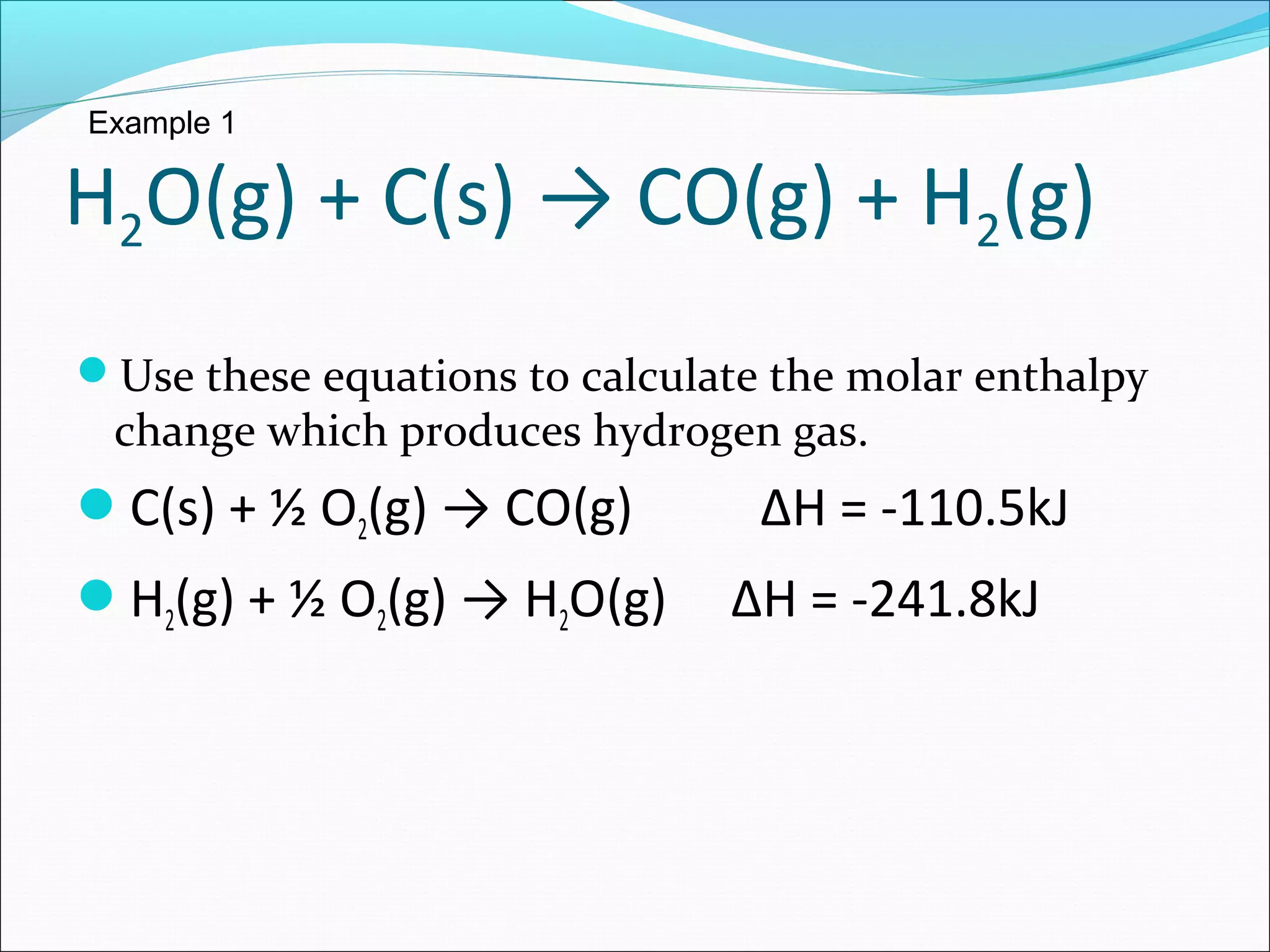
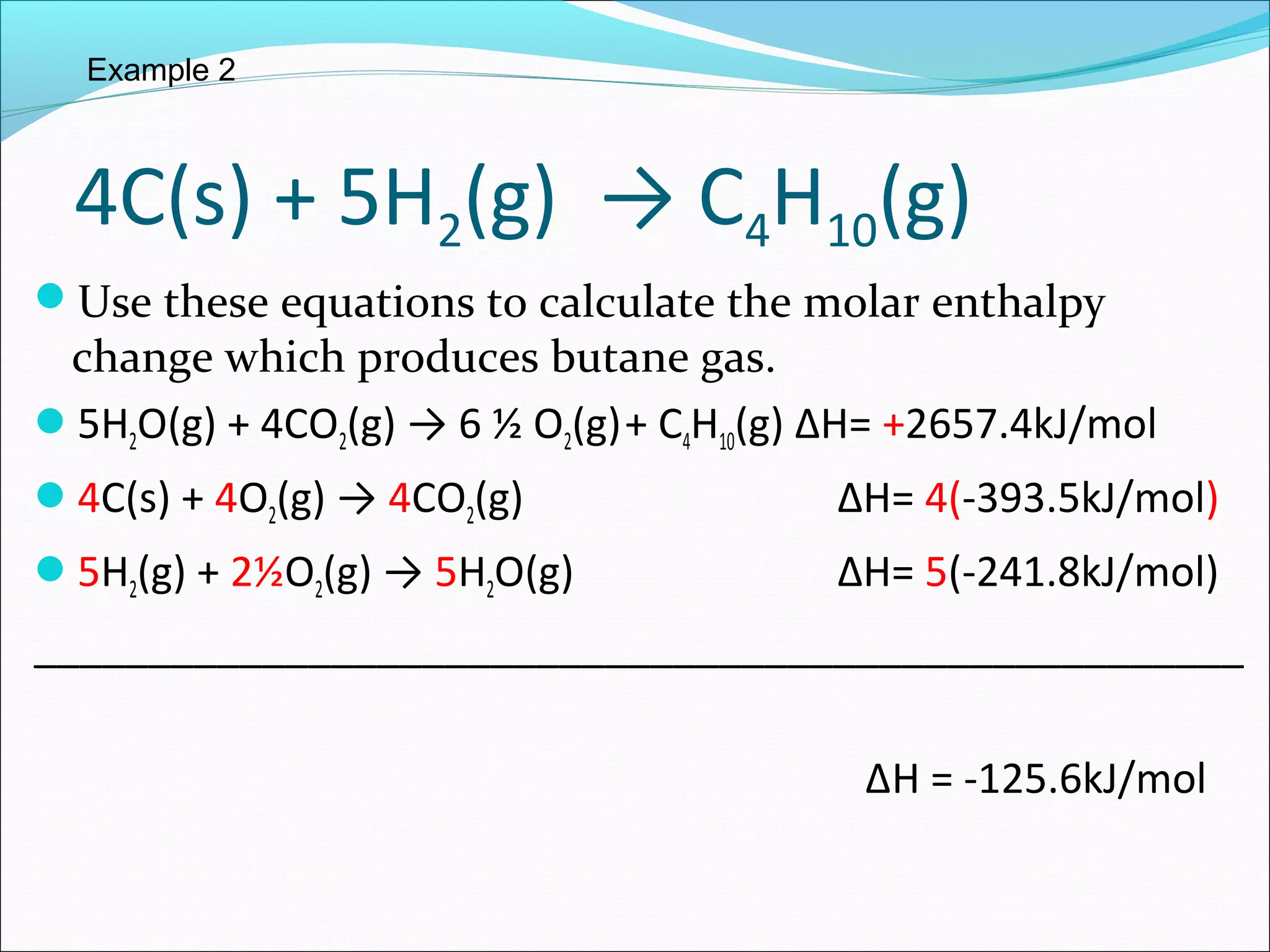
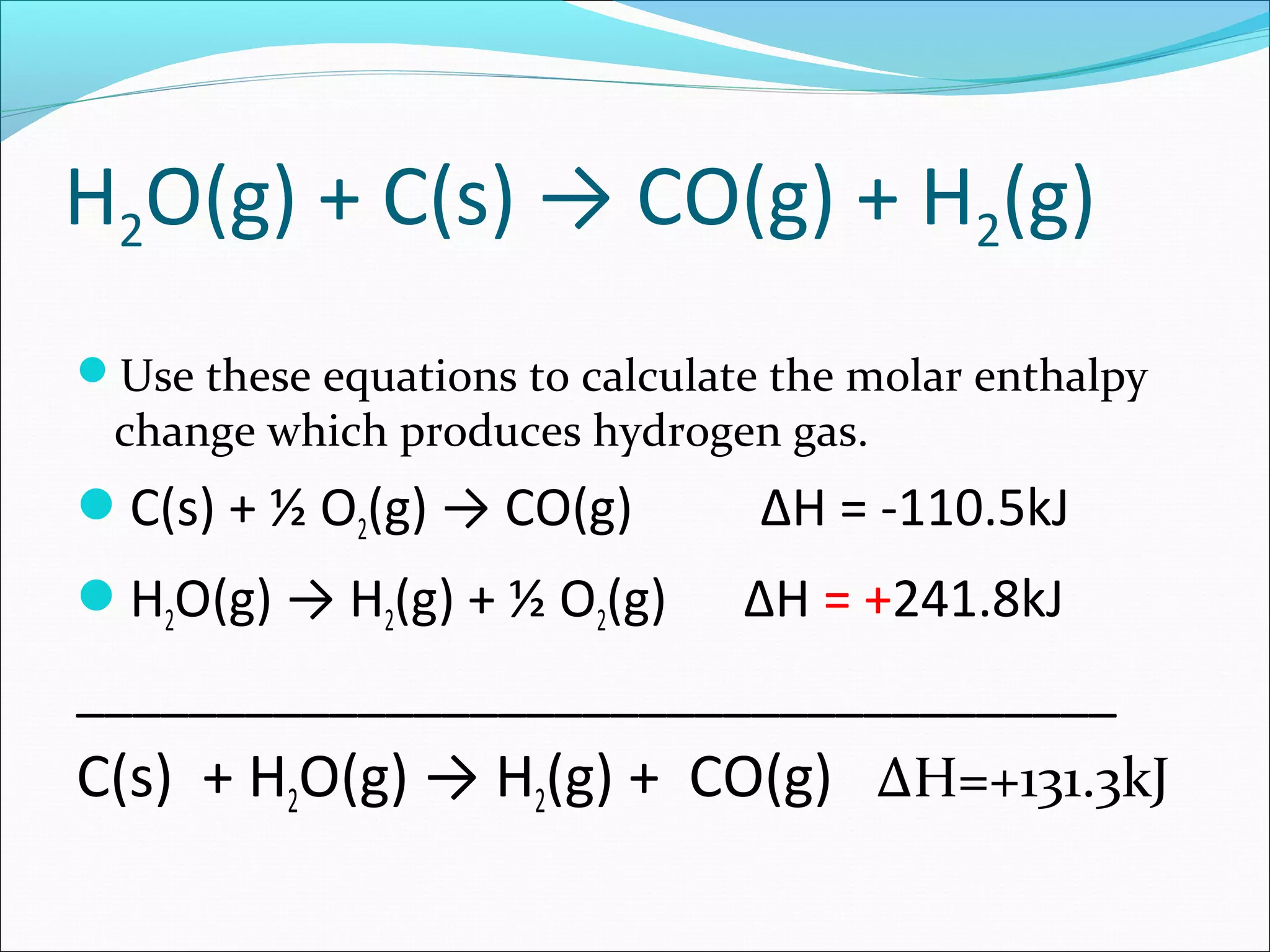The document discusses Hess's law, which states that the heat of reaction is the same whether a chemical process occurs in one or multiple steps. Specifically:
- Hess's law allows adding together multiple chemical equations to determine the enthalpy change of the overall equation.
- Two examples are provided to demonstrate calculating the enthalpy change of an overall reaction by combining individual reaction enthalpies.
- In both examples, the individual reactions are rearranged and combined to produce the overall reaction, and the enthalpy terms are summed to find the enthalpy change of the overall reaction.