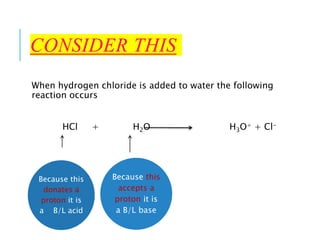
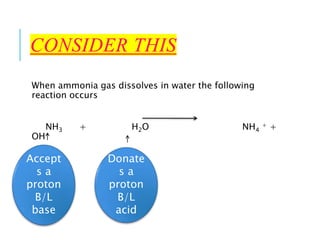
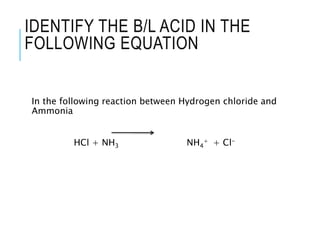
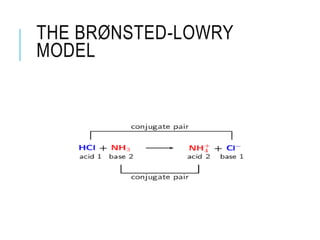
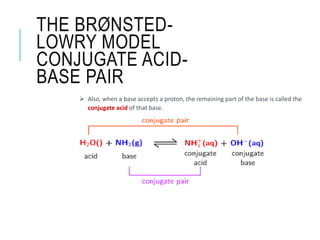
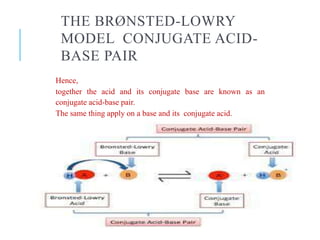
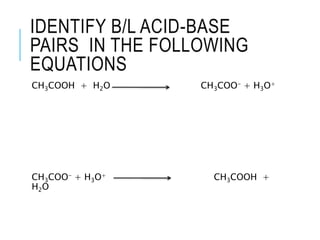
This document discusses the Brønsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases. It defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. An acid-base pair consists of a conjugate acid and conjugate base, where the acid donates a proton to form the conjugate base, or the base accepts a proton to form the conjugate acid. Water is described as amphiprotic because it can act as both an acid and a base. Examples of acid-base reactions and identification of conjugate species are provided.