Embed presentation
Download to read offline




![Calculating the pH
pH = - log [H+]
(Remember that the [ ] mean Molarity)
•pH = - (- 10)
•pH = 10
Example: If [H+] = 1 X 10-10
pH = - log 1 X 10-10
•pH = - (- 4.74)
•pH = 4.74
Example: If [H+] = 1.8 X 10-5
pH = - log 1.8 X 10-5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpart1-200407065908/85/Ph-part-1-6-320.jpg)
![Try These!
FIND THE PH OF THESE: 1) A 0.15 M SOLUTION OF
HYDROCHLORIC ACID
[H+] = 0.15
2) A 3.00 X 10-7 M
SOLUTION OF NITRIC ACID
[H+] = 3.00 X 10-7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpart1-200407065908/85/Ph-part-1-7-320.jpg)



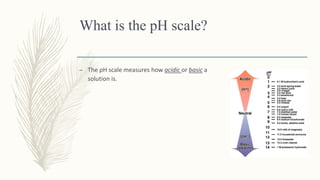
The pH scale measures how acidic or basic a solution is on a scale from 0-14, with 0-7 being acidic and 7-14 being basic/alkaline. The pH is defined as the negative log of the hydrogen ion concentration. A pH of 7 indicates a neutral substance, like water. Examples show how to calculate the pH from given hydrogen ion concentrations using the logarithmic definition of pH.





![Calculating the pH
pH = - log [H+]
(Remember that the [ ] mean Molarity)
•pH = - (- 10)
•pH = 10
Example: If [H+] = 1 X 10-10
pH = - log 1 X 10-10
•pH = - (- 4.74)
•pH = 4.74
Example: If [H+] = 1.8 X 10-5
pH = - log 1.8 X 10-5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpart1-200407065908/85/Ph-part-1-6-320.jpg)
![Try These!
FIND THE PH OF THESE: 1) A 0.15 M SOLUTION OF
HYDROCHLORIC ACID
[H+] = 0.15
2) A 3.00 X 10-7 M
SOLUTION OF NITRIC ACID
[H+] = 3.00 X 10-7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpart1-200407065908/85/Ph-part-1-7-320.jpg)

