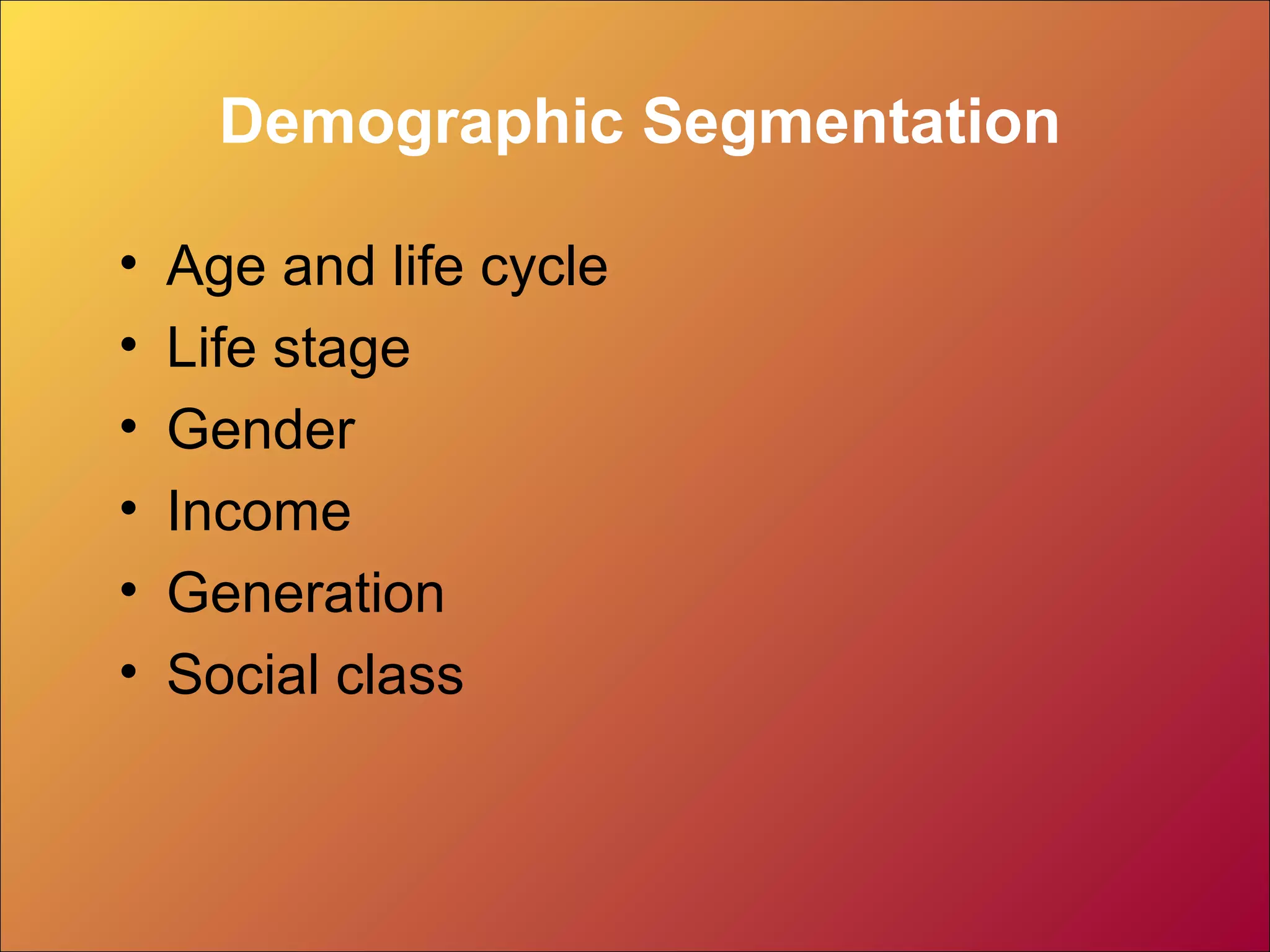
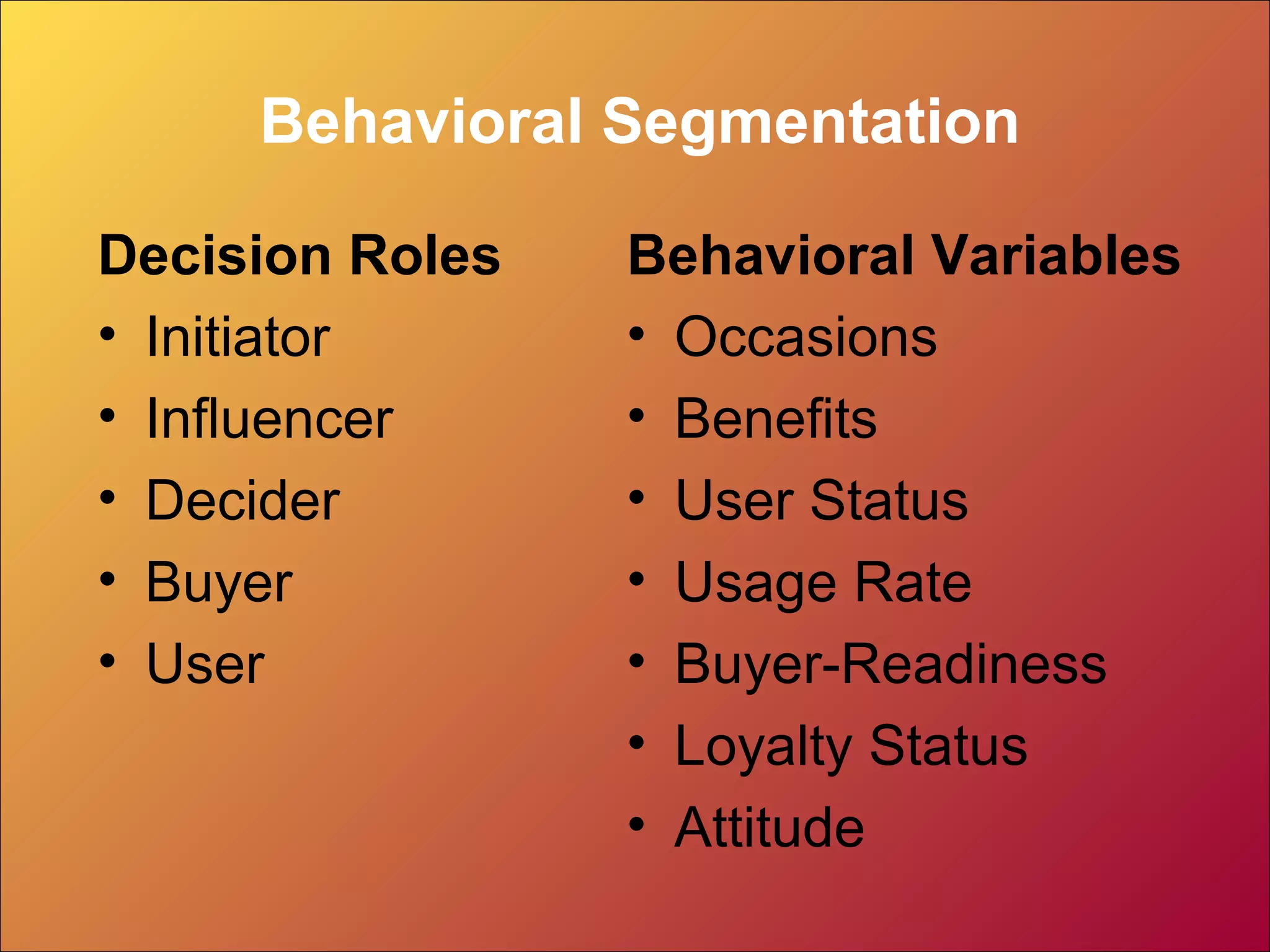
This document discusses market segmentation and targeting. It defines market segmentation as dividing a market into distinct groups based on characteristics like needs, preferences, behaviors or attributes. There are four levels of segmentation from broad segments to niches to local areas to individuals. Effective segmentation requires identifying distinct customer groups, selecting target segments, and establishing unique benefits. The document outlines different bases for segmentation like demographics, psychographics, behaviors and provides several examples of segmentation models and frameworks.