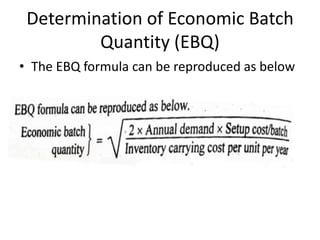
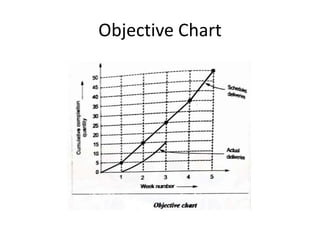
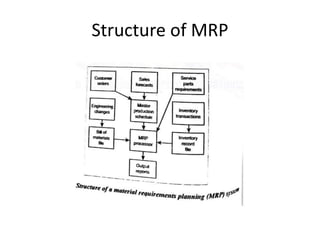
This document discusses various production scheduling techniques. It begins by explaining the functions of production control and scheduling such as releasing orders, assigning work, sequencing jobs, and monitoring capacity and priority status. It then covers topics like machine loading, loading charts, objectives of loading, and data requirements for production scheduling. Finally, it summarizes different scheduling tools and techniques including master scheduling, aggregate planning, material requirements planning, Gantt charts, perpetual scheduling, Johnson's rule for scheduling jobs on multiple machines, batch production scheduling, and line of balance techniques.