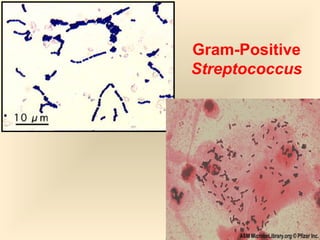
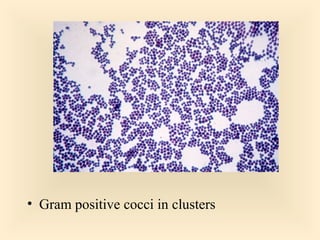
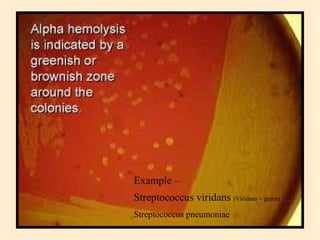
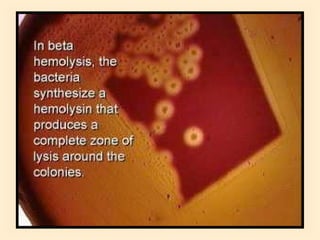
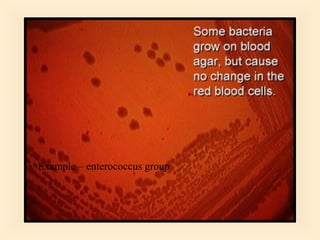
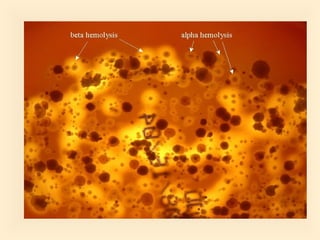
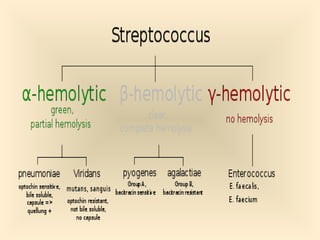
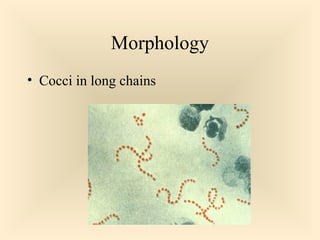
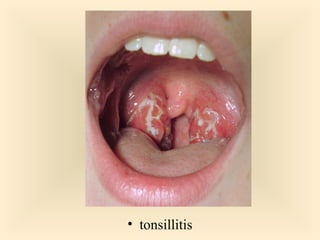
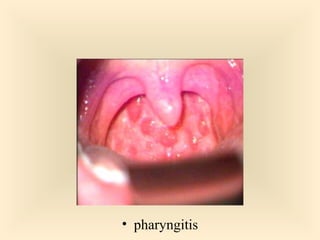
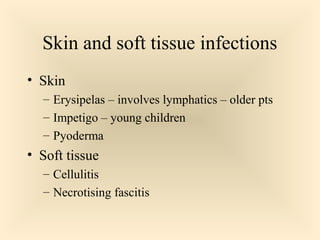
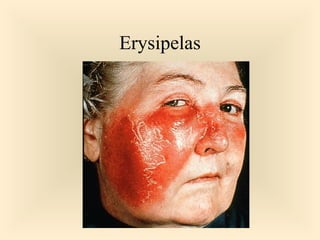
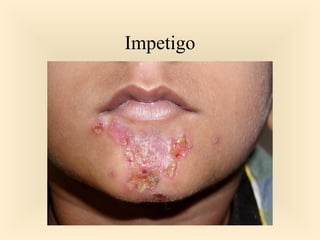
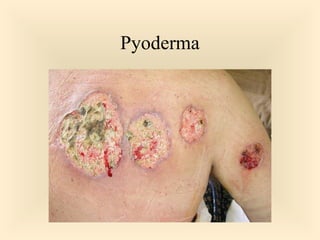
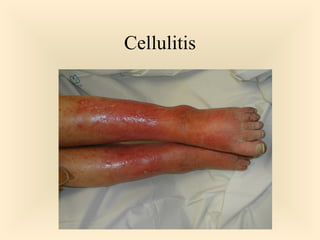
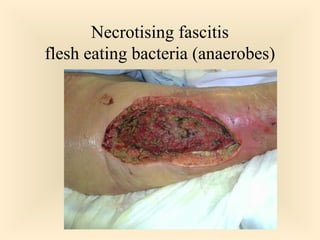
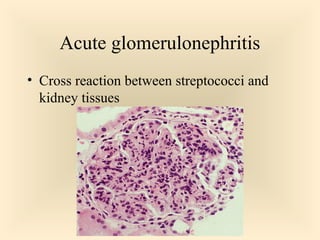
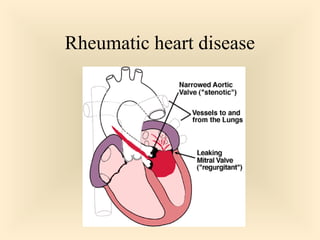
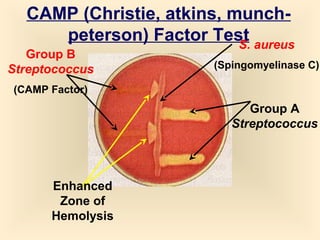
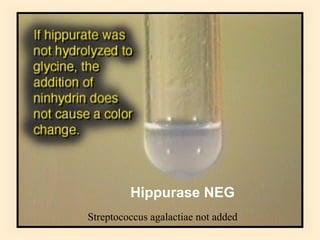
