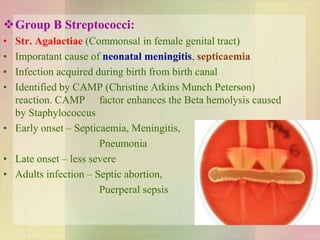
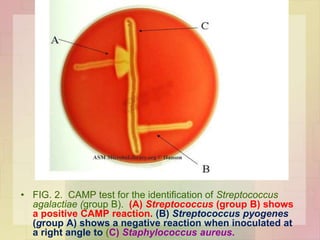
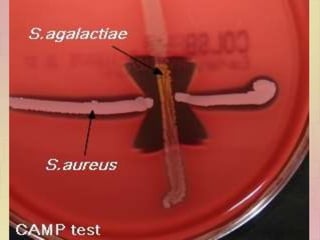
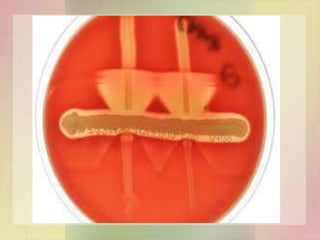
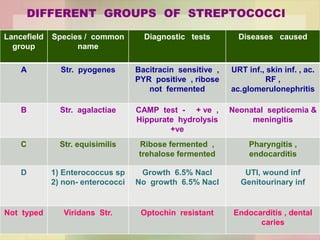
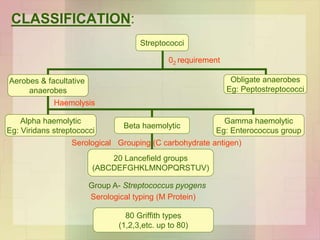
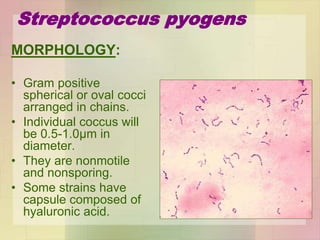
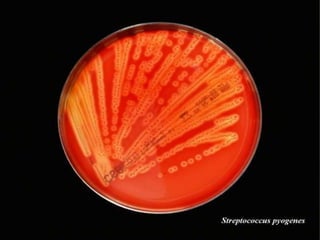
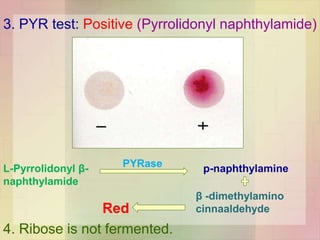
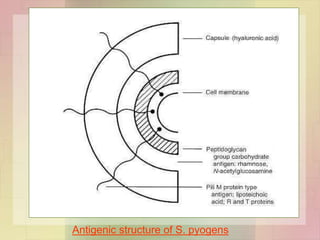
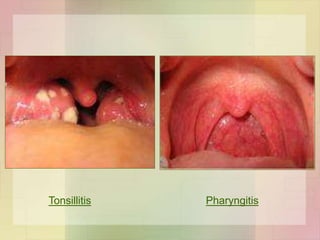
Streptococcus pyogenes, also known as group A Streptococcus, is an important human pathogen. It is a Gram-positive coccus that grows in chains. S. pyogenes can cause both suppurative infections like pharyngitis, impetigo, and necrotizing fasciitis, as well as non-suppurative sequelae including acute rheumatic fever and acute glomerulonephritis. Penicillin is the drug of choice for treating S. pyogenes infections. Prophylactic penicillin is also used to prevent rheumatic fever in individuals with a history of the disease. Group B Streptococcus and Streptococcus pneumoniae are other clinically significant streptococcal species

![Cultural characters
Aerobes & facultative anaerobes
370c [22 -420c]
Blood , serum, sugars
Non selective media:- Sheep blood agar
Selective media - Crystal violet Blood agar (1:500,000)
PNF medium](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streptococcusenterococcus-180926063441/85/Streptococcus-Enterococcus-by-Dr-Rakesh-Prasad-Sah-6-320.jpg)






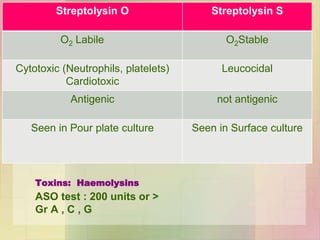

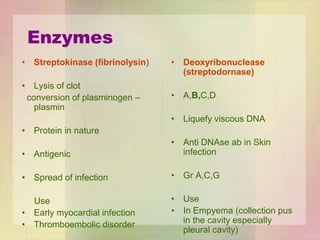
![Enzymes
• Nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotidase
(NADase)
• Acts on NAD
• A,C,G
• Antigenic
• leucotoxic
• Hyaluronidase
• A,B,C,G
• Spread
• Antigenic
• Serum opacity factor
[Lipoproteinase ]
Opaque to agar gel
containing horse or
swine serum](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streptococcusenterococcus-180926063441/85/Streptococcus-Enterococcus-by-Dr-Rakesh-Prasad-Sah-19-320.jpg)





