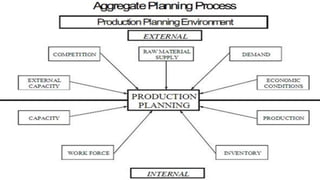
This document discusses aggregate production planning. It defines aggregate production planning as a planning exercise done at an aggregate level to translate demand forecasts into production and capacity levels over a fixed horizon. The document provides an example plan from a garment manufacturer. It discusses why production planning is necessary to address demand and capacity fluctuations. Different planning strategies like level, chase, and mixed strategies are described. The document also covers production scheduling, its objectives and functions in allocating resources and meeting delivery dates.