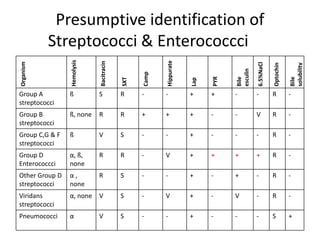
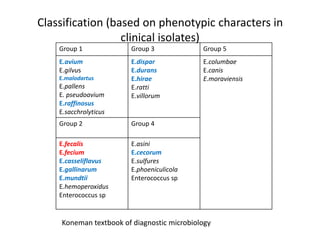
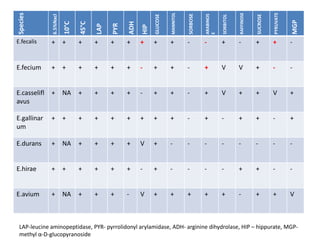
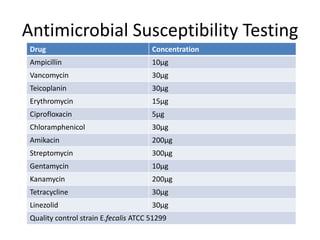
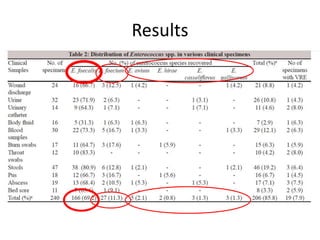
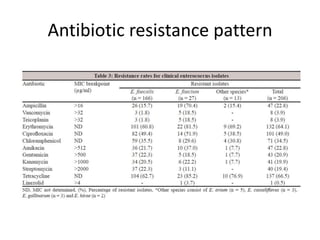
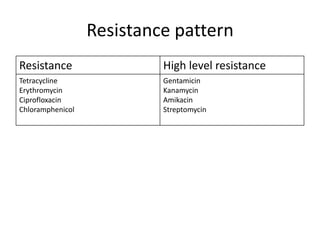
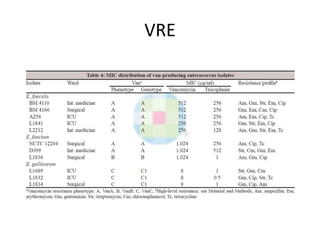
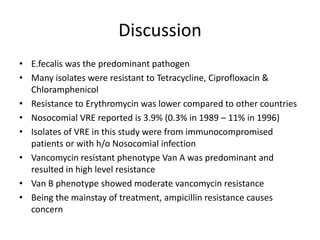
Enterococci are Gram-positive cocci that are natural inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tract. They have become important nosocomial pathogens due to their intrinsic and acquired antibiotic resistance. This study found that Enterococcus faecalis was the most common species isolated from clinical specimens in two Saudi hospitals. Many isolates showed resistance to tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, and chloramphenicol. Vancomycin resistance was observed in 3.9% of isolates, with the VanA phenotype being most common. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis identified identical clones of E. faecalis isolated from different hospital wards, suggesting intra-hospital transmission. The high resistance rates indicate a need for improved infection control and antibiotic steward