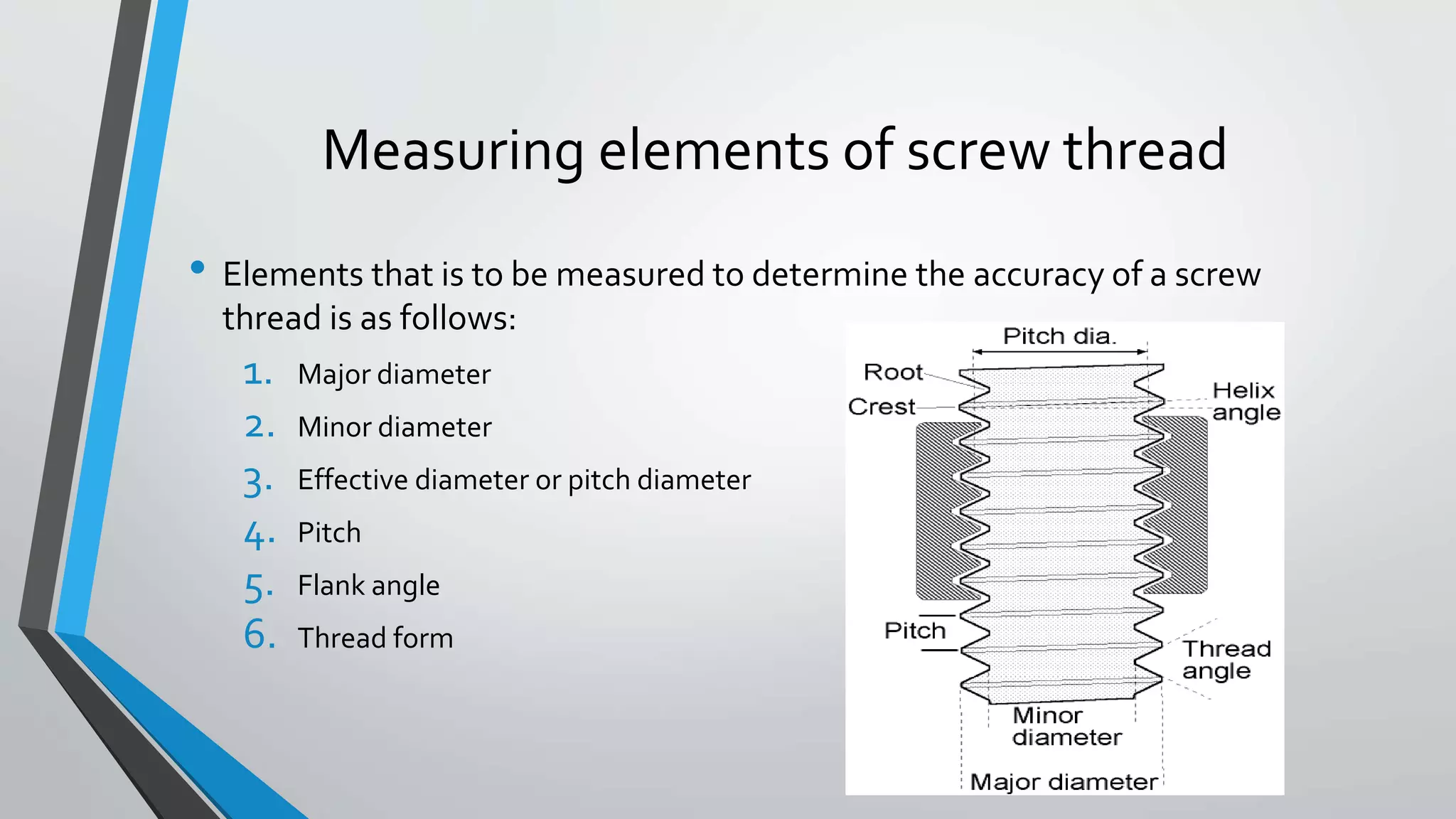
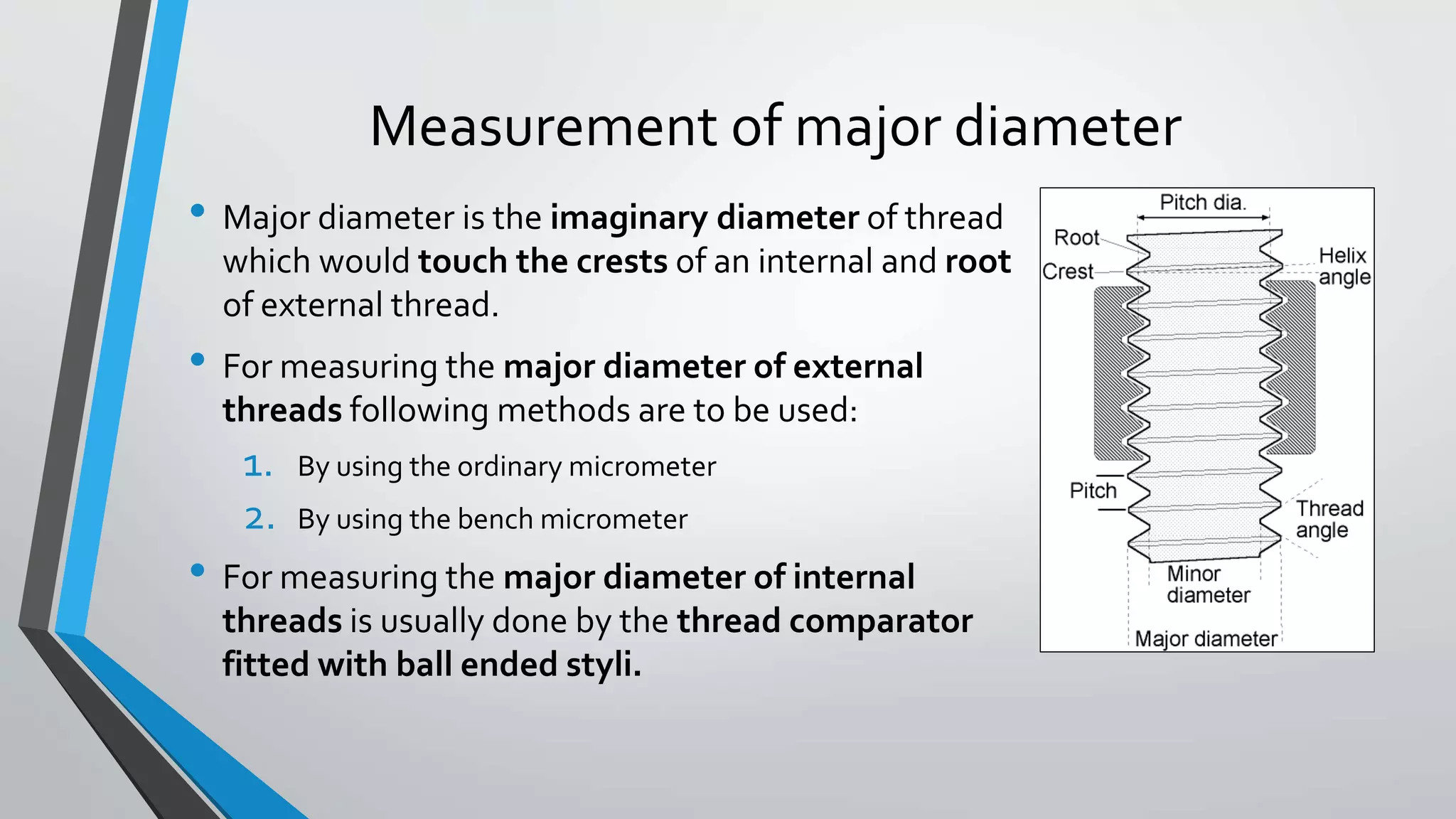
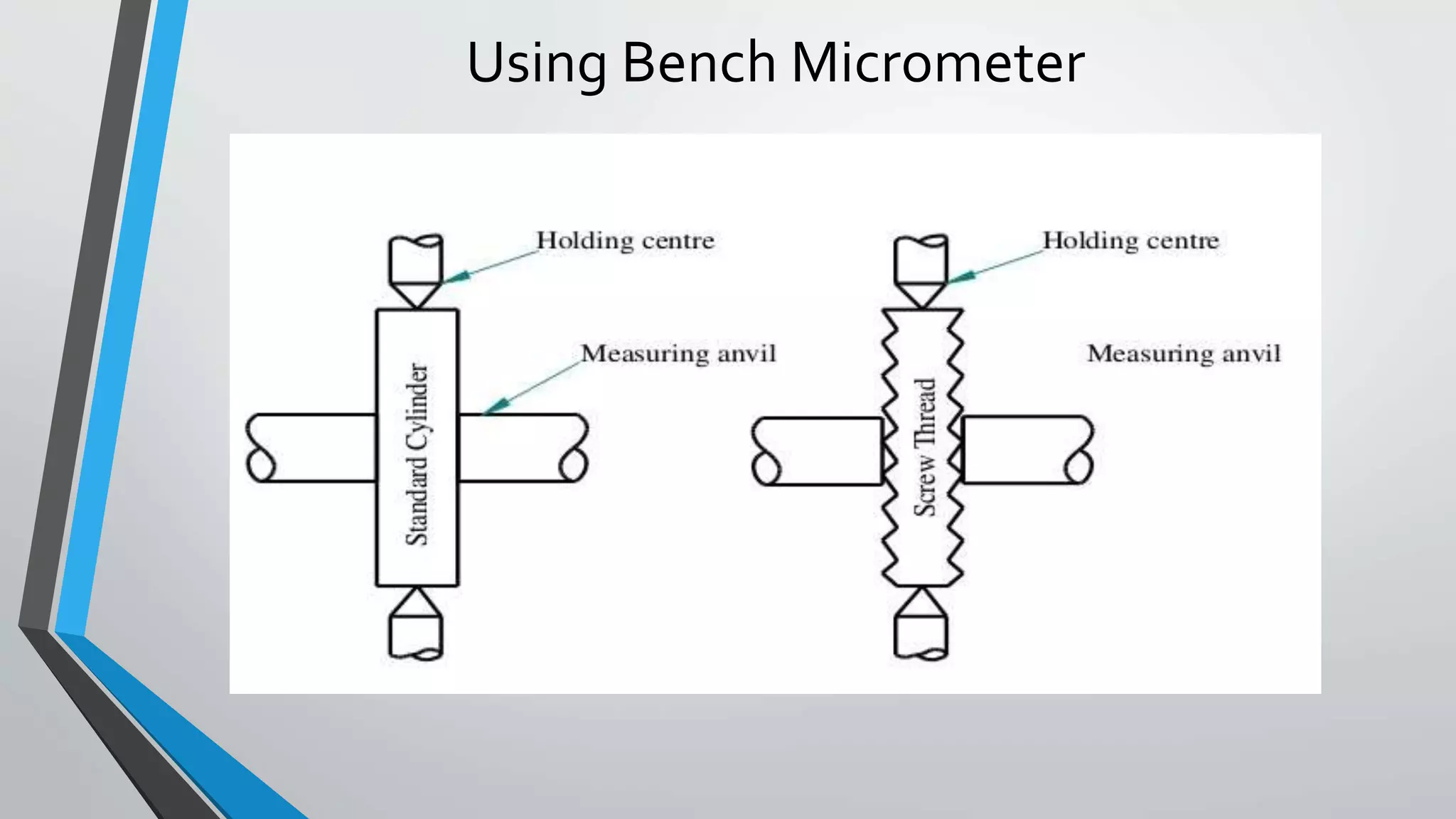
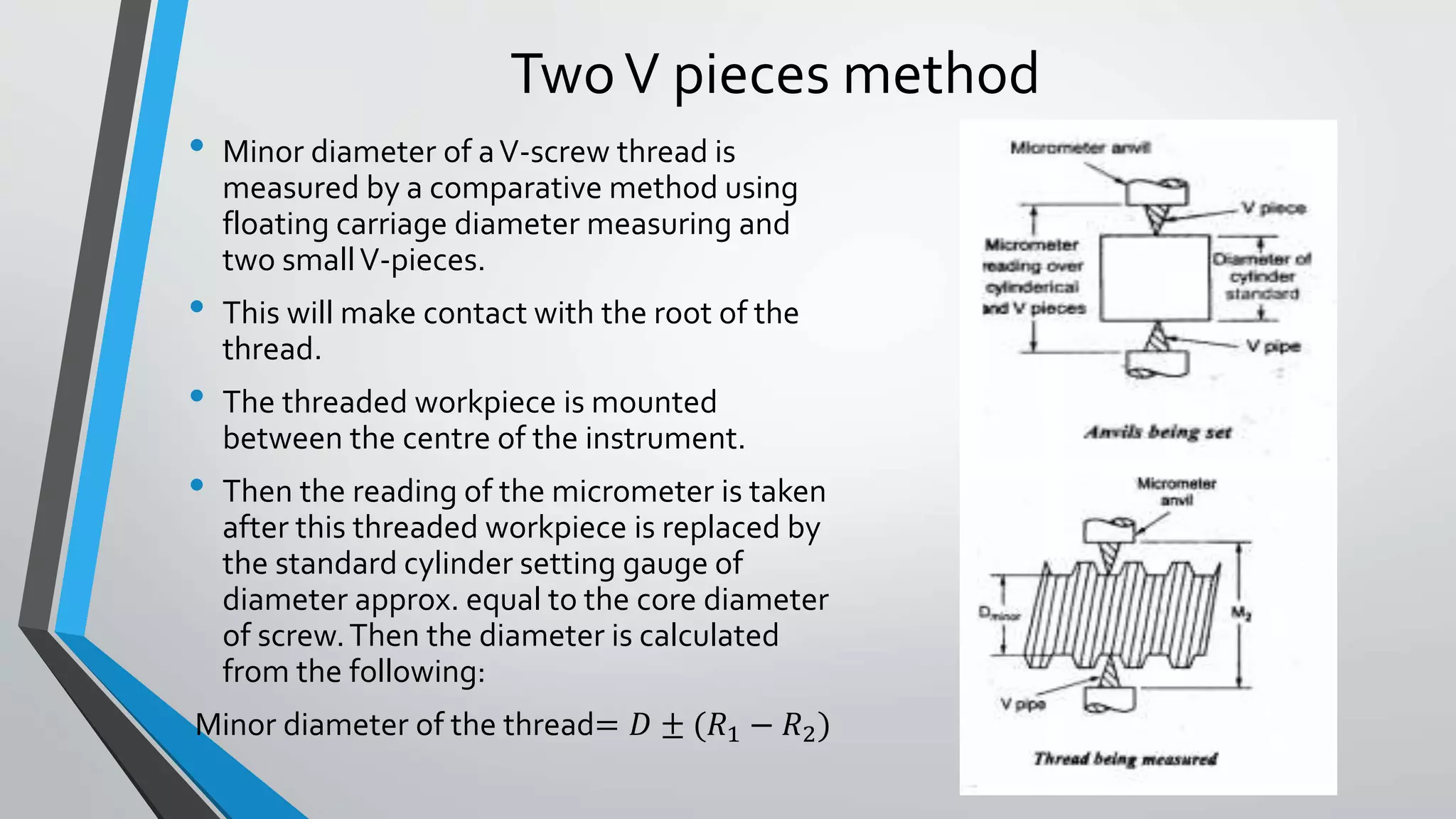
