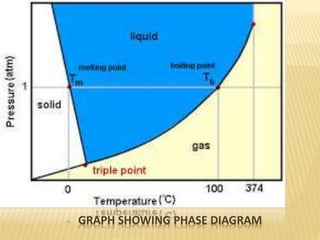
This document discusses the phase rule, which describes the behavior of heterogeneous systems in equilibrium. The phase rule states that the number of degrees of freedom (F) in a system equals the number of components (C) minus the number of phases (P) plus two. A phase is a homogeneous part of a system that has uniform physical and chemical properties throughout. Phase diagrams can be used to predict how changing temperature, pressure, and concentration will affect a heterogeneous system in equilibrium.

















![DERIVATION OF THE PHASE RULE
The states of a system will depend upon a
temperature and pressure and these
variables are always there .
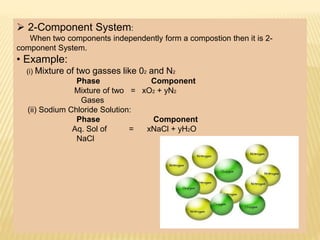
The concentration,however,depend upon the
number of phases.
The total number of variable of the system:
[P(C-1)+2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phaserule-171025111352/85/Phase-rule-20-320.jpg)
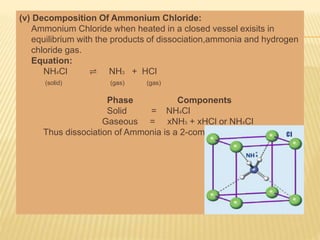
![ Thermodynamic Equilibrium:
when a system is in equilibrium the partial
molal free energy of each constituentsof a
phase is equal to the partialmolal free
energy of the same constituents in every
phase.
F=No. of variables – No. of Equations
= [P(C-1)+2] – [C(P-1)]
= PC-P+2-PC+C
F= C-P+2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phaserule-171025111352/85/Phase-rule-21-320.jpg)