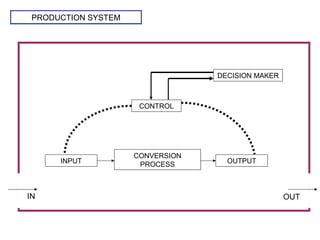
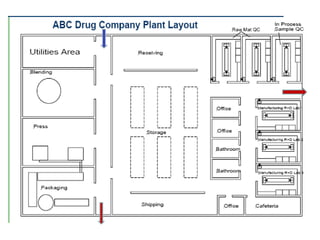
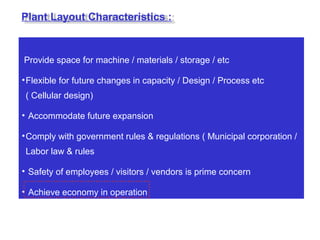
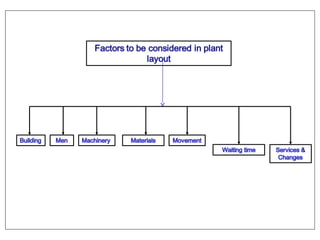
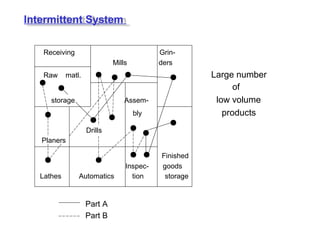
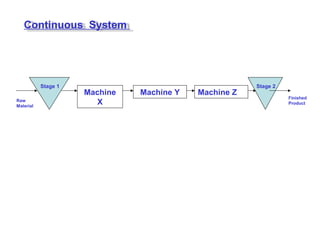
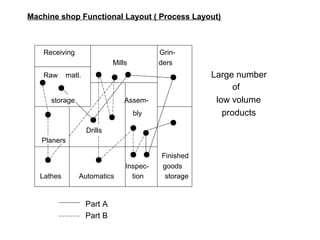
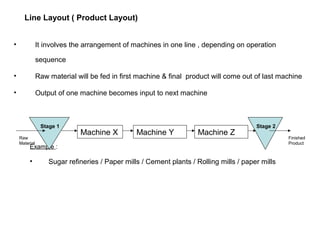
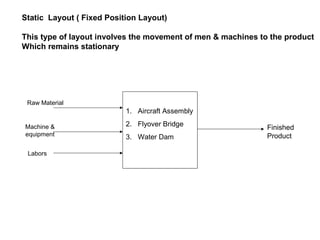
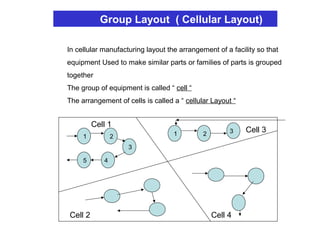
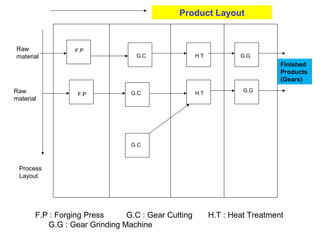
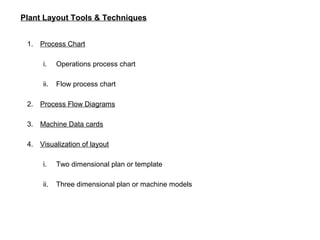
The document discusses various topics related to production management including plant layouts, material handling, inventory management, and quality control. It provides definitions and objectives of plant layouts and describes the main types of layouts - functional layout, line layout, static product layout, group layout, and combination layout. Factors influencing layout decisions and tools for plant layout design such as process charts, flow diagrams, and machine data cards are also covered.