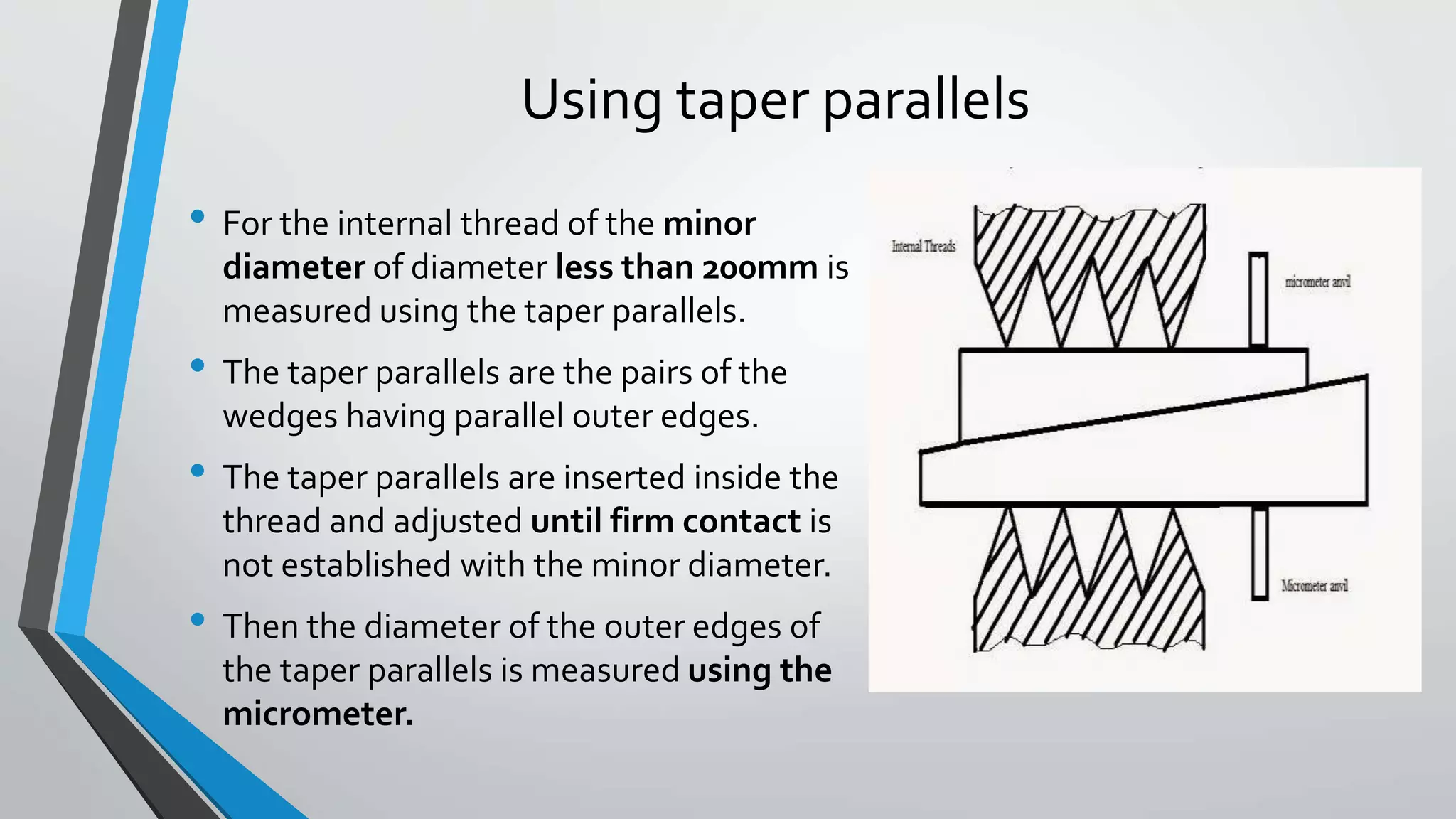
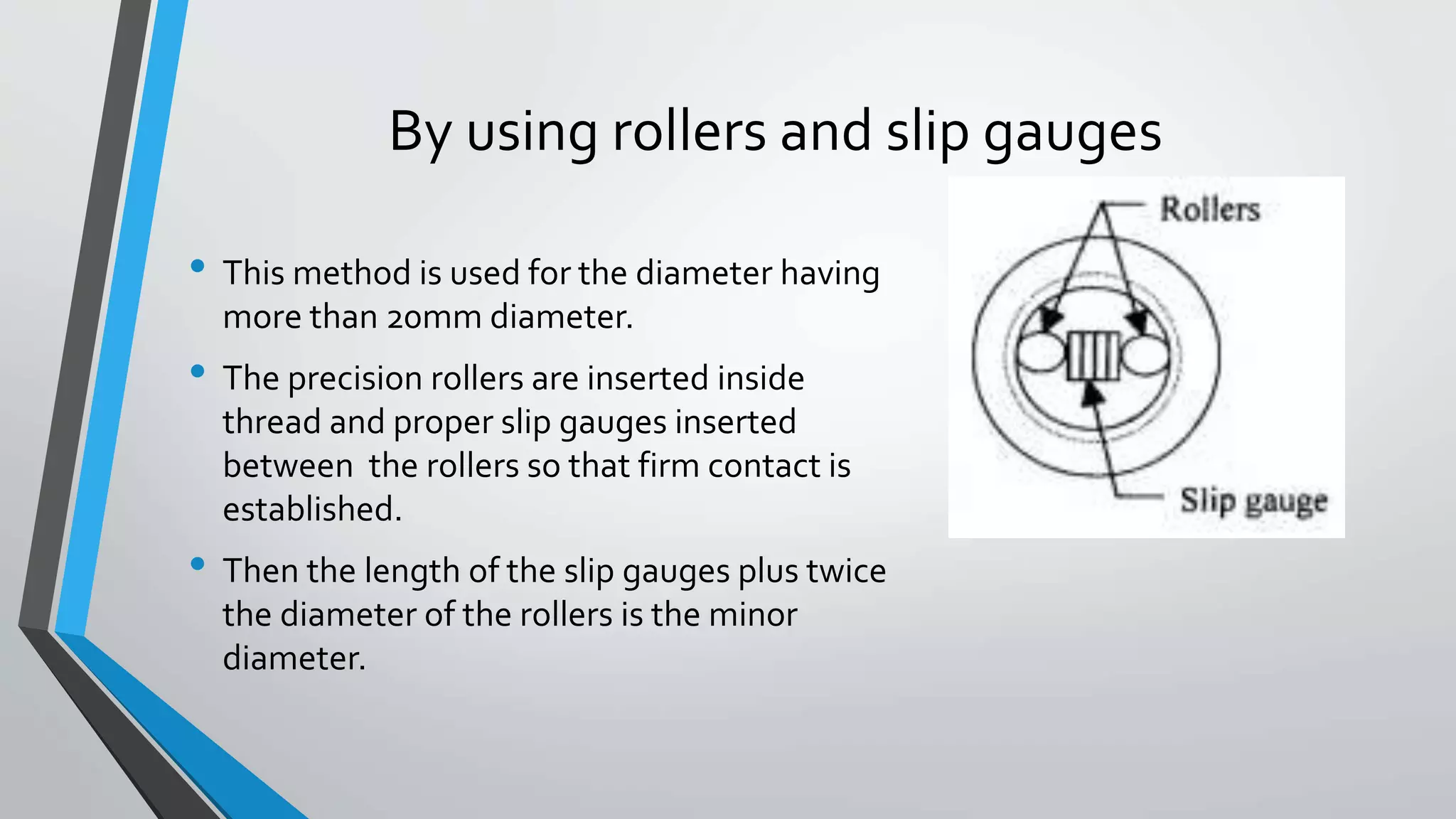
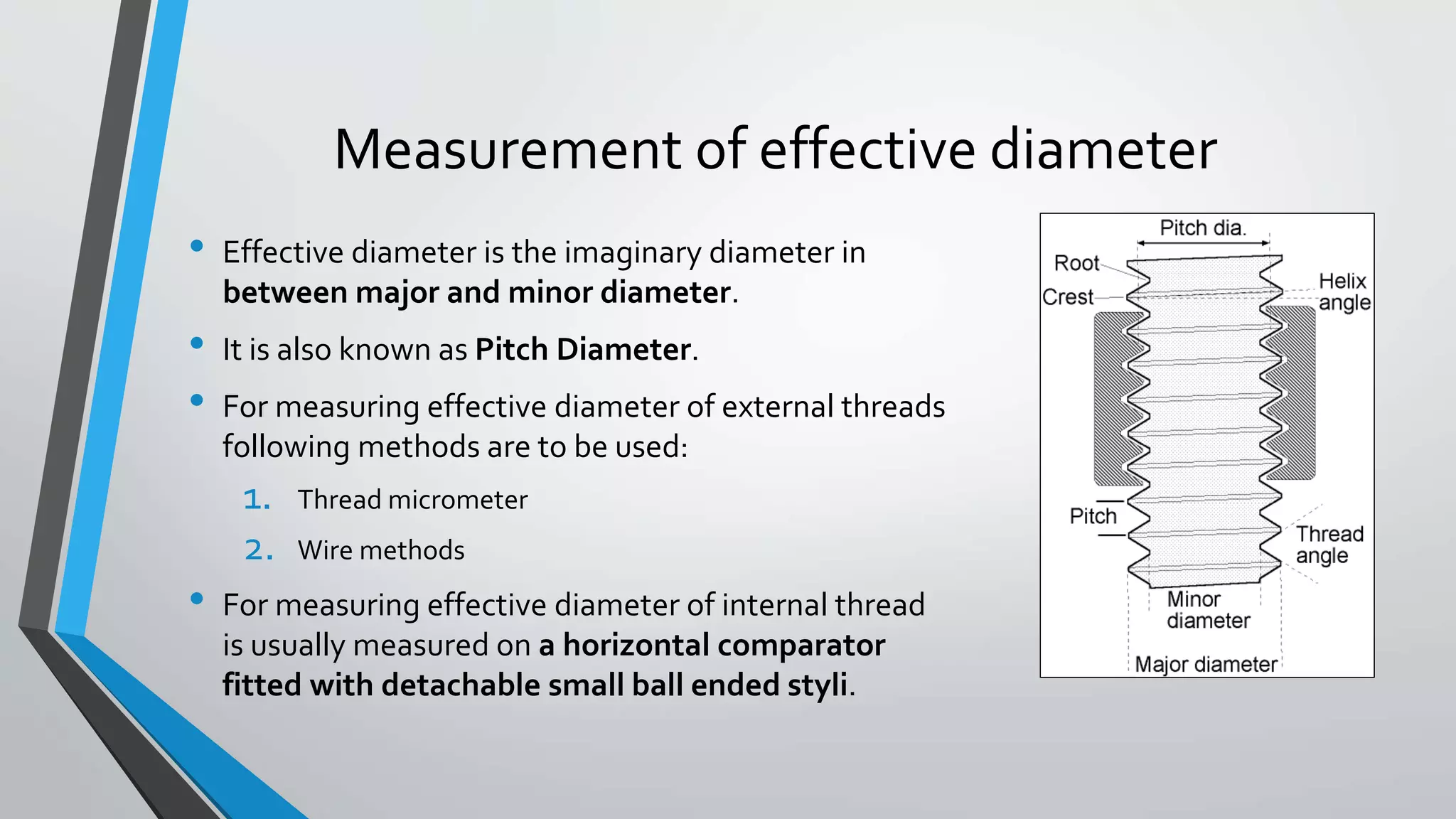
