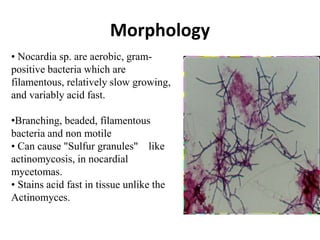
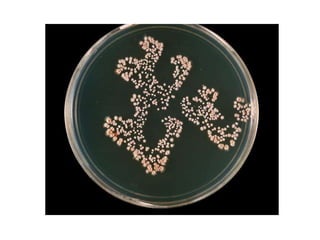
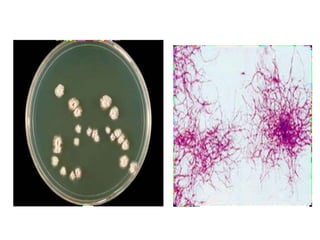
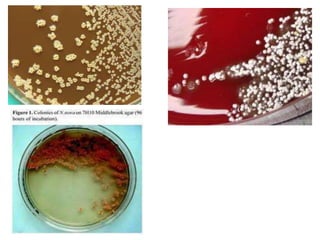
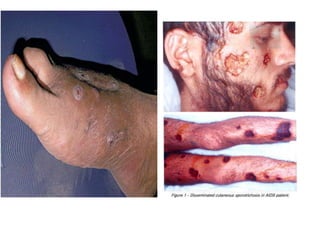
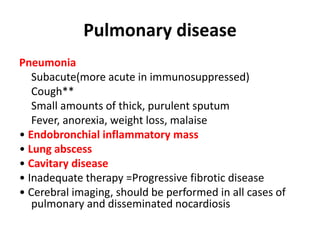
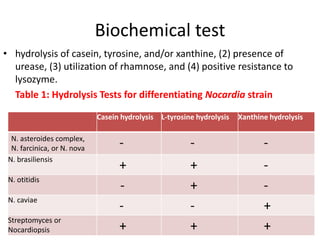
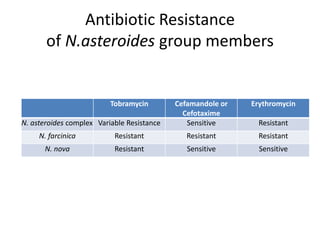
Nocardia are aerobic, gram-positive bacteria that are ubiquitous environmental saprophytes found in soil. They cause opportunistic infections in both immunocompromised and immunocompetent individuals. Nocardia infections can manifest as cutaneous disease, pulmonary disease, disseminated disease, or central nervous system infections such as brain abscesses. Diagnosis involves microscopic examination of samples showing branching filaments, culture growth on selective media, and molecular techniques such as PCR and 16S rRNA sequencing. Treatment involves prolonged courses of antibiotics such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or amikacin depending on the species.