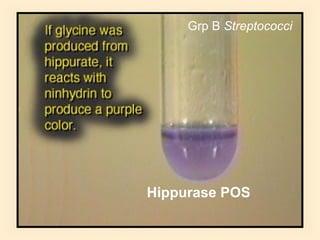
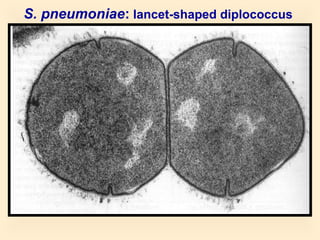
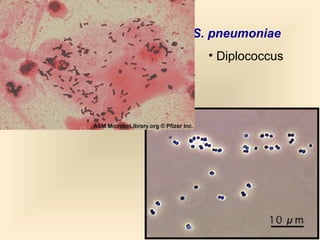
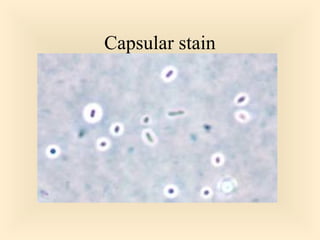
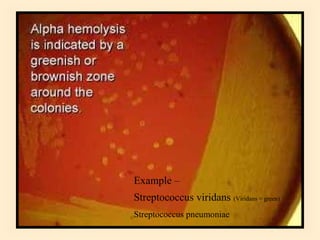
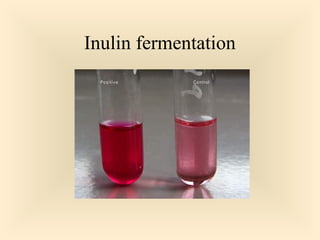
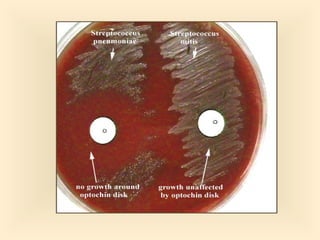
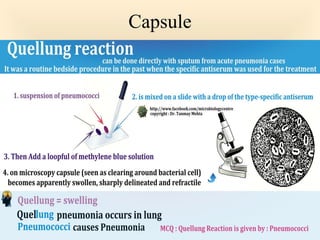
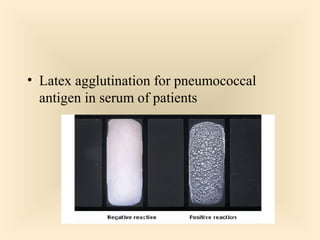
The document discusses the genus Streptococcus, including its classification, morphology, growth characteristics, biochemical reactions, and clinical significance. It describes various species, such as Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus pneumoniae, detailing their pathogenicity, diseases caused, laboratory diagnosis, and treatment options. The document also covers epidemiology, resistance patterns, and specific infections associated with different streptococci groups.