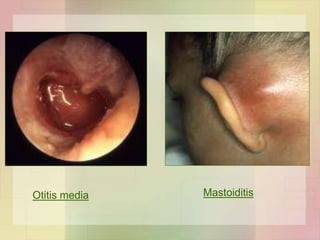
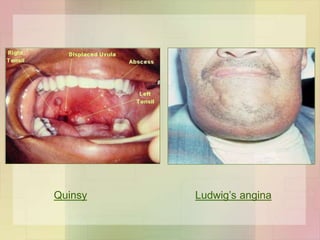
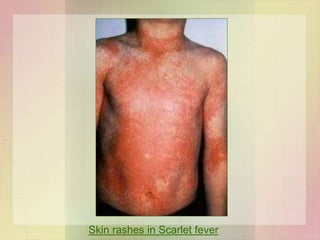
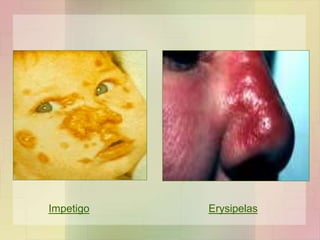
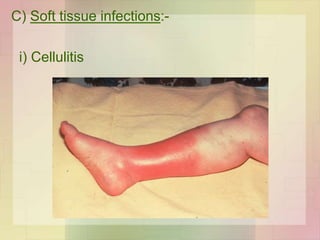
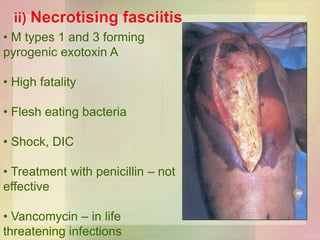
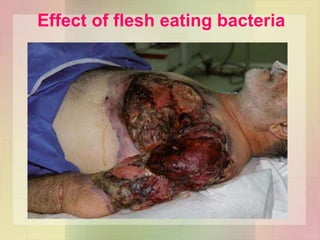
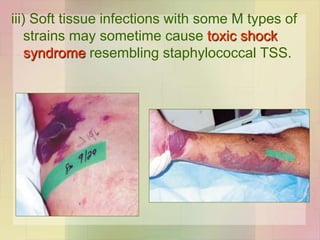
![Skin and soft tissue infections
• Infection of wound / burn
• Lymphangitis & cellulitis
• Erysipelas
• Diffuse infection involving superficial lymphatics
• Red, swollen & indurated sharply demarcated
• Elderly
• Impetigo
• Young children
• Impetigo & streptococcal infection of scabies lesion
G.N. [in children]
• Subcutaneous infections
• Cellulitis to necrotising fascitis [mixed infection / M type 1 & 3
forming pyogenic exotoxin A]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streptococcusenterococcus-180926063441/85/Streptococcus-Enterococcus-by-Dr-Rakesh-Prasad-Sah-29-320.jpg)






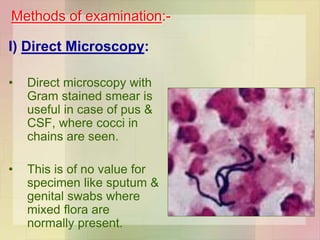

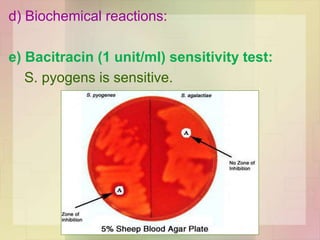
![Lab Diagnosis
Lancefield grouping
Grown in Todd Hewitt broth
Extraction of C carbohydrate – HCL /
formamide /autoclaving /enzyme
(streptomyces albus)
Precipitation with sp antisera
Antigen detection test ELISA /Agglutination
test [throat swab]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streptococcusenterococcus-180926063441/85/Streptococcus-Enterococcus-by-Dr-Rakesh-Prasad-Sah-47-320.jpg)
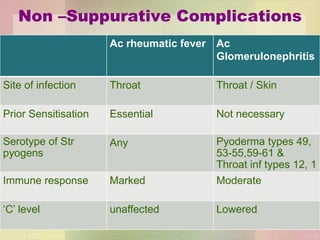
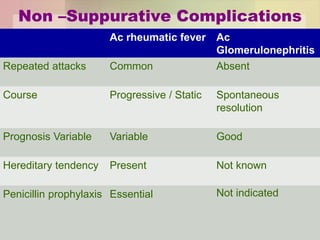
![Lab Diagnosis
Nonsuppurative complications
Rheumatic fever
ASO titre (200 U / more)
Ac G.N.
anti DNAse B titre (300/350 )
[retrospective diagnosis of streptococcal pyoderma]
antihyaluronidase
Streptozyme test [[Passive slide
haemagglutination test ]] : screening test for
all types of streptococcal infection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streptococcusenterococcus-180926063441/85/Streptococcus-Enterococcus-by-Dr-Rakesh-Prasad-Sah-48-320.jpg)