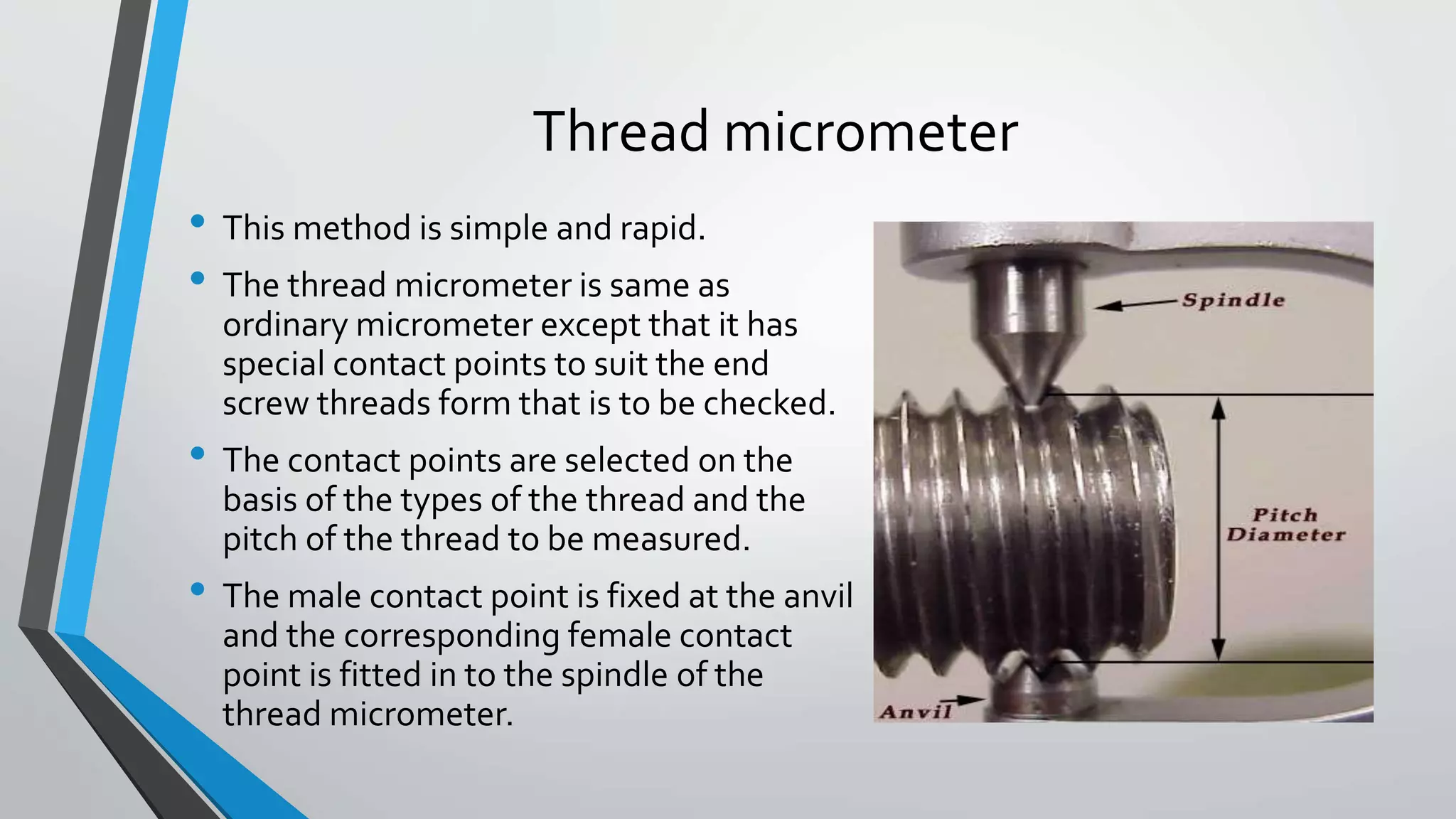
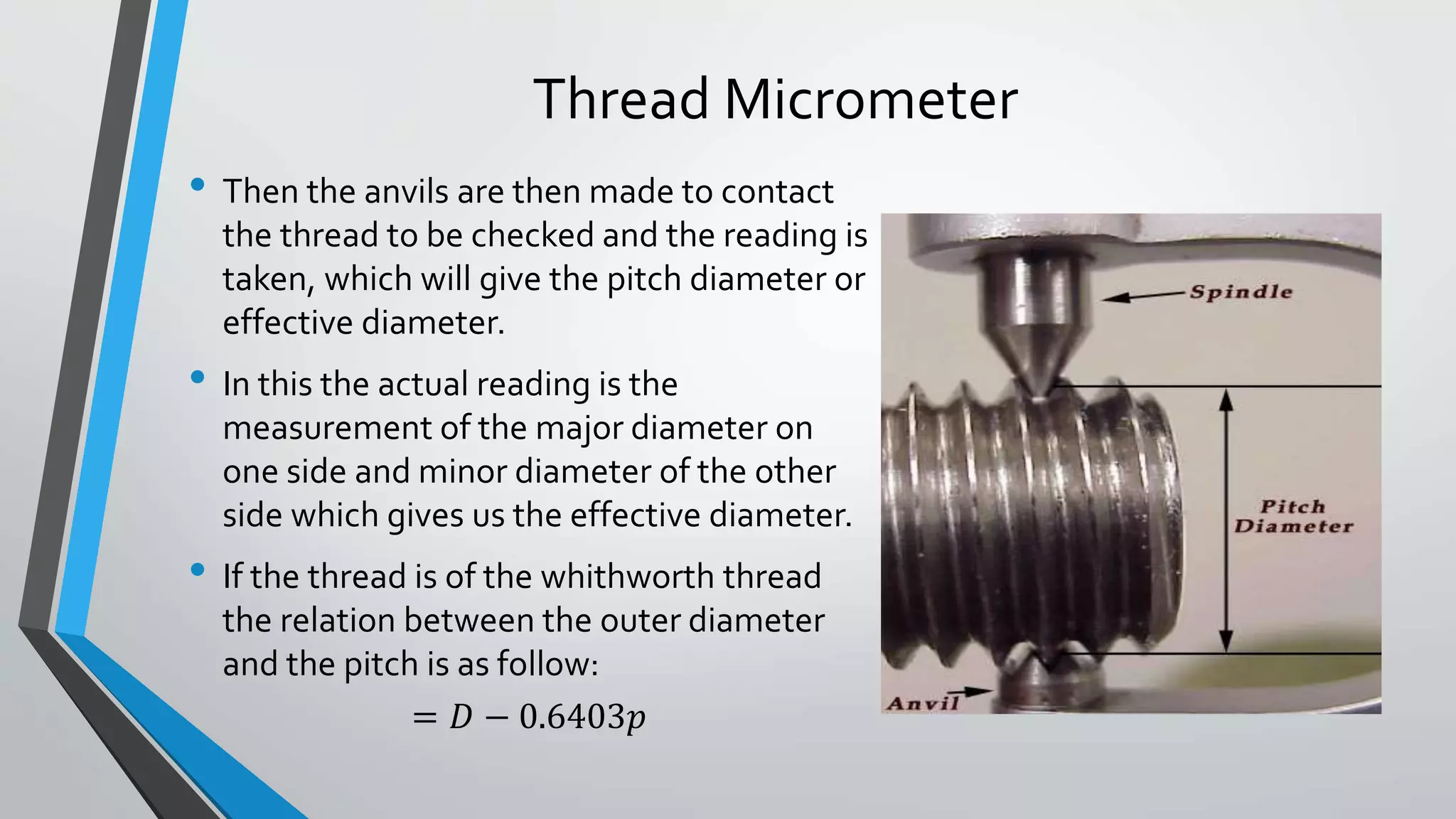
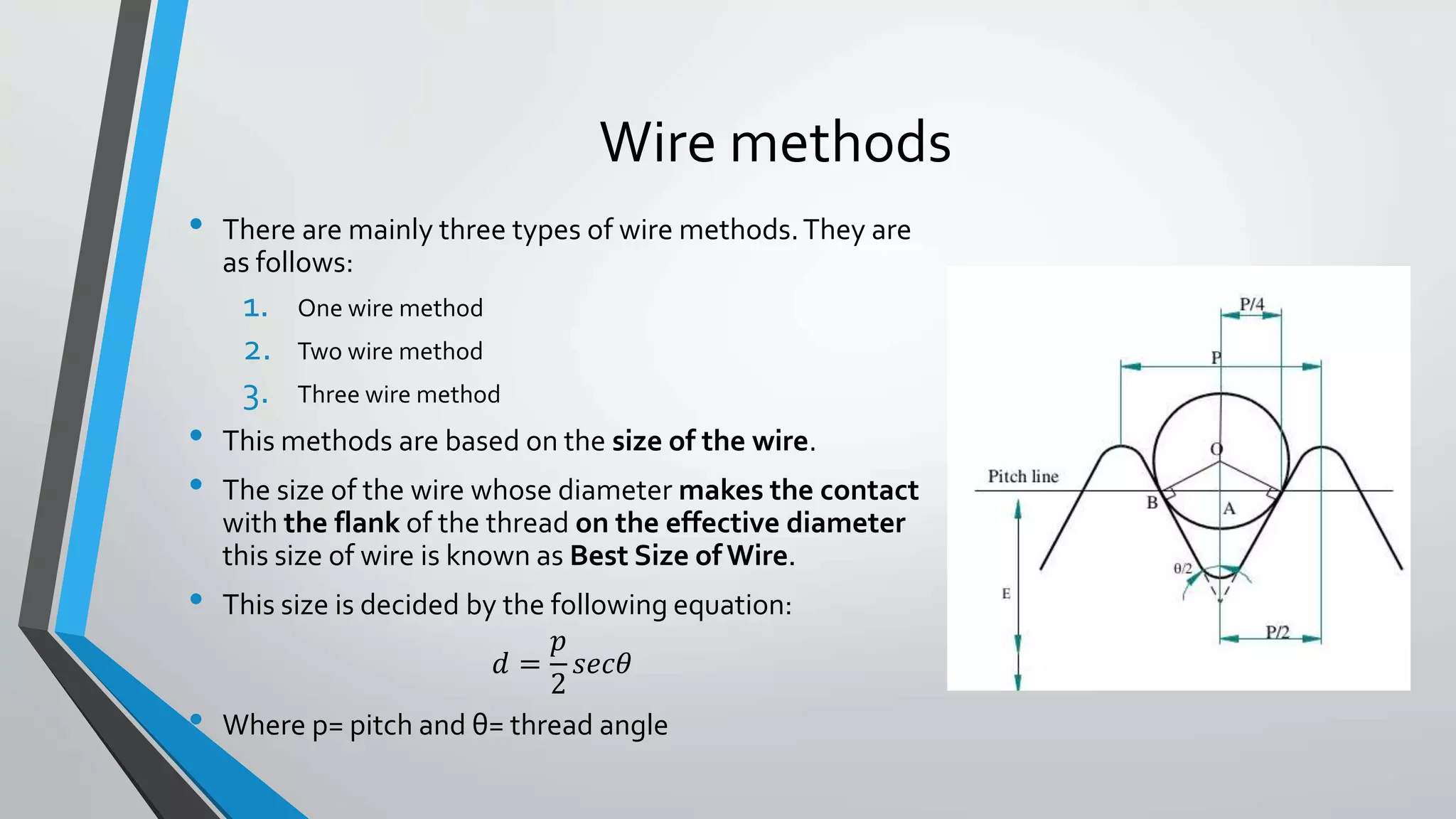
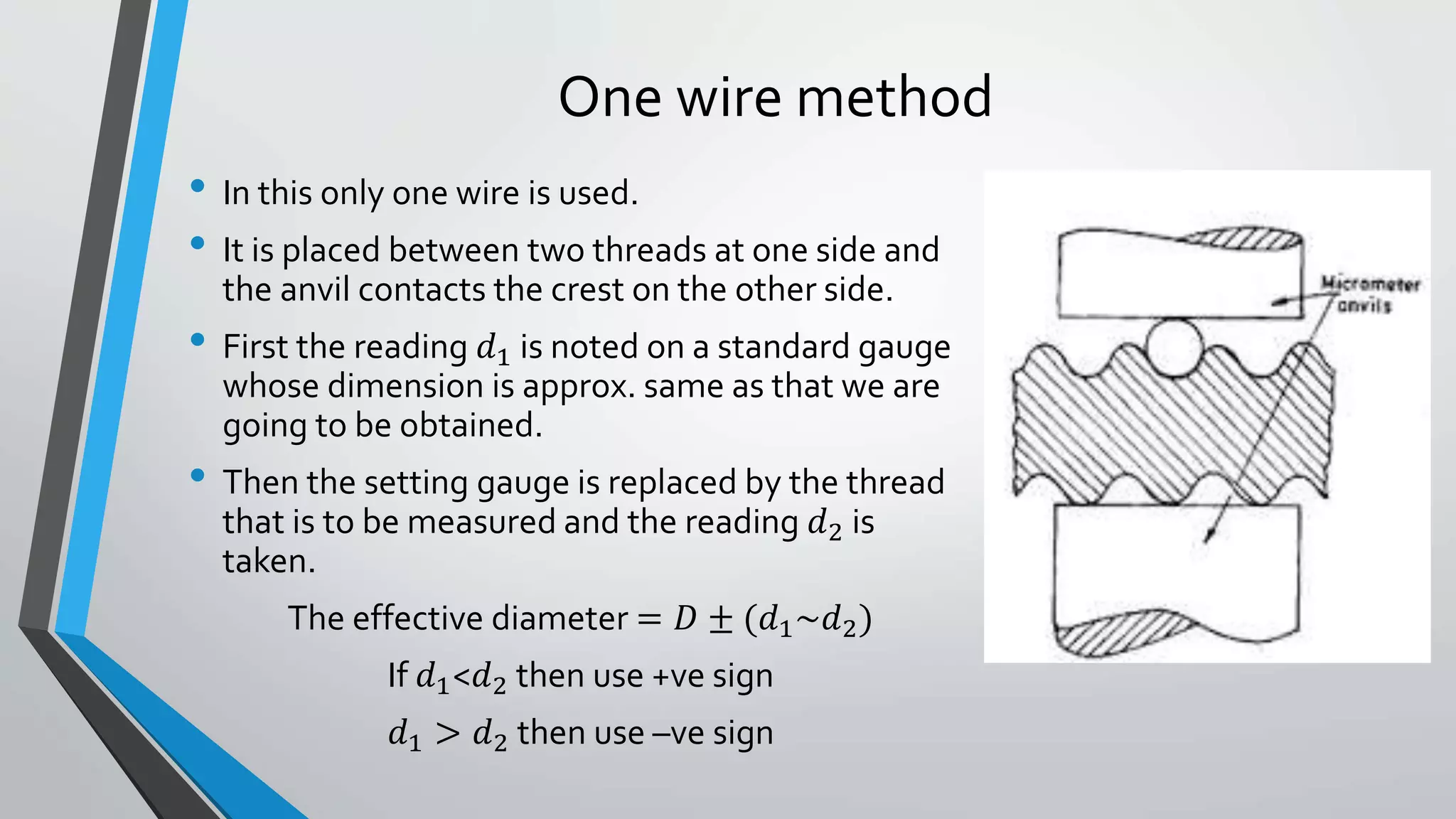
