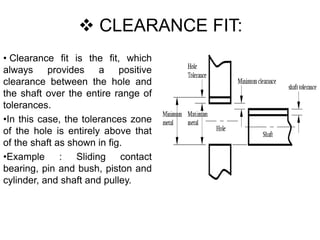
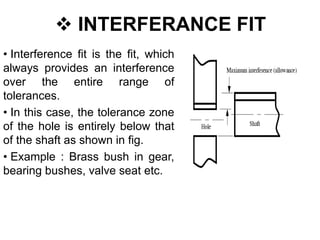
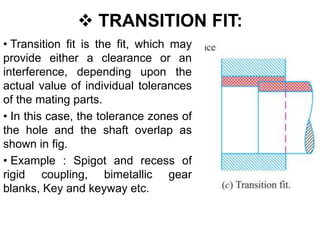
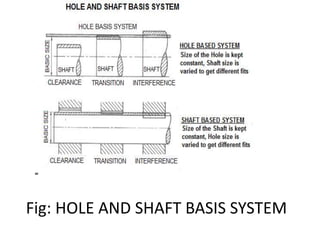
This document discusses limits, fits, and systems of fits in machine design and industrial drafting. It defines limits as the maximum and minimum permissible sizes of a given dimension. It describes fits as the type of assembly that results from the difference in size between a hole and shaft before assembly. The main types of fits are defined as clearance fit, interference fit, and transition fit. Finally, it explains hole basis and shaft basis systems, which determine fits based on tolerances associated with the hole or shaft size, respectively.