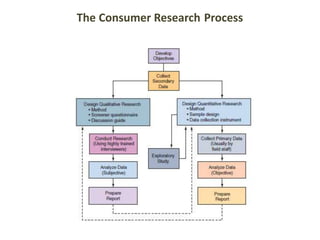
The document discusses the consumer research process, encompassing both secondary and primary research methods used by marketers to understand consumer behavior. It details qualitative methods such as focus groups and in-depth interviews, as well as quantitative techniques like surveys and experimentation. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of defining research objectives and the need for validity and reliability in data collection to make informed marketing decisions.