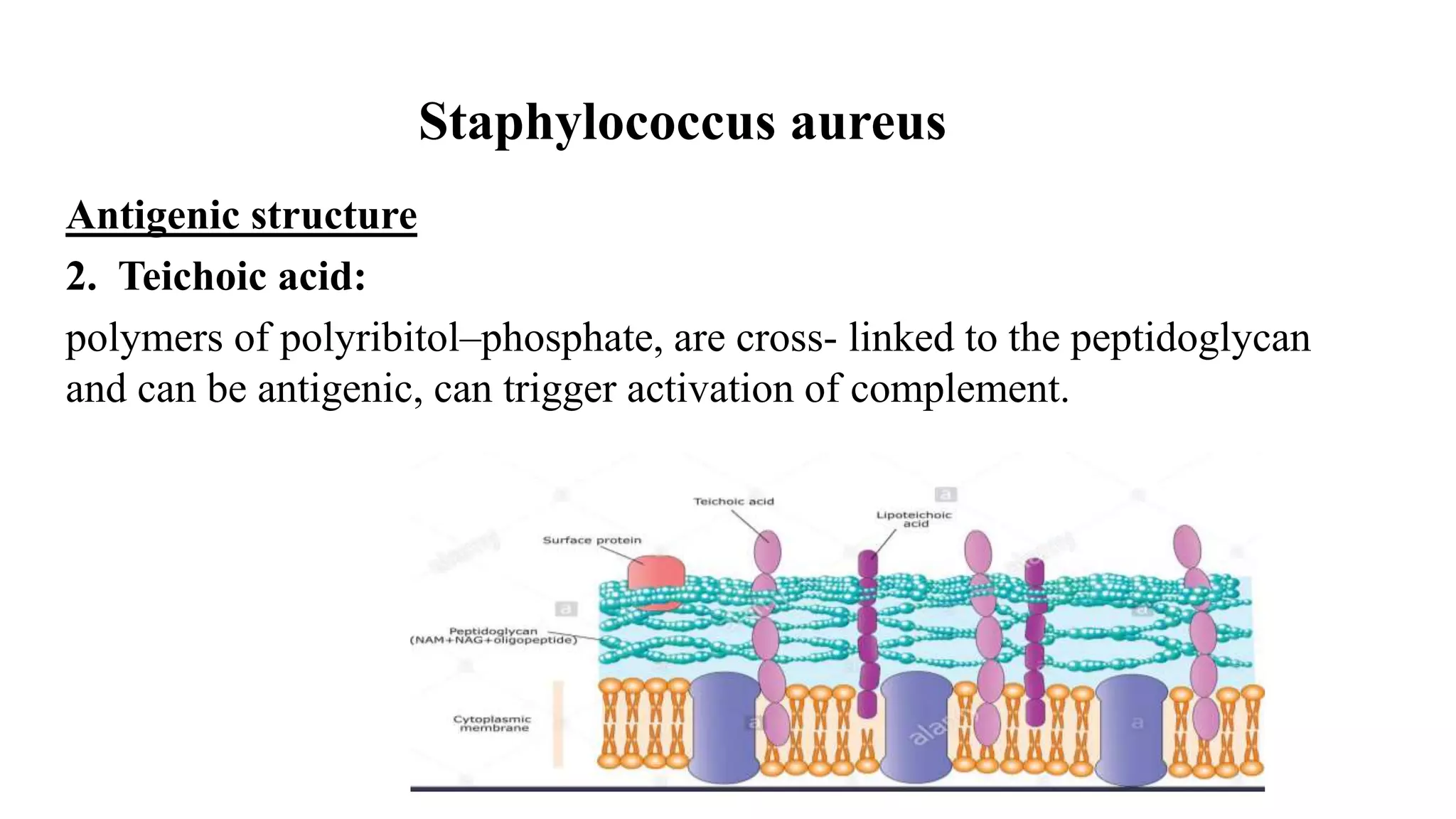
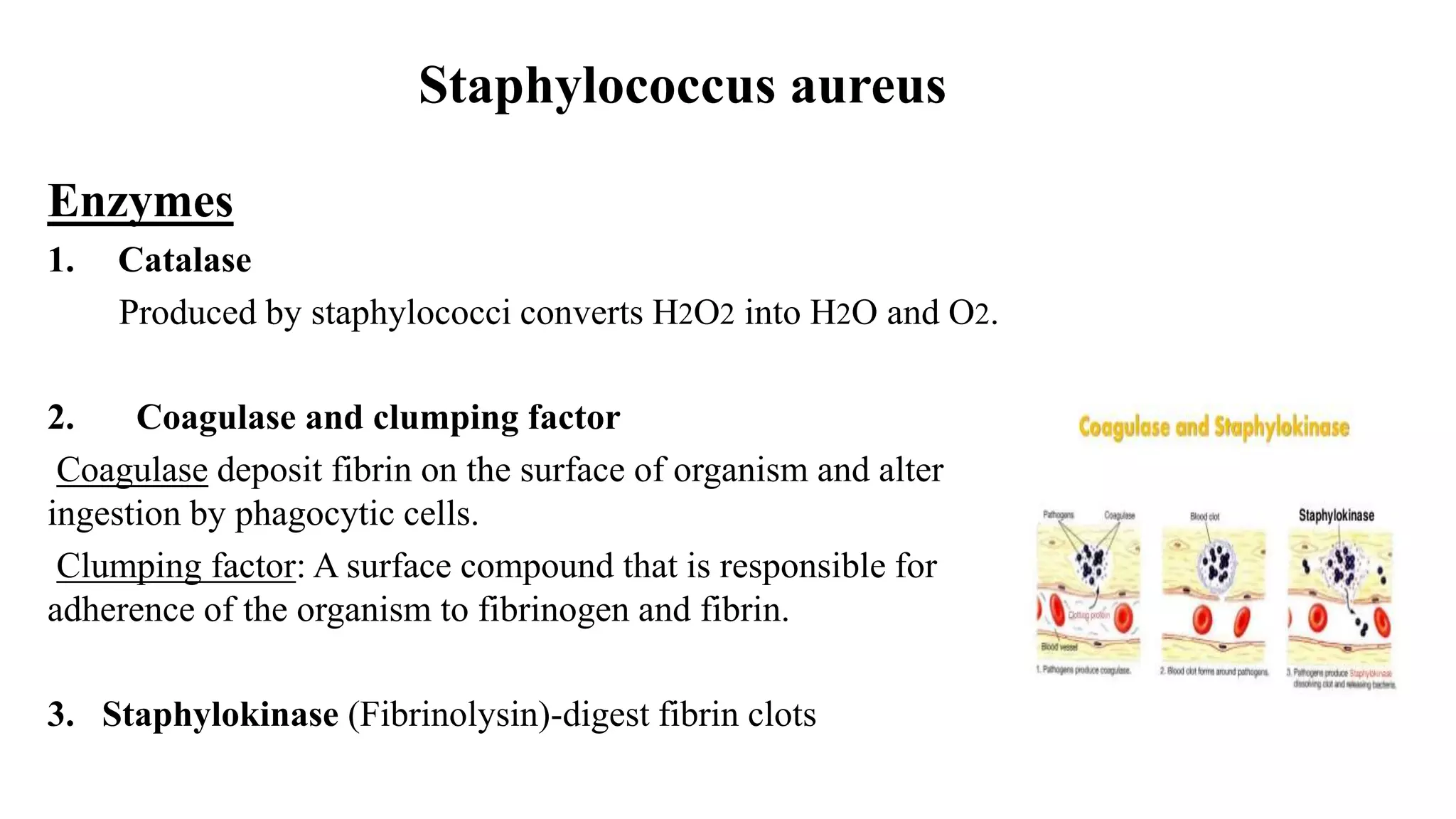
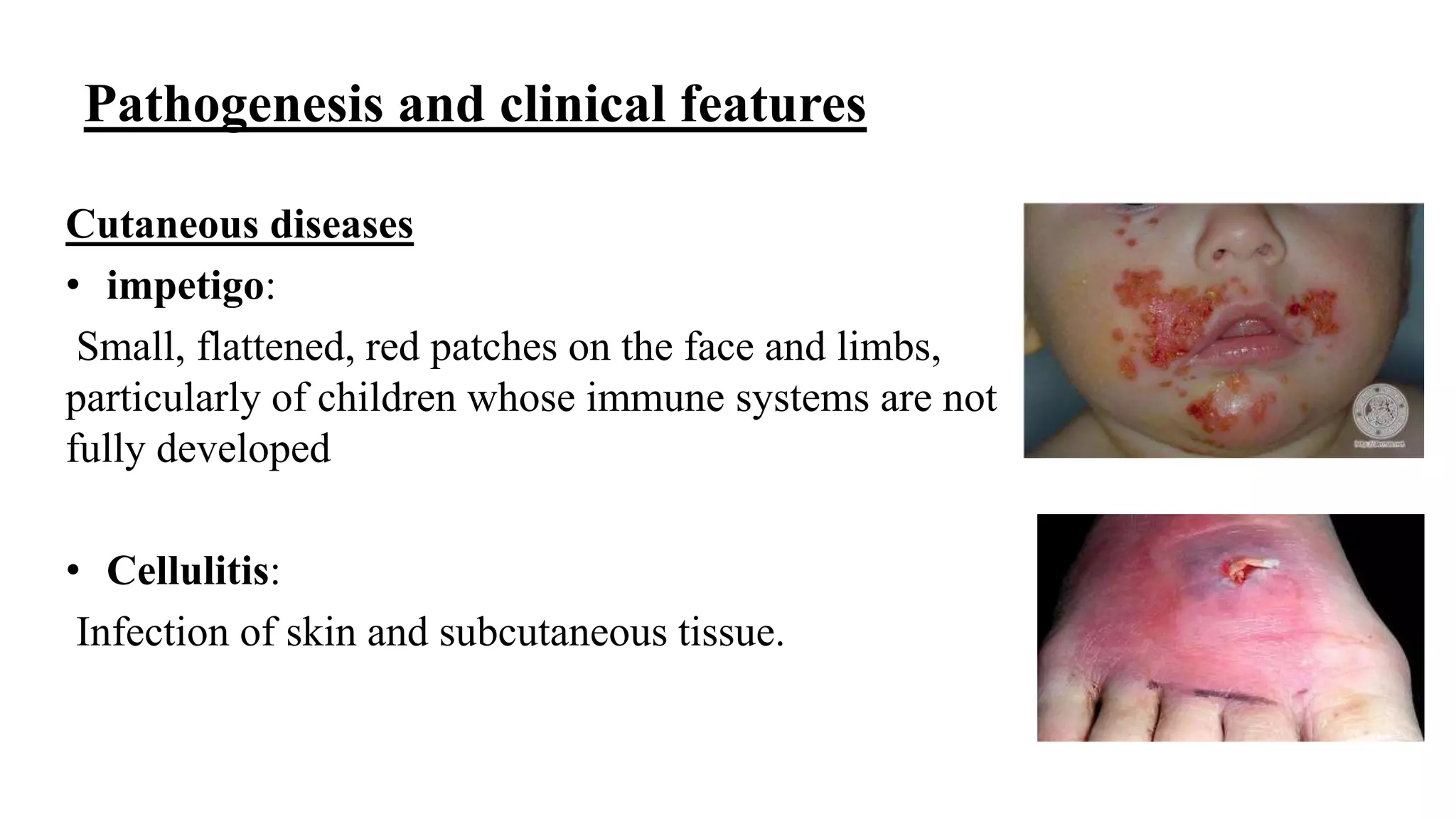
The document discusses the Gram positive cocci genera Staphylococcus and Streptococcus. It focuses on Staphylococcus, describing their characteristics including being facultatively anaerobic, non-motile, salt tolerant cocci that produce catalase. It discusses several medically important Staphylococcus species like S. aureus, S. epidermidis, S. saprophyticus and their roles in diseases ranging from skin infections to bacteremia, endocarditis, pneumonia and food poisoning. Treatment options depend on antibiotic sensitivity and resistance.