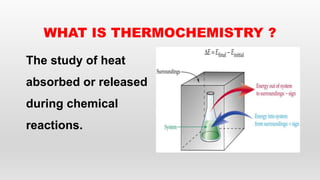
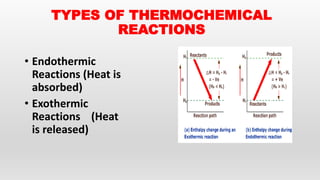
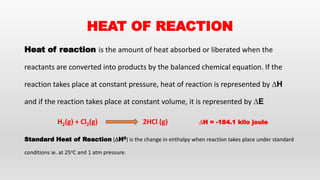
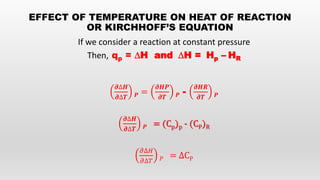
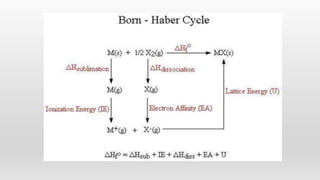
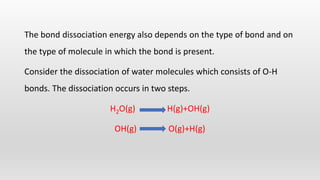
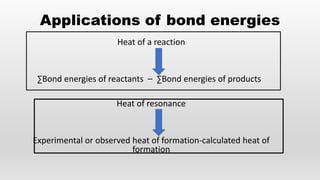
This document provides an overview of thermochemistry topics covered in a physical chemistry course, including:
- Definitions of thermochemistry, thermochemical reactions, and heat of reaction
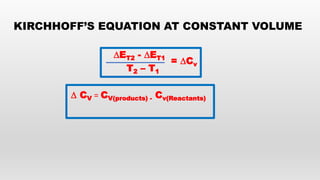
- Kirchoff's equation relating heat of reaction to temperature
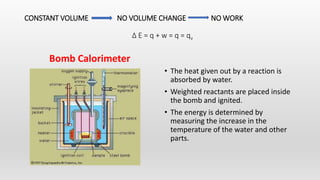
- Calorimetry and bomb calorimetry for measuring heat changes
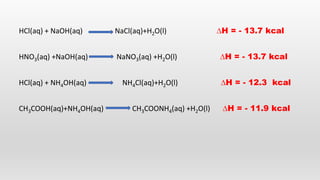
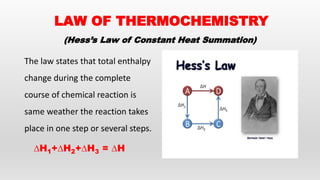
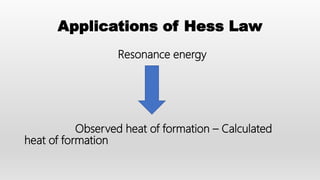
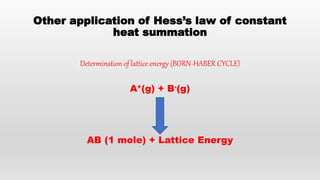
- Hess's law of constant heat summation and its applications
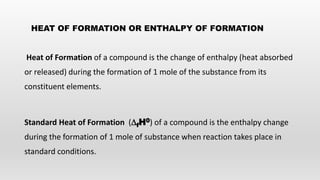
- Bond energies, enthalpies of formation, and using these values to calculate heat of reactions