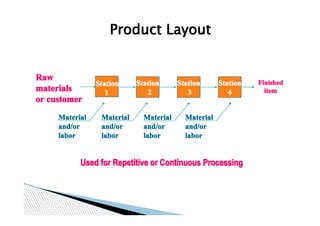
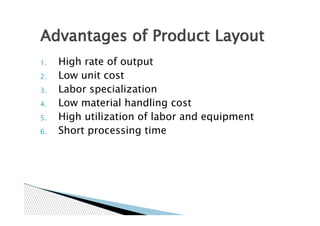
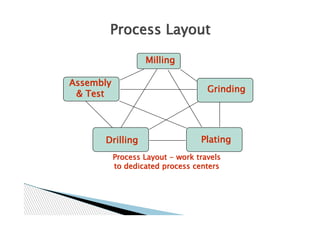
This document presents information on different types of plant layouts. It discusses product layout where machines are arranged according to the sequence of operations for manufacturing. It involves grouping similar machines for varied processing, as in process layout. Fixed position layout keeps the large product stationary while bringing processes to it, exemplified by helicopter and nuclear engineering projects. The objectives and advantages and disadvantages of each layout type are outlined.