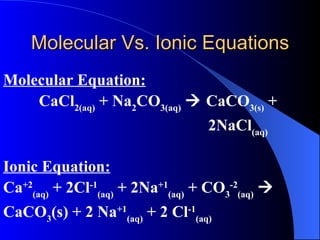
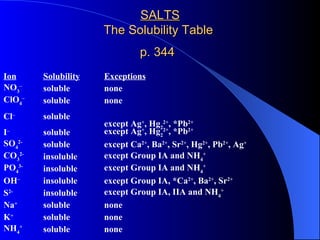
The document discusses net ionic equations, which involve writing molecular and ionic equations and identifying spectator ions. A molecular equation shows all species as whole units, while an ionic equation shows dissolved species as free ions. To write a net ionic equation, the molecular equation is first written and balanced, then molecules are broken into ions. Spectator ions that are present on both sides of the reaction are then canceled to give the net ionic equation. The document also discusses what substances will ionize or dissociate into ions in solution based on their type (salt, acid, base) and whether they are considered strong electrolytes.