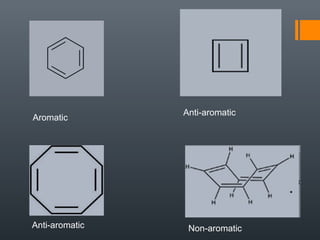
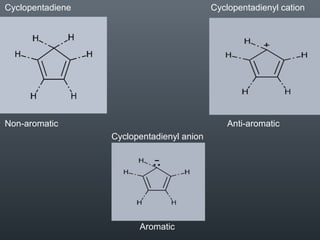
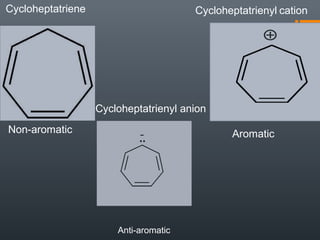
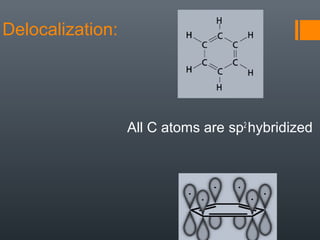
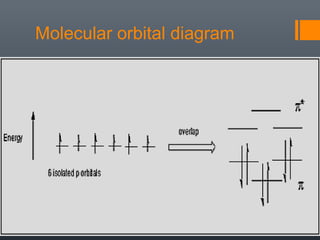
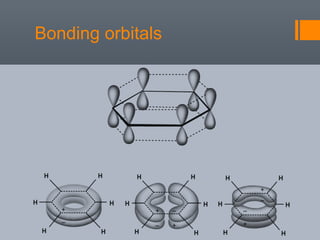
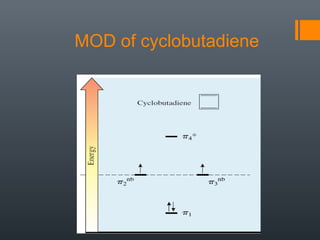
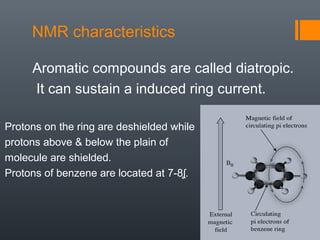
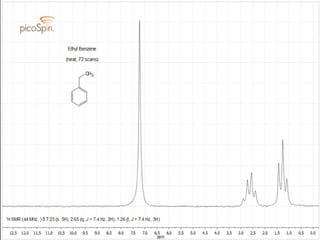
This document discusses aromatic compounds and Hückel's rule for aromaticity. It defines aromatic compounds as cyclic, planar and fully conjugated compounds that have 4n + 2 π electrons according to Hückel's rule. These compounds are highly stable due to delocalization of π electrons over the whole ring. They undergo substitution rather than addition reactions and have intermediate bond lengths and diatropic NMR properties. Anti-aromatic compounds have 4n π electrons and show the opposite NMR characteristics. Molecular orbital theory is used to explain the stability and properties of aromatic compounds.