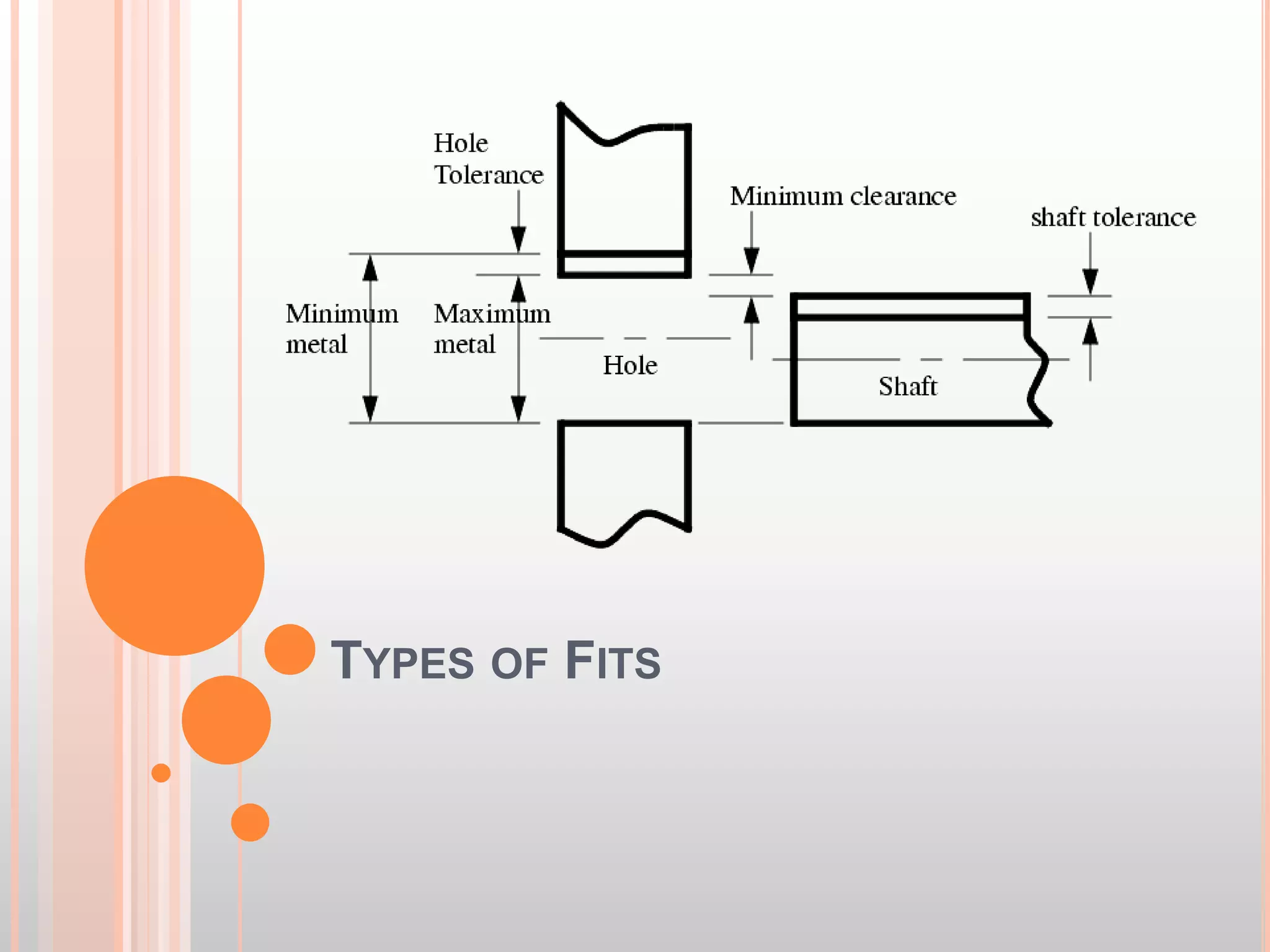
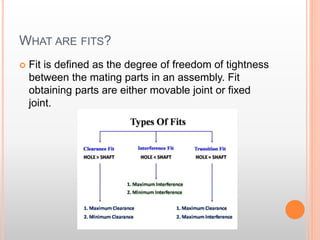
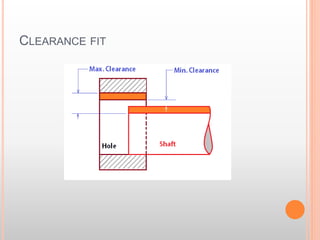
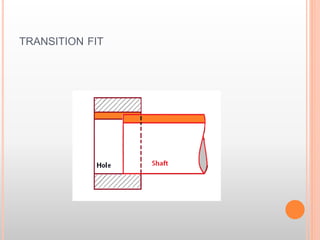
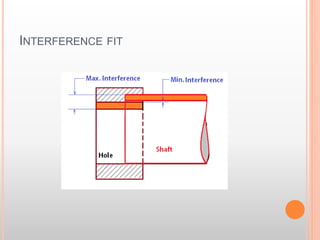
The document describes different types of fits between mating parts in an assembly: clearance fit, transition fit, and interference fit. Clearance fit has a gap between parts, transition fit is neither loose nor tight, and interference fit has no gap and requires parts to be forced together. Each fit type is further broken down, defining features and common examples.