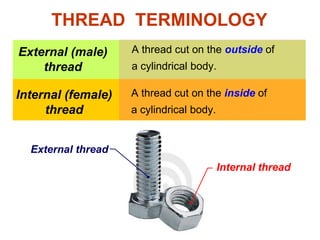
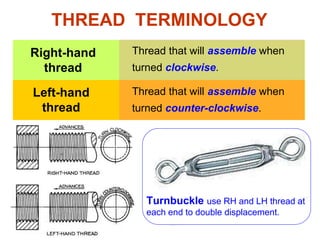
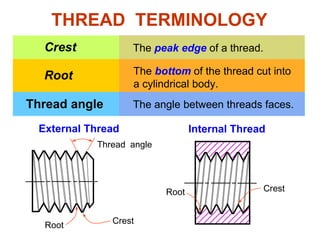
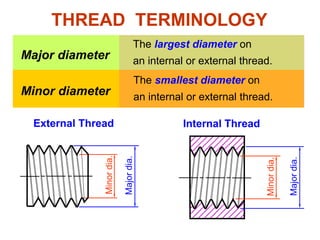
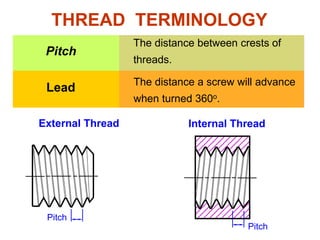
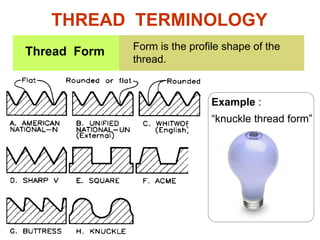
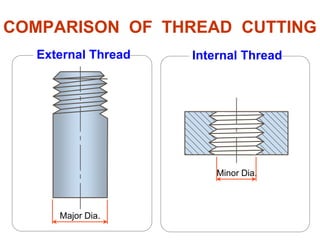
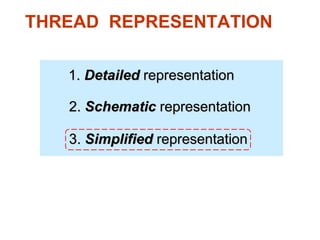
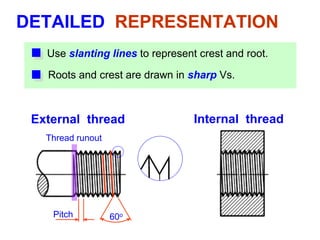
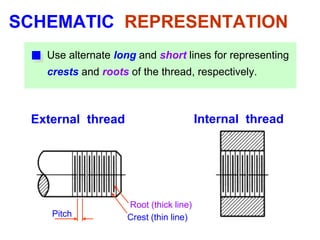
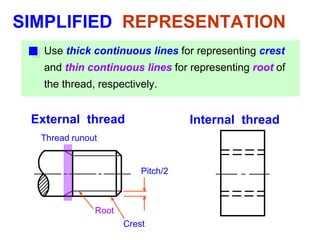
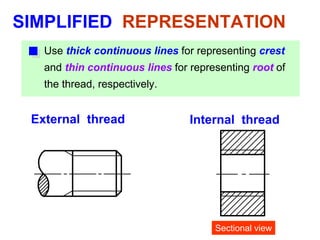
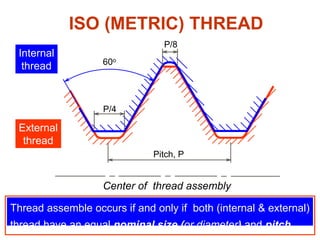
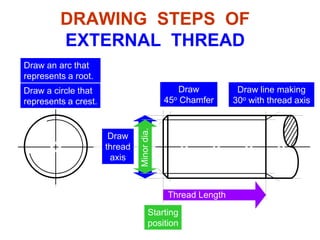
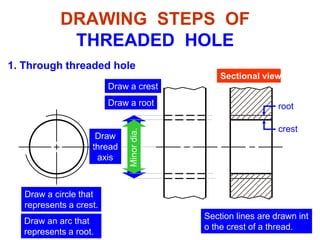
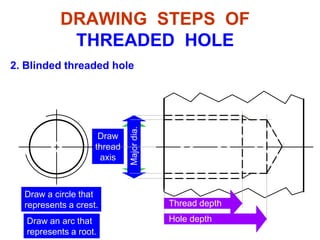
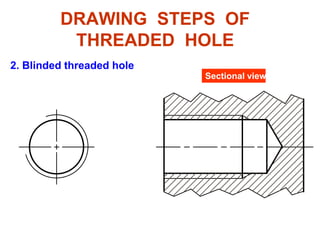
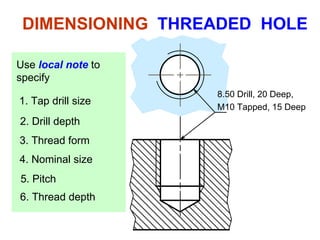
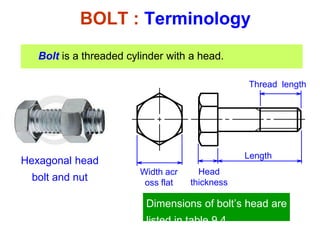
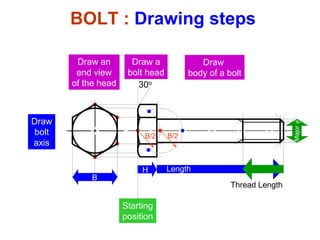
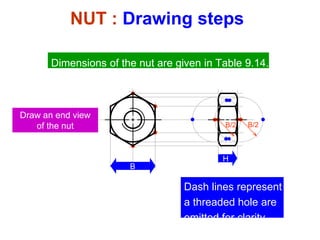
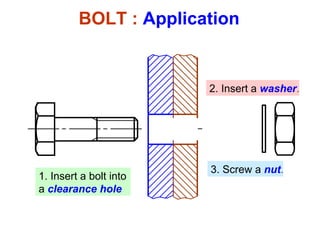
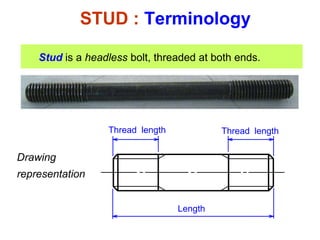
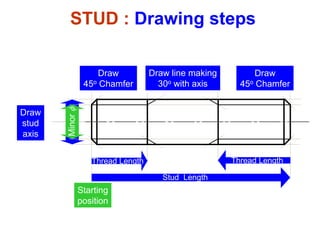
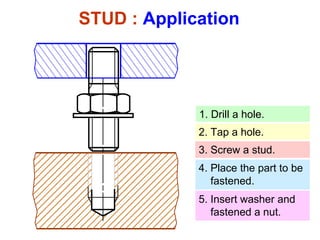
This document discusses threaded fasteners and their terminology. It describes different types of threads including external and internal threads, right-hand and left-hand threads, and thread dimensions. It also outlines methods for drawing threaded components including bolts, nuts, studs, and threaded holes. Key steps are provided for dimensioning these parts and representing threads in drawings. Common applications of bolts, studs, and other threaded fasteners are also highlighted.