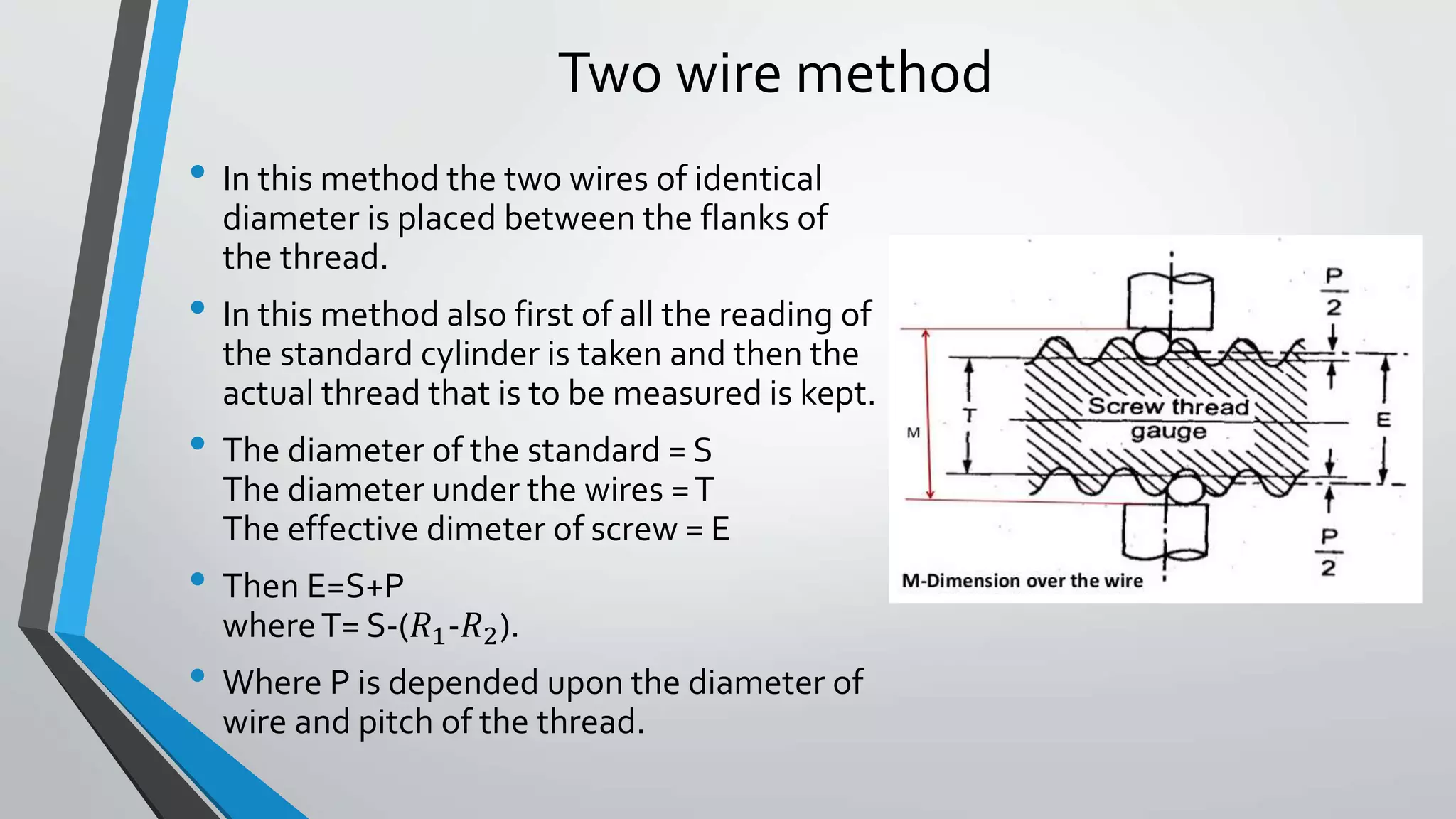
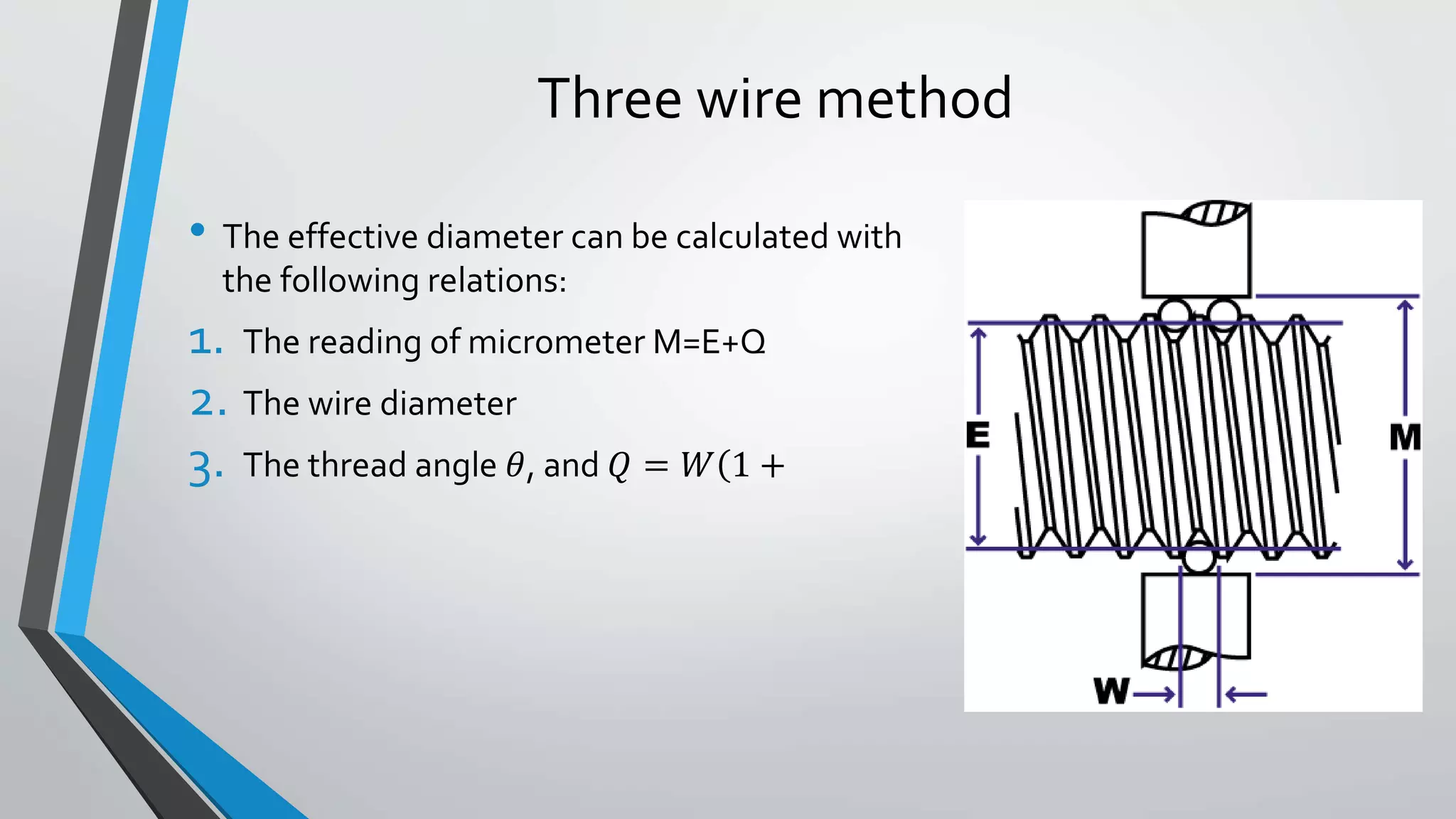
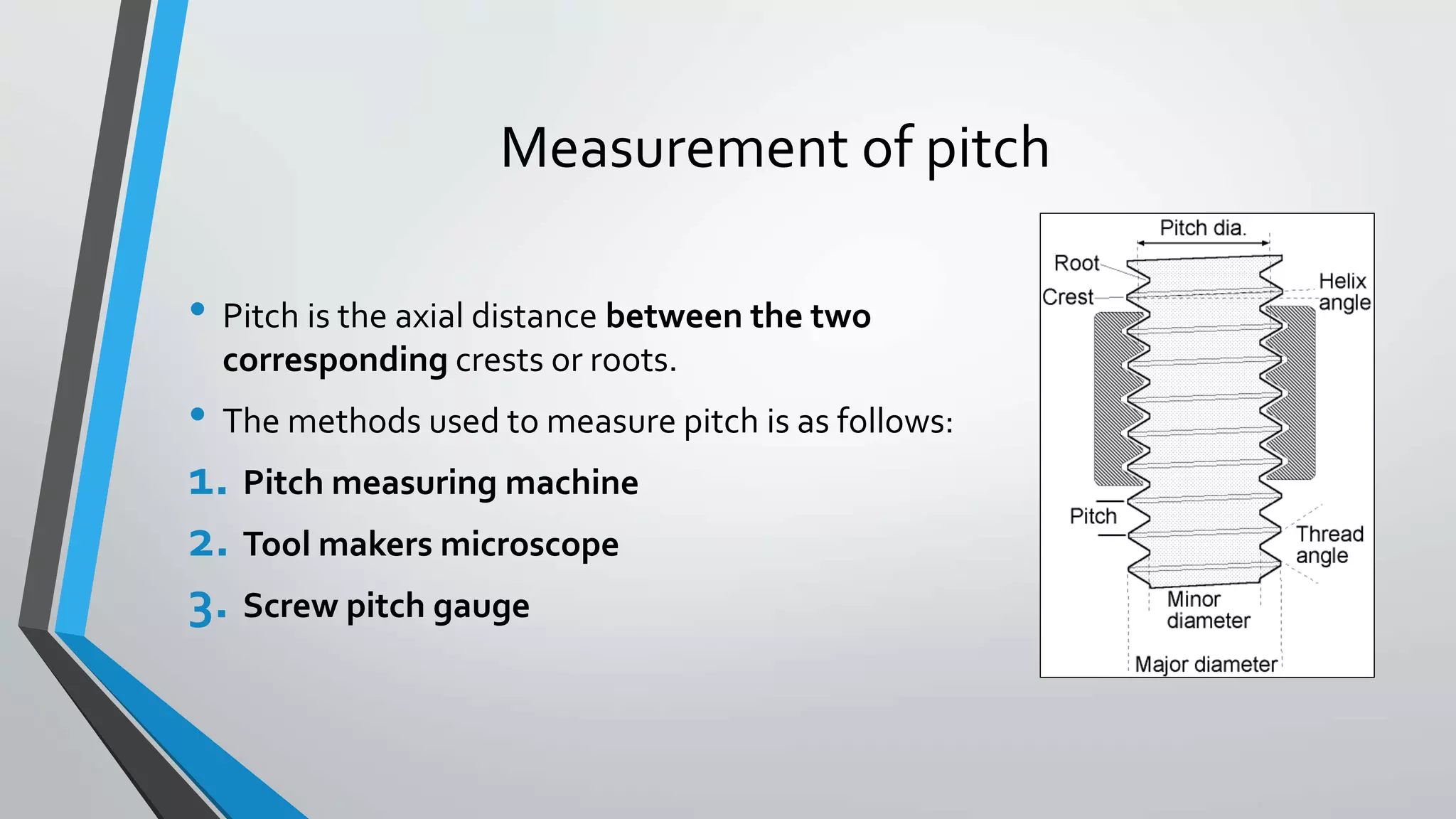
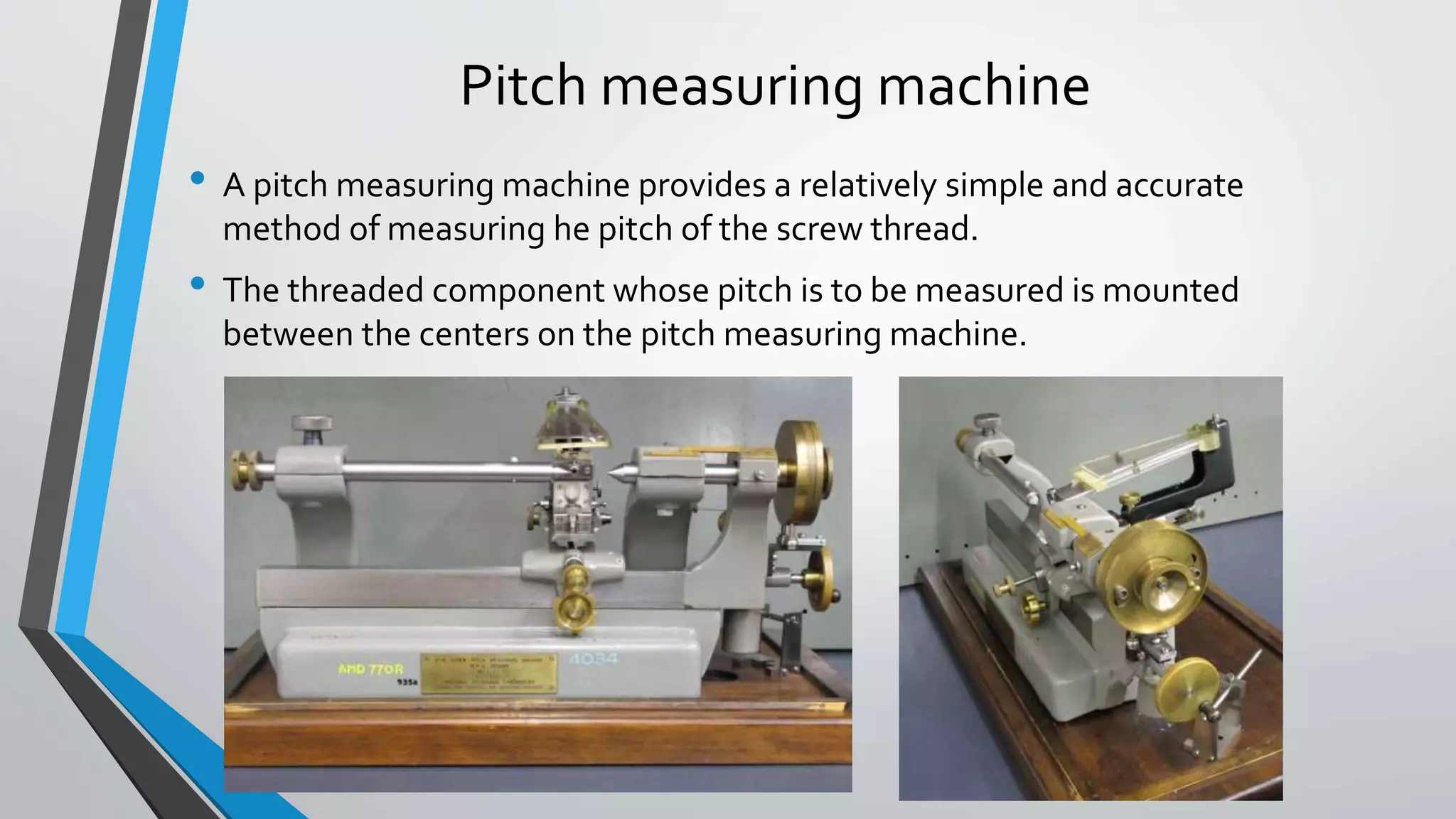
