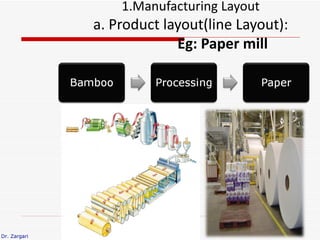
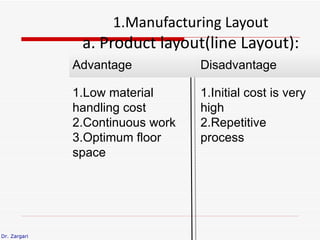
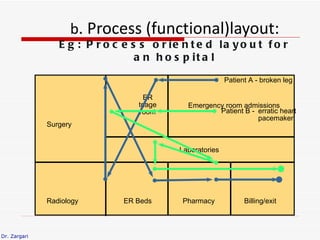
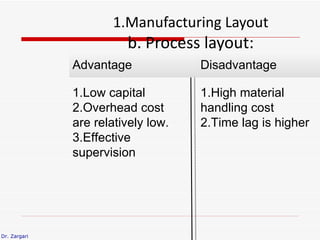
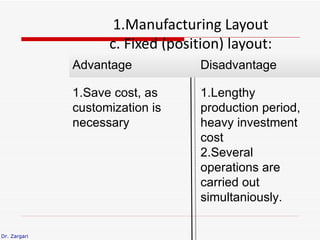
The document discusses different types of plant layouts. It describes four main types: product layout, process layout, fixed position layout, and combined layout. Product layout involves materials moving sequentially between workstations with minimal backtracking. Process layout groups similar machines together. Fixed position layout fixes major production facilities in one location and brings other facilities to them. Combined layout is used when multiple products are produced in batches using a mix of layout types. The objectives of layout include minimizing costs and space while improving efficiency, safety, and productivity.