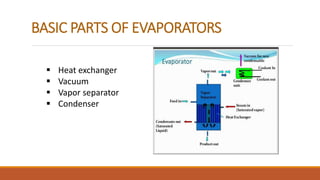
Evaporation is an oldest method of concentration that involves boiling a solution and removing the vapor, leaving behind a concentrated liquid residue. The rate of vaporization depends on diffusion through boundary layers above the liquid. Evaporators are equipment used to evaporate water or other volatile solvents from solutions, concentrating non-volatile solutes. Basic evaporator parts include a heat exchanger, vacuum system, vapor separator, and condenser. Common types are natural circulation, forced circulation, and film evaporators. Multiple effect evaporation improves efficiency by reusing heat from one evaporator in subsequent evaporators. Evaporation has wide applications in pharmaceuticals, food processing, and other industries.