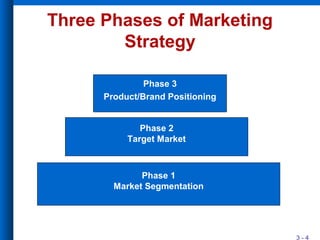
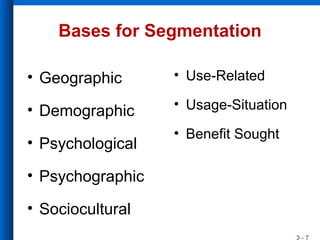
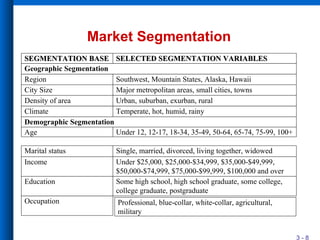
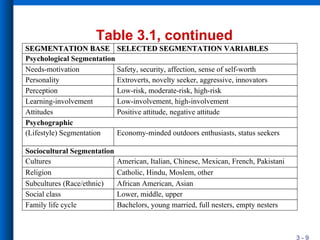
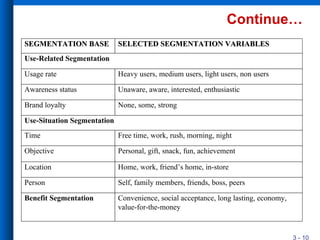
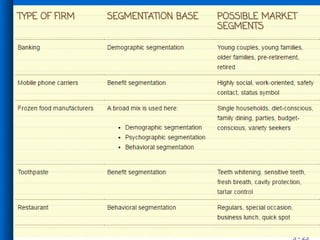
The document discusses market segmentation, including its definition, bases for segmentation, and criteria for effective targeting of segments. It outlines the importance of understanding consumer needs and tailoring products and advertising strategies accordingly. Various segmentation bases such as geographic, demographic, psychological, and benefit segmentation are explored to help identify and reach target markets.