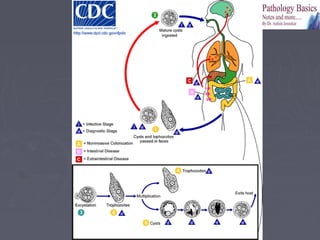
The document provides a comprehensive overview of parasitology, focusing on protozoa and helminths, including their classifications, life cycles, diseases caused, and treatment methods. It details various parasites such as Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia, Trichomonas vaginalis, Leishmania, and Plasmodium, alongside their morphology, pathogenesis, and lab diagnostics. Specific diseases like dysentery, malaria, and trichomoniasis are highlighted with associated symptoms and diagnostic techniques.