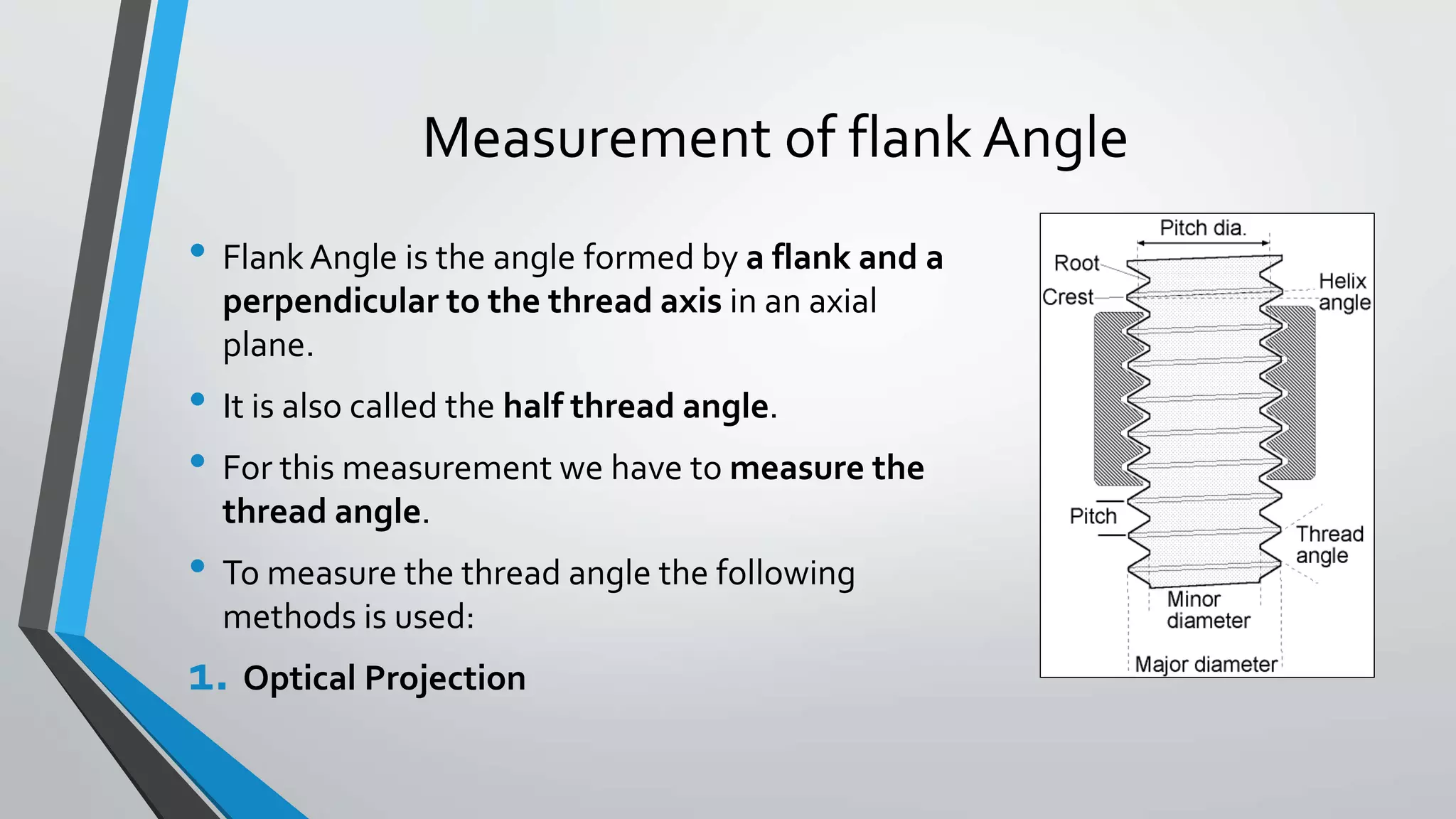
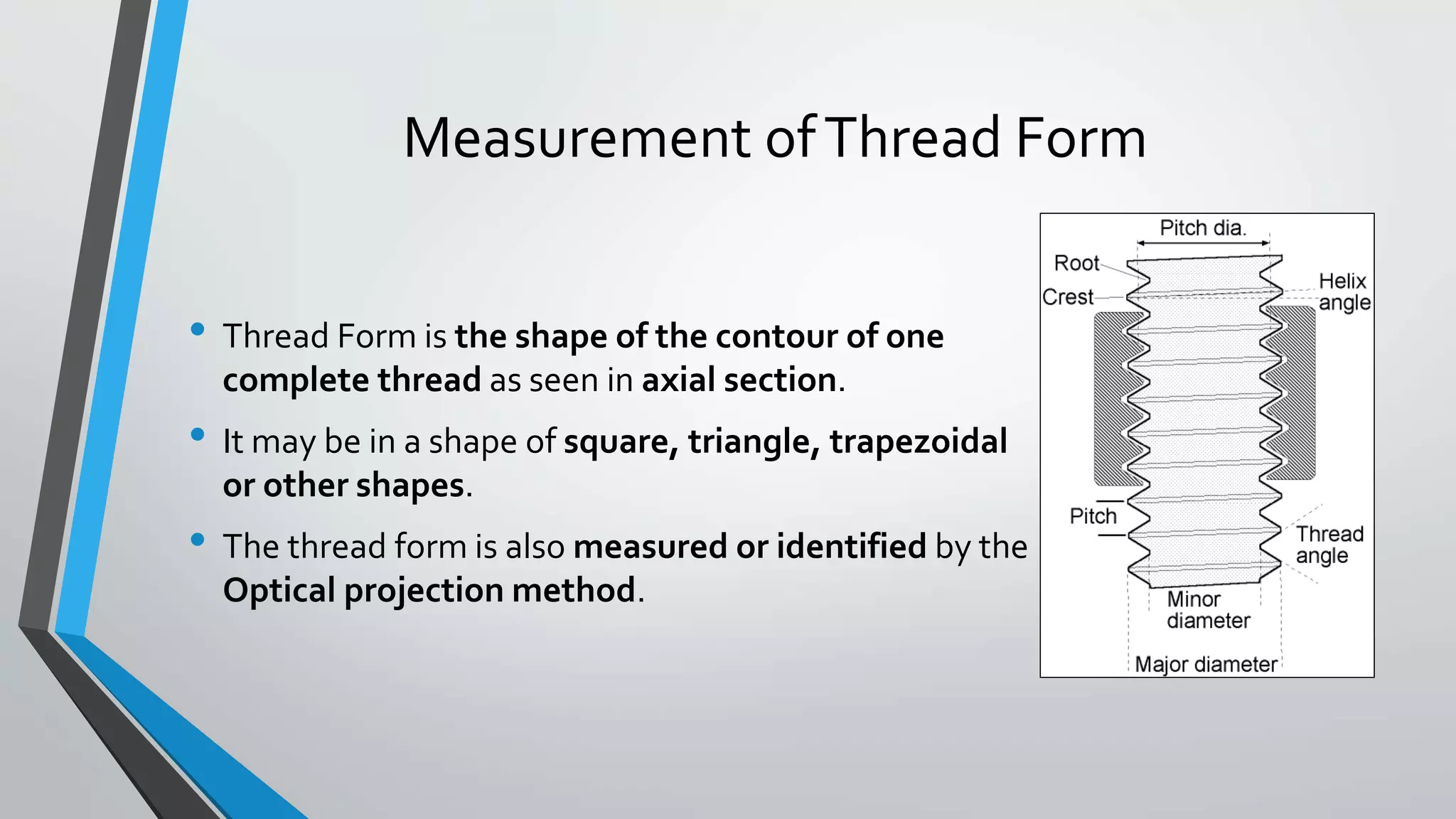
This document discusses methods for measuring various elements of screw threads, including major diameter, minor diameter, effective diameter or pitch diameter, pitch, flank angle, and thread form. Common measurement tools mentioned include micrometers, thread comparators, thread micrometers, tool makers microscopes, and optical projection. Methods like using setting gauges, V-pieces, taper parallels, rollers and slip gauges, and one-, two-, or three-wire techniques are described for different thread measurements.